2025-12-16 藤田医科大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.fujita-hu.ac.jp/news/vsfo8q000000ulek.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-27789-x
スタチンは、ユビキチン様3修飾に依存してPD-L1の小さな細胞外小胞への選別を減弱させる Statins attenuate PD-L1 sorting to small extracellular vesicles dependent on ubiquitin-like 3 modification
Hiroshi Ageta,Yoshihisa Shimada,Tadahiro Nagaoka,Kazuki Takenaka,Yusuke Yoshioka,Kohtaro Konno,Ryosuke Amemiya,Kumiko Nagase,Keisuke Hitachi,Takanori Onouchi,Masahiko Watanabe,Takahiro Ochiya & Kunihiro Tsuchida
Scientific Reports Published:15 December 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-27789-x
Abstract
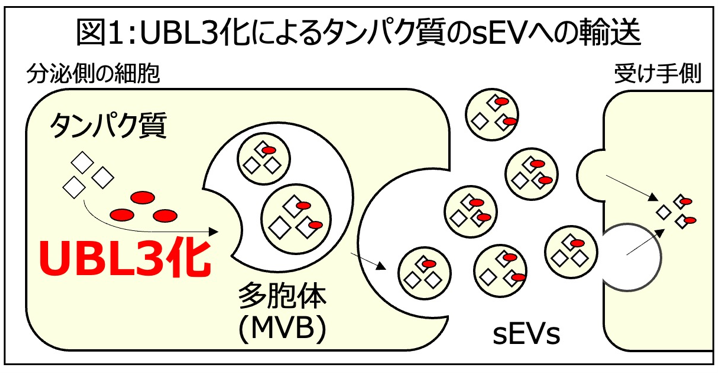
Small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) mediate cell-to-cell communication by carrying RNAs and proteins. Ubiquitin-like 3 (UBL3) functions as a posttranslational modification factor, regulating protein sorting to sEVs. Programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) binds to programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) on immune cells, suppressing their function. Although immune checkpoint inhibitors, anti-PD-L1 and anti-PD-1 antibodies, have improved cancer treatment, efficacy remains limited (~ 25%). Per recent studies, PD-L1-containing sEVs are elevated in cancer patients, contributing to impaired immunotherapy responses. Herein, we discovered that PD-L1 is modified by UBL3 and that its sorting to sEVs is regulated by UBL3. Furthermore, we found that statins, commonly prescribed for hypercholesterolemia, inhibit UBL3 modification, thereby reducing PD-L1 sorting to sEVs. Among patients with a high tumor proportion score, serum levels of PD-L1-containing sEVs were significantly lower in those using statins. Consistently, bioinformatic analysis revealed that UBL3 and PD-L1 expression levels affect lung cancer survival. Integrating statins into existing combination therapies may therefore offer a promising strategy to enhance immunotherapy efficacy.