2025-10-31 東京大学,旭川医科大学
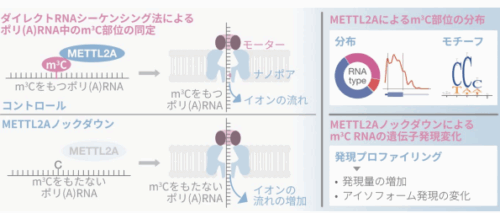
ダイレクト RNA シーケンシング法による、ポリ(A)RNA 中での m3 C 修飾の分布と遺伝子発現制御機能の解明
<関連情報>
ナノポア直接RNAシークエンシングにより、METTL2Aを介したポリ(A)RNA中のm3C部位 が明らかに Nanopore direct RNA sequencing reveals METTL2A-mediated m3C sites in poly(A) RNA
Shuhei Mitsutomi,Anzu Sugawara,Masahide Seki,Yutaka Suzuki,Sotaro Miyao,Haozhe Du,Kenji Takahashi,Yusuke Mizukami,Kenzui Taniue, and Nobuyoshi Akimitsu
Genome Research Published:October 30, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.280269.124
Abstract
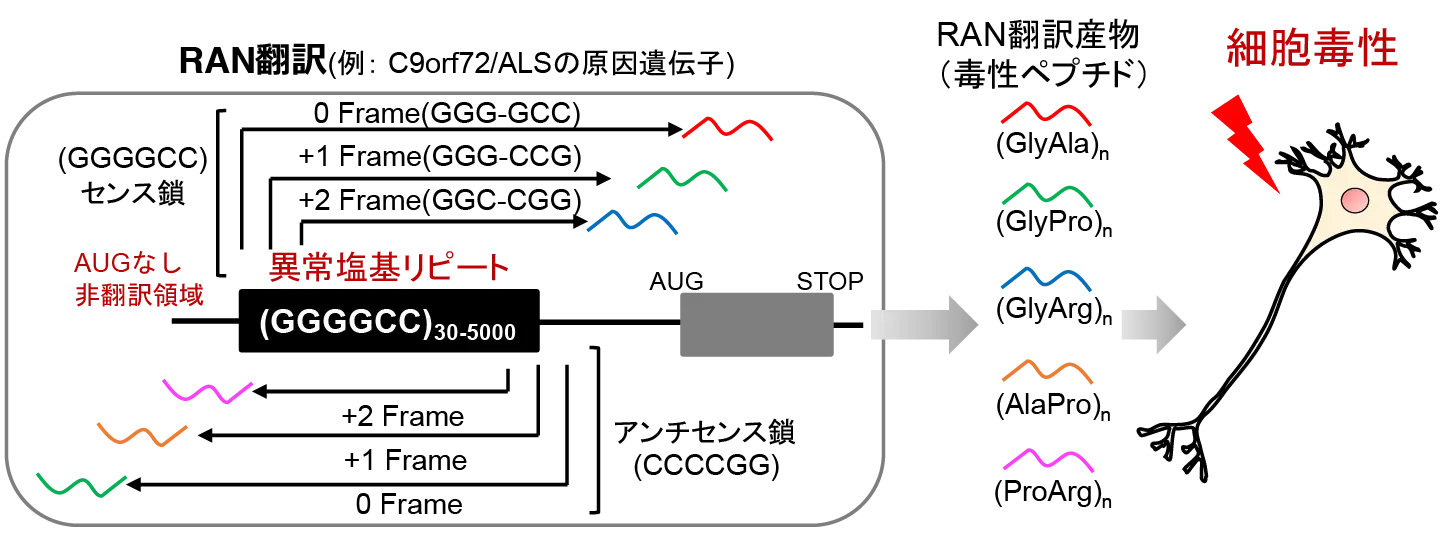
RNA modifications play critical roles in cellular homeostasis and development by regulating gene expression, RNA metabolism, and translation. Their dysregulation contributes to the development of human diseases, including cancer. 3-methylcytidine (m3C) primarily occurs in transfer RNA, where it regulates translation, stem cell pluripotency, and mitochondrial function. m3C has also been detected in polyadenylated (poly[A]) RNA by mass spectrometric analysis; however, its transcriptome-wide distribution and functions remain unknown because of its low abundance and technical challenges. Here, we show that METTL2A, an m3C writer, is upregulated and associated with poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer tumors, while also being essential for pancreatic cancer cell proliferation. Using comparative nanopore direct RNA sequencing, we identify potential METTL2A-mediated m3C sites in poly(A) RNA. These m3C sites are mapped in both messenger RNA and mitochondrial RNA and are enriched in the CC motif and coding sequences. METTL2A knockdown alters expression of S100A4 mRNA isoforms, which contains METTL2A-mediated m3C sites. Notably, many transcripts with METTL2A-mediated m3C sites are upregulated upon METTL2A knockdown. We reveal the transcriptome-wide presence of m3C sites in poly(A) RNA and suggest their potential roles in regulating gene expression.