2026-01-07 国立循環器病研究センター
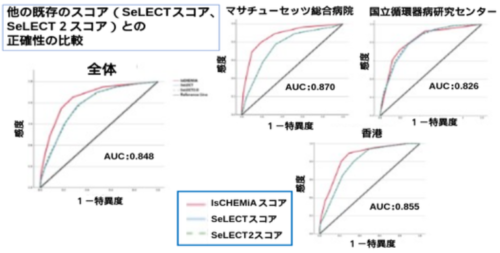
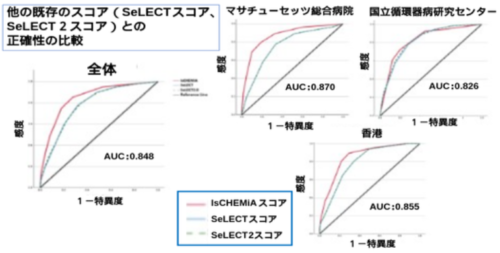
図1:他の既存のスコア(SeLECTスコア/SeLECT2スコア)との正確性の比較
AUC:Area under the curve、統計学的にモデルの正確性を示す指標。1が最高値、0が最低値
出典:本論文を改変
<関連情報>
- https://www.ncvc.go.jp/hospital/topics/topics_36499/
- https://www.neurology.org/doi/10.1212/WNL.0000000000214486
脳卒中後てんかんの予測のための新しい画像ベースのリスクスコア(IsCHEMiA)の開発と国際的検証 Development and International Validation of a Novel Imaging-Based Risk Score (IsCHEMiA) for the Prediction of Poststroke Epilepsy
William C.Y. Leung, Tomotaka Tanaka, Rachel A. Donahue, Kandace Chi Wing Chan , Jianing Wang, Tommy Ho Fung Chung, Yuen Kwun Wong, …, and Aneesh B. Singhal
Neurology Published:January 5, 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000214486
Abstract
Background and Objectives
Stroke is one of the most common causes of adult-onset epilepsy. We aimed to develop a model to predict poststroke epilepsy (PSE) after a first-ever ischemic stroke, incorporating neuroimaging features of incident stroke.
Methods
We analyzed clinical and neuroimaging features of patients with first-ever acute ischemic stroke consecutively admitted to Massachusetts General Hospital, United States. We performed competing risk regression with all-cause mortality as a competing event and derived the final multivariable model using backward stepwise elimination by the Akaike Information Criterion. We externally validated the model in 3 international cohorts in Hong Kong (Queen Mary Hospital [HK-QMH], Ruttonjee Hospital [HK-RH]) and Japan (National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center) by discrimination and calibration and compared its performance with the SeLECT and SeLECT2.0 scores.
Results
We included a final derivative cohort of 1,436 patients with a mean age of 67.4 years and a slight male predominance (54.7%), along with a total of 2,534 patients in the validation cohorts. PSE, defined as the occurrence or recurrence of unprovoked seizure >7 days after stroke, occurred in 5.5% of the overall study population. Six variables (infarct size [Is], cortical involvement [C], hemorrhagic transformation [H], early seizures [E], MCA involvement [Mi], and age younger than 65 [A]) were independent predictors included in the final model and formed the IsCHEMiA score. Model discrimination was consistent across all cohorts, with c-statistics of 0.870 (United States), 0.852 (HK-QMH), 0.857 (HK-RH), and 0.826 (Japan). The model was well calibrated at 1 and 3 years after stroke in the overall validation cohort. The IsCHEMiA score improved the prediction of PSE compared with SeLECT in all cohorts and the overall study population (c-statistic 0.848 vs 0.782, z = 5.170, p < 0.0001). For example, an IsCHEMiA score of 3 predicts a low risk of PSE at 1 year (2%) and 5 years (6%) while an IsCHEMiA score ≥8 predicts a high risk at 1 year (67%) and 5 years (78%).
Discussion
The IsCHEMiA score is an improved and readily applicable predictive model developed and validated using international stroke cohorts in the modern era of reperfusion therapies. It serves as a foundation for personalized management and may guide future clinical trials on antiepileptogenic therapies in acute ischemic stroke.