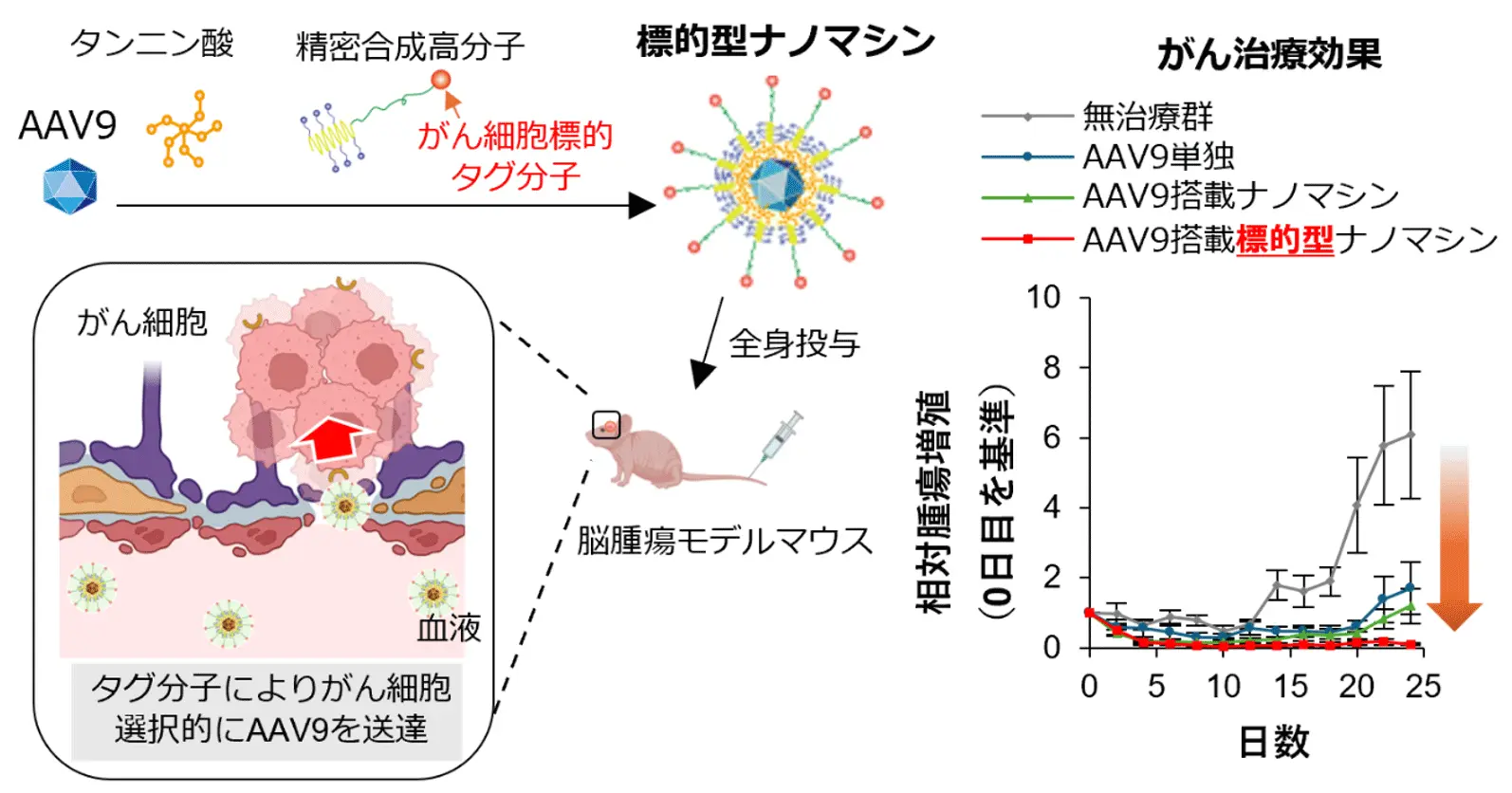
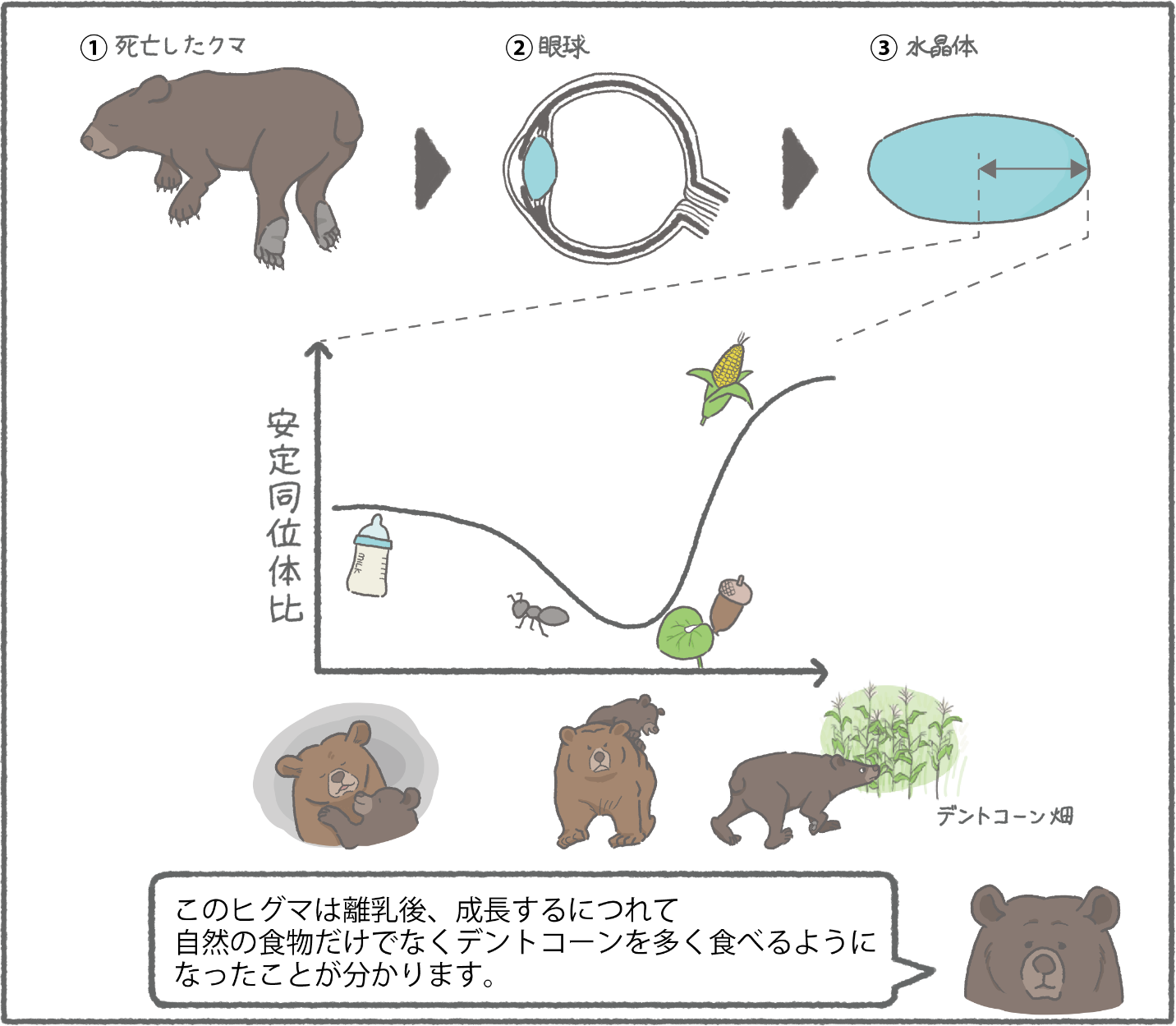
2025-12-24 東京科学大学
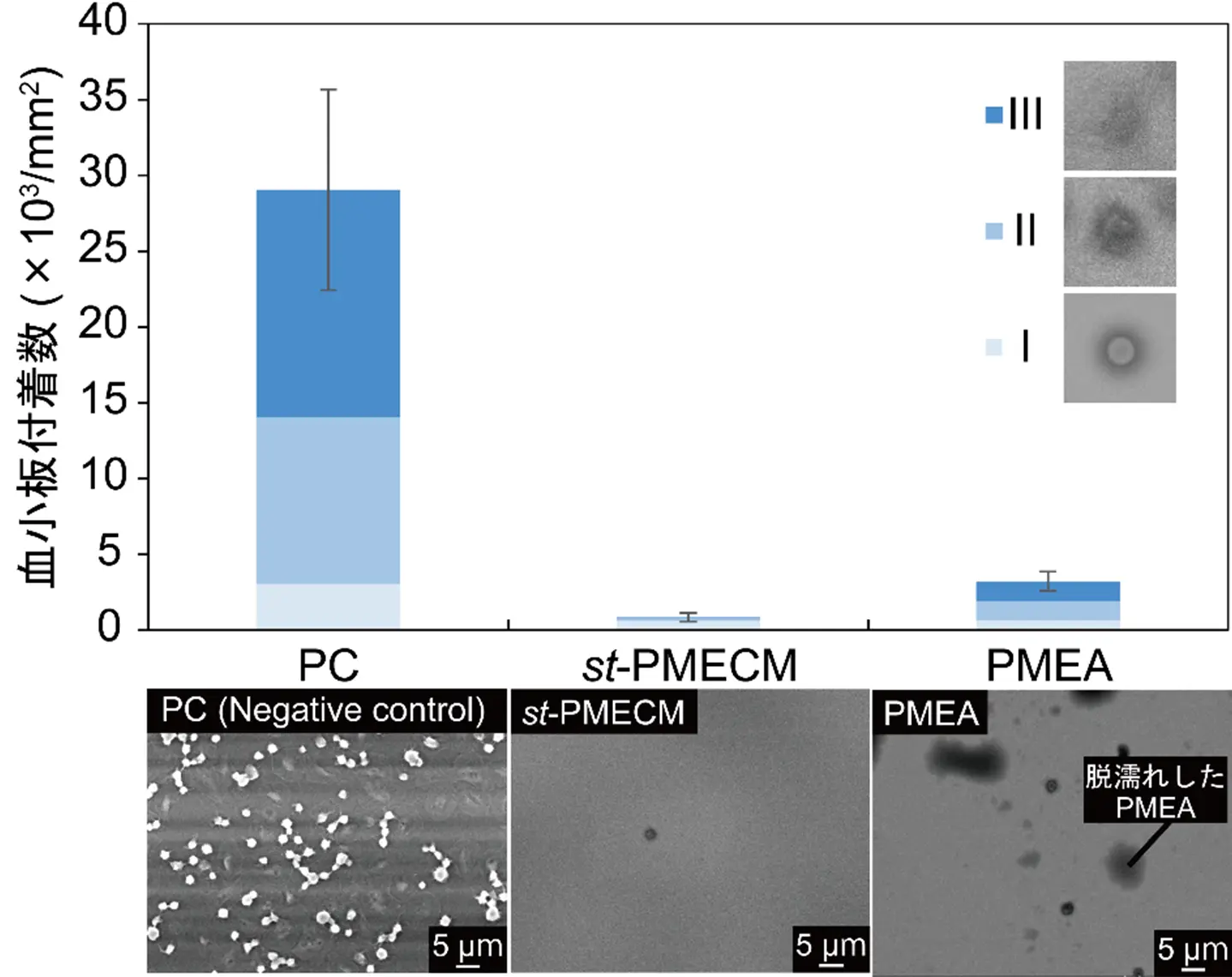
図1. 血小板付着試験後の走査型電子顕微鏡画像と活性化度ごとに計測された血小板付着数。血小板の活性化度はIが最も低い球状形態、IIIが最も高い扁平状態である。本試験ではポリカーボネート(PC)をネガティブコントロール(陰性の対照実験)として用いた。
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/zpq68mqevpwf
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=2945&prevId=&key=bda250190cc3afd767cb7a57bee7dd2b.pdf
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsabm.5c01687
固体フィルム表面に高度に伸長した側鎖のメトキシエチル末端を高密度に充填した、優れた抗血栓性シンジオタクチックポリ(置換メチレン) Superior Antithrombogenic Syndiotactic Poly(Substituted Methylene) with Densely Packed Methoxyethyl Ends of Highly Extended Side Chains at the Solid Film Surface
Naruki Kurokawa,Masamichi Kiyoura,Hidetoshi Matsumoto,Masatoshi Tokita
ACS Applied Bio Materials Published: October 26, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.5c01687
Abstract
A syndiotactic poly(substituted methylene) (st-PM) featuring (2-methoxyethoxy)carbonyl side chains (st-PMECM) exhibited considerably superior antithrombogenicity compared to a typical conventional antithrombogenic polyacrylate comprising the same side chain (i.e., poly(2-methoxyethyl acrylate); PMEA). The number of adherent platelets on the surface of the st-PMECM films was 0.8 × 103 mm–2, which was one-fourth of that on the PMEA films (3.2 × 103 mm–2), and 75% of these platelets were in the lowest activation state. During the platelet adhesion test, the st-PMECM films maintained surface wettability on the substrates, addressing the commonly observed dewetting issue in the practical applications of conventional antithrombogenic polyacrylates. In addition, the st-PMECM films retained their surface structure upon exposure to plasma, as indicated by the unchanged water contact angle over time, unlike in the case of polyacrylates. These characteristics of st-PMECM are attributed to the formation of liquid crystal structure, with the backbone arranged into a two-dimensional lattice and with the side chains stretched at an angle to the backbone axis. Owing to this structure, the methoxy moieties at the ends of the side chains were exposed to the outermost surface and hydrated with water, enabling the st-PMECM films to possess a larger amount of intermediate water on the surface than the PMEA films. The results demonstrate that st-PMs more effectively enhance the functionality of the side chains than polyacrylates featuring the same side chains, enabling st-PMECM to exhibit superior antithrombogenicity attributed to methoxy moieties. To the best of our knowledge, st-PMECM is the first inherently solid-like polymer that simultaneously exhibits outstanding antithrombogenicity.