2025-12-04 オックスフォード大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.ox.ac.uk/news/2025-12-04-rapid-low-cost-tests-can-help-prevent-child-deaths-contaminated-medicinal-syrups
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-26670-1
低コストで現場で展開可能なアッセイを用いた原材料および医薬品シロップ中のエチレングリコールおよびジエチレングリコールの迅速スクリーニング Rapid screening of ethylene glycol and diethylene glycol in raw materials and medicinal syrups using low-cost field deployable assays
Benediktus Yohan Arman,Isabelle Legge,John Walsby-Tickle,Tehmina Bharucha,Julia Gabel,Gesa Gnegel,Michael Deats,Sneha Banerjee,Robert Stokes,Hamid A. Merchant,Pavel Matousek,James McCullagh,Céline Caillet,Paul N. Newton,Nicole Zitzmann & Bevin Gangadharan
Scientific Reports Published:03 December 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-26670-1
Abstract
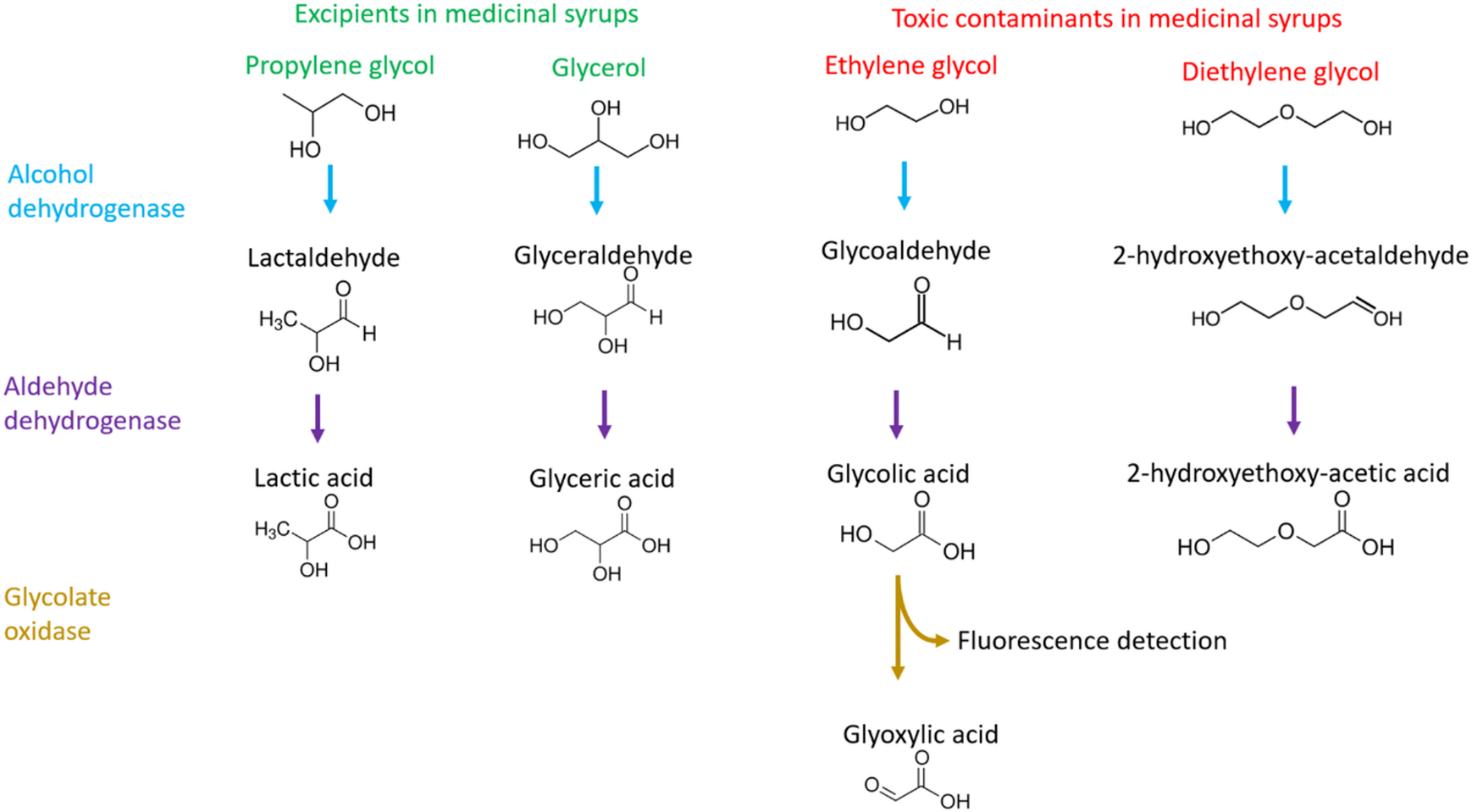
There have been hundreds of child deaths due to contamination of medicinal syrups with diethylene glycol (DEG) and ethylene glycol (EG). Detection of DEG and EG is usually performed by gas chromatography, a method that is costly, laborious, time-consuming, and not readily available in many low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Thin-layer chromatography is relatively lower cost and portable; however, as with gas chromatography, it requires time and trained personnel. Alternative rapid, low-cost and simple methods to determine DEG/EG contamination are needed. We tested the suitability of enzymatic, chemical and antibody-based assays to determine DEG/EG. Assays using alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase alone as well as in combination with glycolate oxidase could determine EG in raw materials and at less than 0.1% m/m in some finished products. Saliva and breast milk alcohol test strips, containing alcohol oxidase and costing $1, could determine EG with a detection limit of 0.5 to 2% m/m in under 2 minutes. Disposable breathalysers, costing only $1, could determine both DEG and EG from other alcohols in only 10 seconds. The methods described provide simple, rapid and low-cost alternatives to help determine DEG and EG contamination in pharmaceutical supply chains to help prevent deaths where equipment and trained human resources are limited.