2025-11-27 カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/point-of-care-rapid-tests-can-improve-screening-for-latent-tuberculosis
- https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaf561/8341627
ベトナムにおける結核感染症に対するSTANDARD F TB-Feron FIAアッセイの診断精度:横断的研究 Diagnostic Accuracy of the STANDARD F TB-Feron FIA Assay for Tuberculosis Infection in Vietnam: A Cross-Sectional Study
Han Thi Nguyen, Luan Nguyen Quang Vo, Andrew James Codlin, Rachel Forse, Tom Wingfield, Kristi Sidney Annerstedt, Emily Lai-Ho MacLean, Jacob Creswell, Beatrice Kirubi, Hoa Binh Nguyen …
Clinical Infectious Diseases Published:26 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaf561
Graphical Abstrac
Abstract
Background
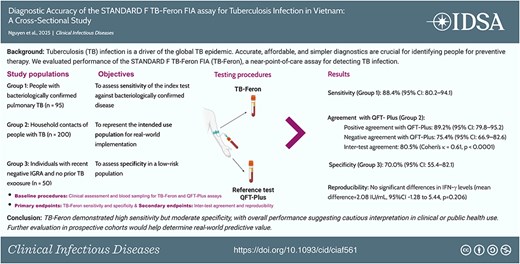
Tuberculosis (TB) infection is a driver of the global TB epidemic. Accurate, affordable, and simpler diagnostics are crucial for identifying people for preventive therapy. We evaluated the diagnostic performance of the STANDARD F TB-Feron FIA (TB-Feron), a near-point-of-care (POC) assay for detecting TB infection.
Methods
From June to December 2024, we conducted a cross-sectional study at the Vietnam National Lung Hospital, enrolling 352 participants, including 345 eligible participants: 95 with microbiologically confirmed pulmonary TB (Group 1), 200 household contacts of people with pulmonary TB (Group 2), and 50 with a recent history of a negative QFT-Plus result and no known TB exposure (Group 3). Participants were tested with TB-Feron and the reference standard, QuantiFERON TB Gold Plus (QFT-Plus). Results were compared for sensitivity and specificity (primary endpoints), with inter-test agreement (Cohen’s κ) and reproducibility (Bland–Altman analysis) as secondary outcomes.
Results
Among 345 eligible participants, TB-Feron sensitivity was 88.4% (95% confidence interval [CI] 80.2–94.1) in Group 1, and specificity was 70.0% (55.4–82.1) in Group 3. In Group 2, positive and negative agreements with QFT-Plus were 89.2% (79.8–95.2%) and 75.4% (66.9–82.6), respectively, with inter-test agreement of 80.5% (Cohen’s κ=0.6069, P < .0001). Intra-test reproducibility showed no significant differences in IFN-γ levels (mean difference = 2.08 IU/mL, 95% CI -1.28 to 5.44, P = .206).
Conclusions
With high sensitivity, the TB-Feron assay is a potential near-POC alternative to the QFT-Plus assay for diagnosing TB infection, but requires consideration of its suboptimal specificity.