2025-12-23 産業技術総合研究所
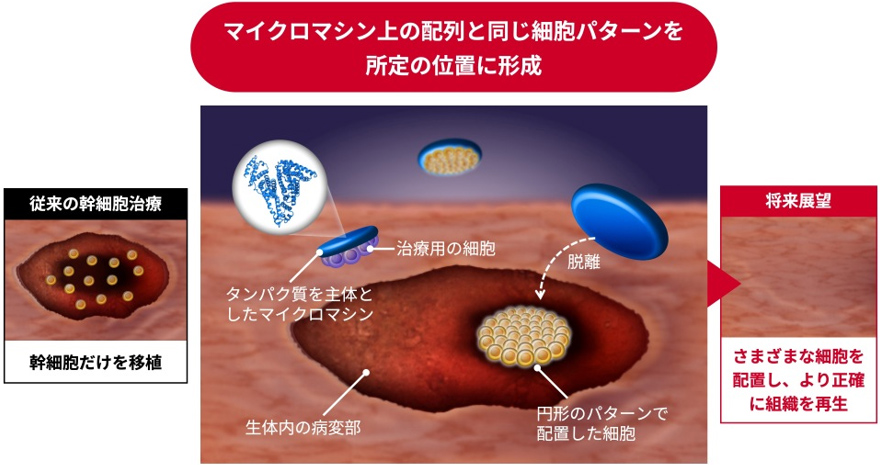
マイクロマシンを用いた生体内での細胞配置
※原論文の図を引用・改変したものを使用しています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.aist.go.jp/aist_j/press_release/pr2025/pr20251223/pr20251223.html
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2590006425012554
組織工学アプリケーション向けに特別に設計されたマイクロロボットを使用した生体内細胞パターン形成 Cell patterning in vivo using microrobot specifically designed for tissue engineering applications
Hironori Yamazoe, Yoshiaki Yamano, Yuji Teramura, Shinichiro Shinzaki
Materials Today Bio Available online: 17 December 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102683
Abstract
The arrangement of cells in a desired pattern at target positions, known as cell patterning, is a crucial technique for constructing desirable tissues. While cell patterning has been traditionally performed on substrates, in vivo approaches remain largely unexplored. In vivo cell-patterning techniques show potential for achieving accurate and reliable tissue regeneration by building new tissues at lesion sites in a highly controlled manner using various therapeutic cells. This study introduces a pioneering approach for cell patterning in vivo using a microrobot specifically designed for tissue engineering applications. The body of the microrobot was fabricated using serum albumin and magnetic nanoparticles, and cell membrane-anchoring regents were bound to its surface. This robot effectively captured cells and rapidly released them at target sites, minimizing the burden on the recipient. Using this robot, cellular patterns formed successfully on various biological components, including Matrigel, other cell types, and inflamed colon tissues, in 30 min. Furthermore, as a proof-of-concept, cell patterning was performed inside the colon of mice with colitis. To ensure clinical applicability, the cell-loaded microrobot was introduced near the target site via an endoscope and subsequently guided by a magnetic field to create stem cell patterns in damaged colon tissues. This microrobot-based cell patterning will contribute to the establishment of a new field, in vivo cell patterning, and the advancement of sophisticated stem cell-based therapies.