UCI主導の発見により、治療法の改善が期待される UCI-led finding helps propel search for improved treatments
2022-07-19 カリフォルニア大学校アーバイン校(UCI)
この発見は、特に危険なメラノーマや膵臓腺がん、最も一般的な小児脳腫瘍や成人の皮膚がんに対する治療法の可能性につながる可能性があります。
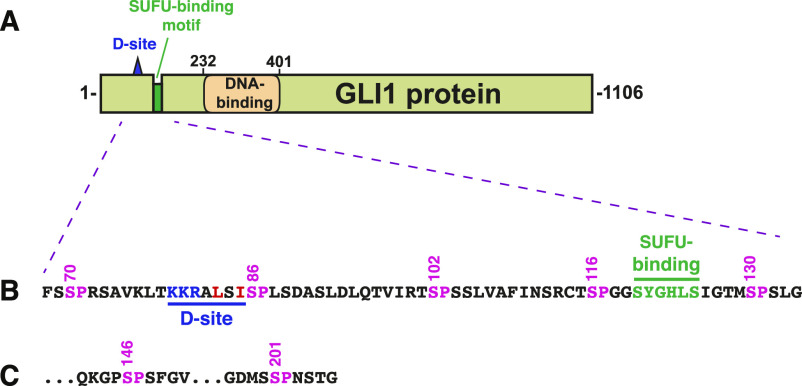
GLI1は、通常、SUFUと呼ばれるタンパク質としっかり結合しています。このタンパク質は、GLI1が細胞核に侵入して遺伝子をオンにするのを妨げ、GLI1を抑制している。研究チームは、GLI1タンパク質のうち、リン酸化される可能性のある7つの部位を調査した。
GLI1とSUFUの結合を弱めるためにリン酸化される可能性のある3つの部位を特定し、その部位全てがリン酸化されることで、1つだけ、あるいは2つだけでもリン酸基を受け取る場合に比べて、SUFUからのGLI1の脱出が著しく高くなることを指摘しました。
<関連情報>
- https://news.uci.edu/2022/07/18/how-a-protein-breaks-free-to-cause-deadly-cancers/
- https://www.life-science-alliance.org/content/5/11/e202101353
ERK2 MAPキナーゼはGLI1のマルチサイトリン酸化によりSUFUの結合を制御する ERK2 MAP kinase regulates SUFU binding by multisite phosphorylation of GLI1
A Jane Bardwell, Beibei Wu,Kavita Y Sarin, Marian L Waterman, Scott X Atwood, Lee Bardwell
Life Science Alliance Published 13 July 2022
DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202101353
Abstract
Crosstalk between the Hedgehog and MAPK signaling pathways occurs in several types of cancer and contributes to clinical resistance to Hedgehog pathway inhibitors. Here we show that MAP kinase-mediated phosphorylation weakens the binding of the GLI1 transcription factor to its negative regulator SUFU. ERK2 phosphorylates GLI1 on three evolutionarily conserved target sites (S102, S116, and S130) located near the high-affinity binding site for SUFU; these phosphorylations cooperate to weaken the affinity of GLI1–SUFU binding by over 25-fold. Phosphorylation of any one, or even any two, of the three sites does not result in the level of SUFU release seen when all three sites are phosphorylated. Tumor-derived mutations in R100 and S105, residues bordering S102, also diminish SUFU binding, collectively defining a novel evolutionarily conserved SUFU affinity–modulating region. In cultured mammalian cells, GLI1 variants containing phosphomimetic substitutions of S102, S116, and S130 displayed an increased ability to drive transcription. We conclude that multisite phosphorylation of GLI1 by ERK2 or other MAP kinases weakens GLI1-SUFU binding, thereby facilitating GLI1 activation and contributing to both physiological and pathological crosstalk.