2026-01-09 東京科学大学
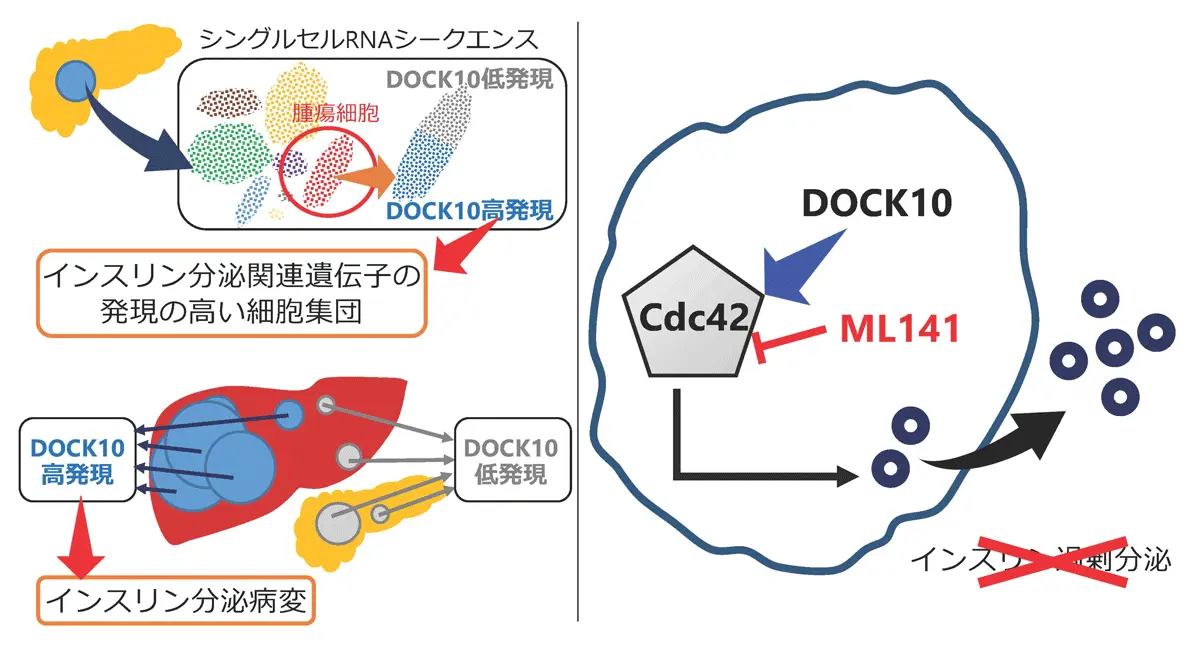
図2. DOCK10はインスリノーマの新規診断マーカーおよび新規治療薬として有用である
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/vpyar6s83cqs
- https://www.cmghjournal.org/article/S2352-345X(25)00247-4/fulltext
DOCK10はインスリノーマにおけるインスリン過剰分泌を制御し、診断および治療の標的として機能する DOCK10 Regulates Insulin Hypersecretion in Insulinoma and Serves as a Diagnostic and Therapeutic Target
Hiromune Katsuda ∙ Go Ito ∙ Franziska Kimmig ∙ … ∙ Mamoru Watanabe ∙ Philip Rosenstiel ∙ Ryuichi Okamoto
Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology Published:December 11, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmgh.2025.101705
Abstract
Background & Aims
Insulinomas are rare pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (pan-NENs) characterized by inappropriate insulin secretion. Despite advances in imaging techniques, the reliable identification of insulin-secreting lesions remains challenging. In addition, medical treatment options are limited and have seen little development in recent years, highlighting the unmet need for improved diagnostic tools and therapeutic strategies. This study aimed to identify the molecular mechanisms underlying insulin hypersecretion in insulinomas.
Methods
We established a biobank of human insulinoma surgical specimens and matched organoids. Comprehensive transcriptomic analyses—including bulk RNA sequencing, single-cell RNA sequencing, quantitative polymerase chain reaction, and immunohistochemistry—were conducted to identify genes enriched in insulin-secreting components. Functional validation was performed using MIN6 cells, a xenograft mouse model, and long-term cultured human insulinoma organoids.
Results
We identified dedicator of cytokinesis 10 (DOCK10) as a gene selectively overexpressed in insulin-secreting components of insulinomas. DOCK10 knockdown impaired glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in both mouse insulinoma cells and patient-derived organoids. Inhibition of the downstream effector Cdc42 with ML141 reduced insulin hypersecretion and improved survival in a MIN6 xenograft mouse model. These findings uncover a previously unrecognized role of the DOCK10–Cdc42 axis in regulating insulin secretion in insulinoma.
Conclusions
This study suggests that DOCK10 may serve as a diagnostic marker for insulin-secreting lesions and a potential therapeutic target in insulinoma. It provides mechanistic insights that may inform future strategies for precision diagnostics and treatment of functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.