2025-11-13 カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/genes-may-predict-suicide-risk-in-depression
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41588-025-02396-8
ゲノムワイド関連解析により、早発性うつ病と晩発性うつ病の異なる遺伝子構造が特定された Genome-wide association analyses identify distinct genetic architectures for early-onset and late-onset depression
John R. Shorter,Joëlle A. Pasman,Siim Kurvits,Andreas Jangmo,Joonas Naamanka,Arvid Harder,Espen Hagen,Kaarina Kowalec,Nelli Frilander,Richard Zetterberg,Joeri J. Meijsen,Jesper R. Gådin,Jacob Bergstedt,Ying Xiong,Sara Hägg,Mikael Landén,Christian Rück,John Wallert,Alkistis Skalkidou,Elise Koch,Bayram C. Akdeniz,Oleksandr Frei,FinnGen,Iiris Hovatta,… ,Yi Lu
Nature Genetics Published:13 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-025-02396-8
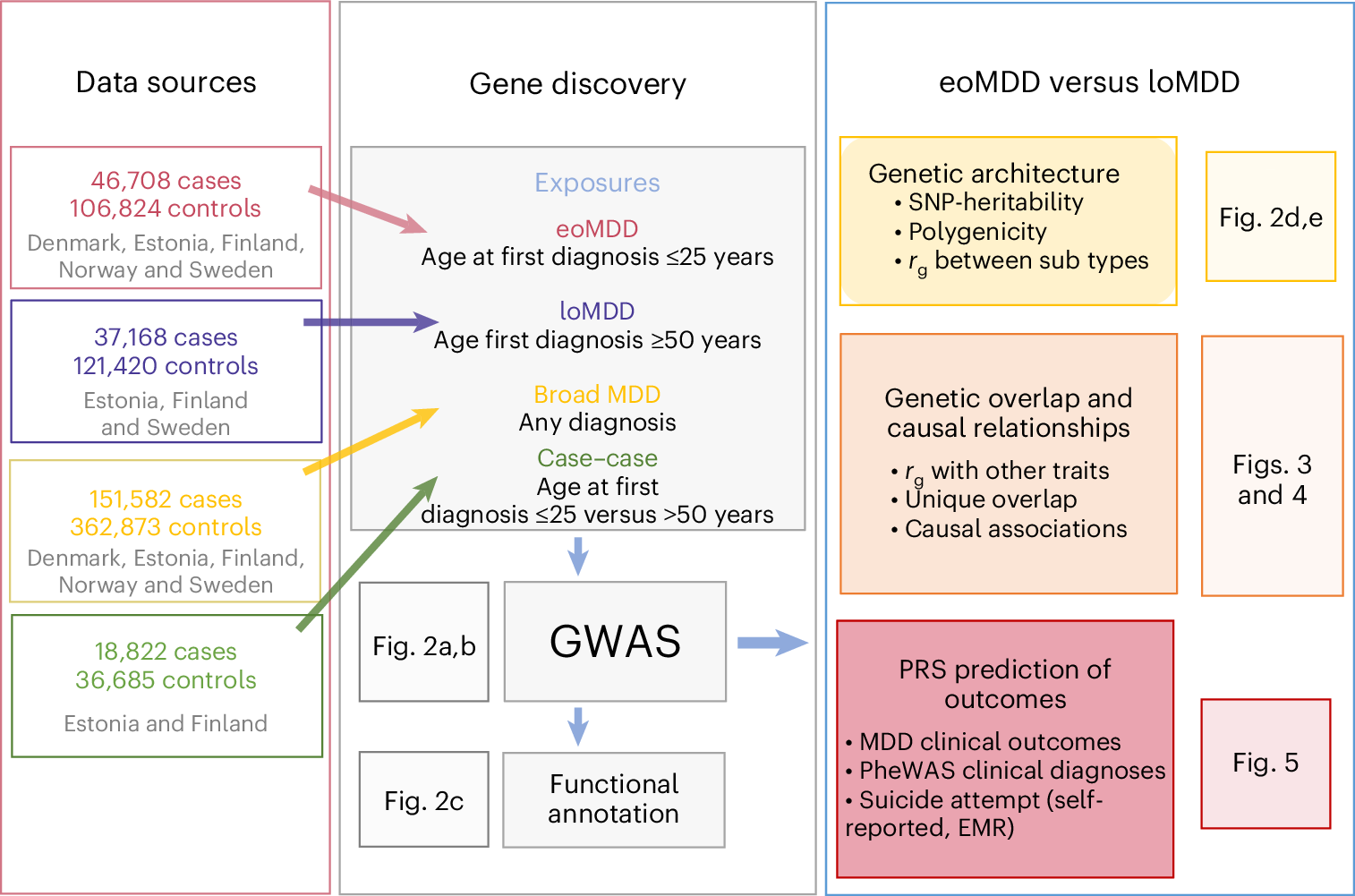
Abstract
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a common and heterogeneous disorder of complex etiology. Studying more homogeneous groups stratified according to clinical characteristics, such as age of onset, can improve the identification of the underlying genetic causes and lead to more targeted treatment strategies. We leveraged Nordic biobanks with longitudinal health registries to investigate differences in the genetic architectures of early-onset (eoMDD; n = 46,708 cases) and late-onset (loMDD; n = 37,168 cases) MDD. We identified 12 genomic loci for eoMDD and two for loMDD. Overall, the two MDD subtypes correlated moderately (genetic correlation, rg = 0.58) and differed in their genetic correlations with related traits. These findings suggest that eoMDD and loMDD have partially distinct genetic signatures, with a specific developmental brain signature for eoMDD. Importantly, we demonstrate that polygenic risk scores (PRS) for eoMDD predict suicide attempts within the first 10 years after the initial diagnosis: the absolute risk for suicide attempt was 26% in the top PRS decile, compared to 12% and 20% in the bottom decile and the intermediate group, respectively. Taken together, our findings can inform precision psychiatry approaches for MDD.


