2025-11-05 マウントサイナイ医療システム(MSHS)
<関連情報>
- https://www.mountsinai.org/about/newsroom/2025/protective-microglia-subtype-offers-potential-new-therapeutic-pathway-in-alzheimers-disease
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09662-z
リンパ系遺伝子の発現は神経保護ミクログリア機能をサポートする Lymphoid gene expression supports neuroprotective microglia function
Pinar Ayata,Jessica M. Crowley,Matthew F. Challman,Vinaya Sahasrabuddhe,Maud Gratuze,Sebastian Werneburg,Diogo Ribeiro,Emma C. Hays,Violeta Durán-Laforet,Travis E. Faust,Philip Hwang,Francisco Mendes Lopes,Chrysa Nikopoulou,Sarah Buchholz,Robert E. Murphy,Taoyu Mei,Anna A. Pimenova,Carmen Romero-Molina,Francesca Garretti,Tulsi A. Patel,Claudia De Sanctis,Angie V. Ramirez Jimenez,Megan Crow,Felix D. Weiss,… Anne Schaefer
Nature Published:05 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09662-z
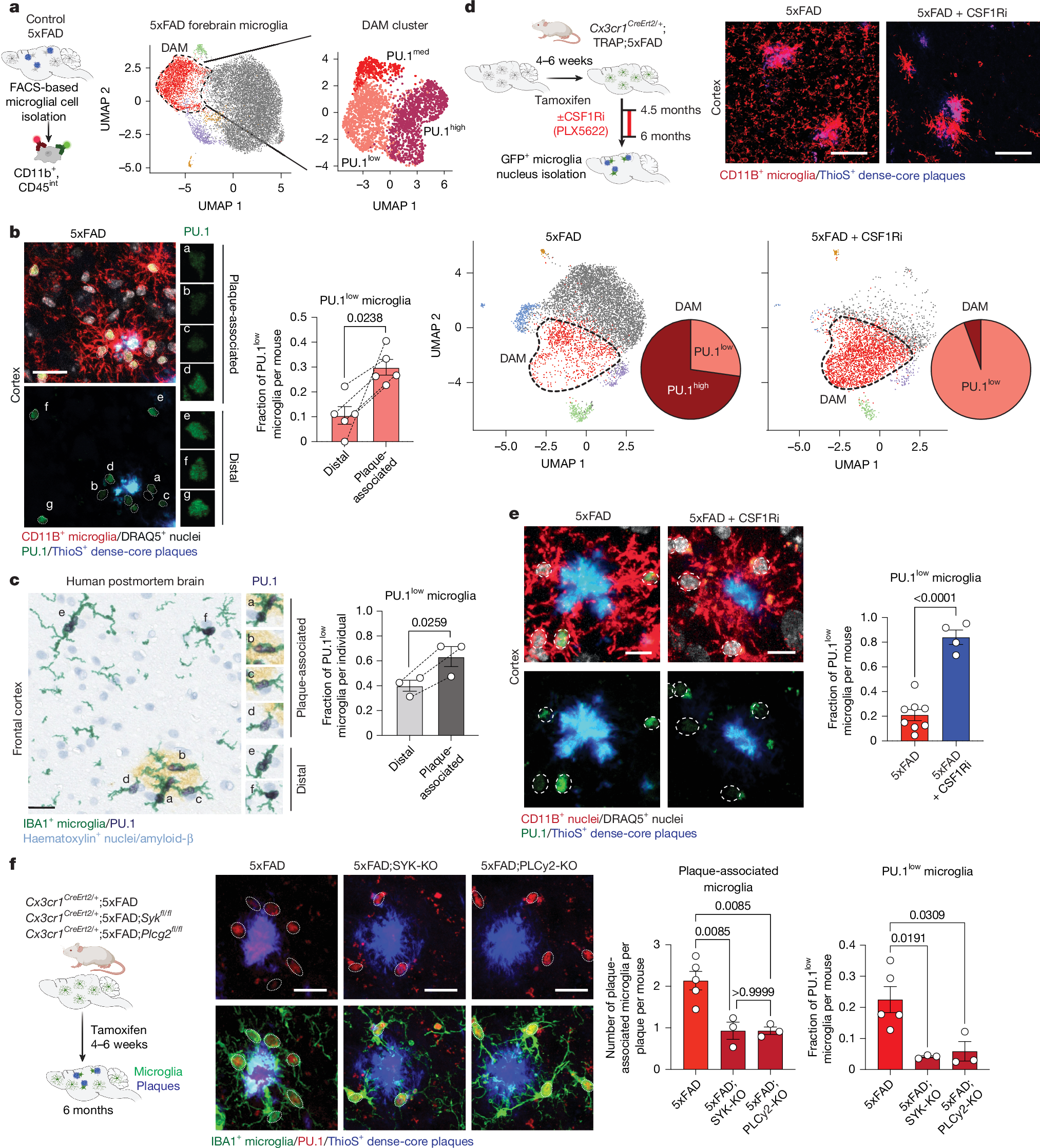
Abstract
Microglia, the innate immune cells of the brain, play a defining role in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease (AD)1. The microglial response to amyloid plaques in AD can range from neuroprotective to neurotoxic2. Here we show that the protective function of microglia is governed by the transcription factor PU.1, which becomes downregulated following microglial contact with plaques. Lowering PU.1 expression in microglia reduces the severity of amyloid disease pathology in mice and is linked to the expression of immunoregulatory lymphoid receptor proteins, particularly CD28, a surface receptor that is critical for T cell activation3,4. Microglia-specific deficiency in CD28, which is expressed by a small subset of plaque-associated PU.1low microglia, promotes a broad inflammatory microglial state that is associated with increased amyloid plaque load. Our findings indicate that PU.1low CD28-expressing microglia may operate as suppressive microglia that mitigate the progression of AD by reducing the severity of neuroinflammation. This role of CD28 and potentially other lymphoid co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory receptor proteins in governing microglial responses in AD points to possible immunotherapy approaches for treating the disease by promoting protective microglial functions.