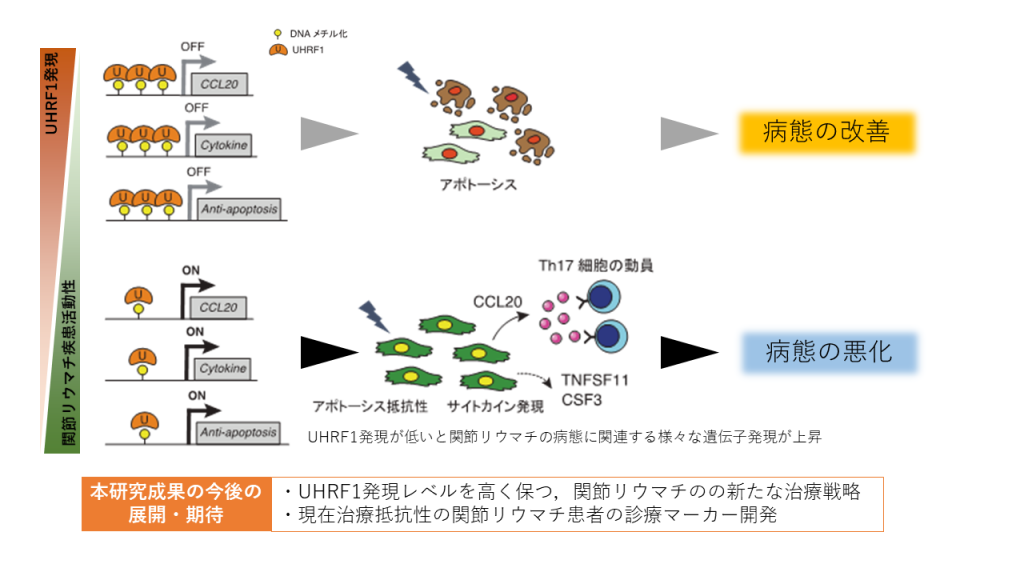
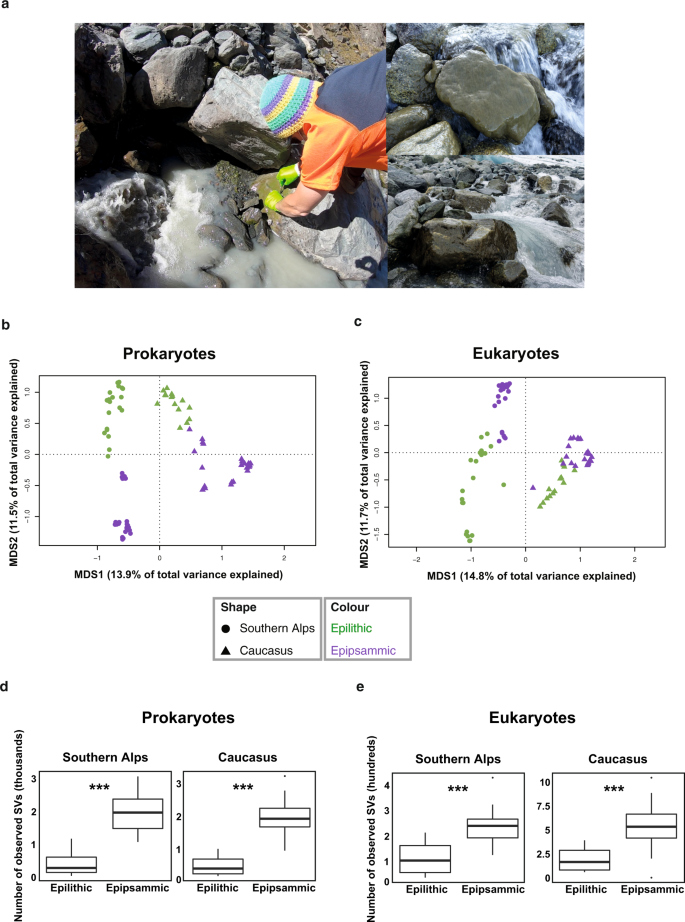
2022-04-27 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
氷河を水源とする河川の生態系は、何千年にもわたって栄養不足の過酷な環境条件を生き抜いてきた。これは、EPFLの建築・土木・環境工学部(ENAC)に属するEPFL河川生態系研究所(RIVER)の科学者が発表した2つの研究結果の結論である。
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/climate-warming-alters-glacier-fed-stream-ecosyste/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-29914-0
氷河渓流におけるバイオフィルムの生態学的好機に対するゲノムおよび代謝適応に関する研究 Genomic and metabolic adaptations of biofilms to ecological windows of opportunities in glacier-fed streams
Susheel Bhanu Busi,Massimo Bourquin,Stilianos Fodelianakis,Grégoire Michoud,Tyler J. Kohler,Hannes Peter,Paraskevi Pramateftaki,Michail Styllas,Matteo Tolosano,Vincent De Staercke,Martina Schön,Laura de Nies,Ramona Marasco,Daniele Daffonchio,Leïla Ezzat,Paul Wilmes & Tom J. Battin
Nature Communications Published: 20 April 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29914-0
Abstract
In glacier-fed streams, ecological windows of opportunity allow complex microbial biofilms to develop and transiently form the basis of the food web, thereby controlling key ecosystem processes. Using metagenome-assembled genomes, we unravel strategies that allow biofilms to seize this opportunity in an ecosystem otherwise characterized by harsh environmental conditions. We observe a diverse microbiome spanning the entire tree of life including a rich virome. Various co-existing energy acquisition pathways point to diverse niches and the exploitation of available resources, likely fostering the establishment of complex biofilms during windows of opportunity. The wide occurrence of rhodopsins, besides chlorophyll, highlights the role of solar energy capture in these biofilms while internal carbon and nutrient cycling between photoautotrophs and heterotrophs may help overcome constraints imposed by oligotrophy in these habitats. Mechanisms potentially protecting bacteria against low temperatures and high UV-radiation are also revealed and the selective pressure of this environment is further highlighted by a phylogenomic analysis differentiating important components of the glacier-fed stream microbiome from other ecosystems. Our findings reveal key genomic underpinnings of adaptive traits contributing to the success of complex biofilms to exploit environmental opportunities in glacier-fed streams, which are now rapidly changing owing to global warming.