2025-10-30 自治医科大学
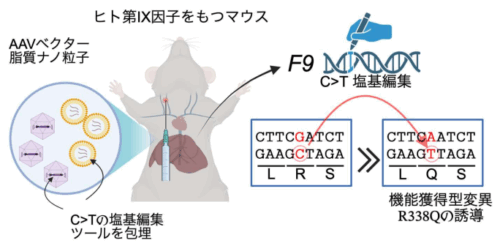
機能獲得型変異を誘導する血友病 B に対するゲノム編集治療のコンセプト
<関連情報>
- https://www.jichi.ac.jp/news/research/2025103001/
- https://www.jichi.ac.jp/wp/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/20251029_R338Q.pdf
- https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/doi/10.1182/blood.2024027870/547865/Therapeutic-base-editing-to-generate-a-gain-of
血友病Bの機能獲得型F9バリアントを生成するための治療的塩基編集 Therapeutic base editing to generate a gain-of-function F9 variant for hemophilia B
Nemekhbayar Baatartsogt,Yuji Kashiwakura,Takafumi Hiramoto,Rina Ito,Rikako Sato,Yasumitsu Nagao,Hina Naruoka,Haruka Takata,Morisada Hayakawa,Khishigjargal Batjargal,Tomoki Togashi,Atsushi Hoshino,Taro Shimizu,Yusuke Sato,Tatsuhiro Ishida,Osamu Nureki,Tsukasa Ohmori
Blood Published:October 23, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2024027870
Key Points
- Cytosine base editing to generate a gain-of-function F9 variant enhances FIX activity in a broad subset of hemophilia B variants.
- Liver-targeted base-editing to introduce a gain-of-function F9 variant may represent a therapeutic option for hemophilia B.
The repair of pathological gene variants is an ultimate aim for treating genetic diseases; however, the development of different therapeutic reagents for each of the many variants that can occur in a gene may not be scalable. Here, we investigated whether base editing to introduce a gain-of-function variant in blood coagulation factor IX (FIX) can increase FIX activity as a targeted therapeutic approach for hemophilia B. We engineered a G:C to A:T substitution at c.1151 of F9 by cytosine base editing to generate R338Q, known as the Shanghai F9 variant, which markedly potentiates coagulation factor activity. An adeno-associated virus vector harboring the base editor converted more than 60% of the target G:C to A:T and increased FIX activity in HEK293 cells harboring patient-derived F9 variants, as well as in knock-in mice harboring a human F9 cDNA. Furthermore, administration of lipid nanoparticles embedded with the base editor mRNA and gRNA increased FIX activity in mice. These data indicate that cytosine base editing to generate R338Q in FIX is a broadly applicable genome editing approach for hemophilia B with residual FIX activity.