2023-03-29 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
腫瘍の生物学的起源を理解することは、この病気に対する新しい治療法の開発に役立つ可能性があります。米国では、毎年約8万人の膀胱がん患者が診断されています。治療計画には、免疫チェックポイント阻害剤と呼ばれる免疫療法の一種が含まれることがあります。しかし、膀胱がんの大部分はこのチェックポイント阻害剤に耐性があり、効果があった患者さんでも、最終的には腫瘍が治療に抵抗することがあります。
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/research/story/different-types-bladder-cancer-cells-share-common-genetic-ancestry/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-34251-3
扁平上皮分化した膀胱がんにおいて、FOXA1抑制が系統の可塑性と免疫異質性を駆動する FOXA1 repression drives lineage plasticity and immune heterogeneity in bladder cancers with squamous differentiation
Joshua I. Warrick,Wenhuo Hu,Hironobu Yamashita,Vonn Walter,Lauren Shuman,Jenna M. Craig,Lan L. Gellert,Mauro A. A. Castro,A. Gordon Robertson,Fengshen Kuo,Irina Ostrovnaya,Judy Sarungbam,Ying-bei Chen,Anuradha Gopalan,Sahussapont J. Sirintrapun,Samson W. Fine,Satish K. Tickoo,Kwanghee Kim,Jasmine Thomas,Nagar Karan,Sizhi Paul Gao,Timothy N. Clinton,Andrew T. Lenis,Timothy A. Chan,Ziyu Chen,Manisha Rao,Travis J. Hollman,Yanyun Li,Nicholas D. Socci,Shweta Chavan,Agnes Viale,Neeman Mohibullah,Bernard H. Bochner,Eugene J. Pietzak,Min Yuen Teo,Gopa Iyer,Jonathan E. Rosenberg,Dean F. Bajorin,Matthew Kaag,Suzanne B. Merrill,Monika Joshi,Rosalyn Adam,John A. Taylor III,Peter E. Clark,Jay D. Raman,Victor E. Reuter,Yu Chen,Samuel A. Funt,David B. Solit,David J. DeGraff & Hikmat A. Al-Ahmadie
Nature Communications Published:02 November 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-34251-3
Abstract
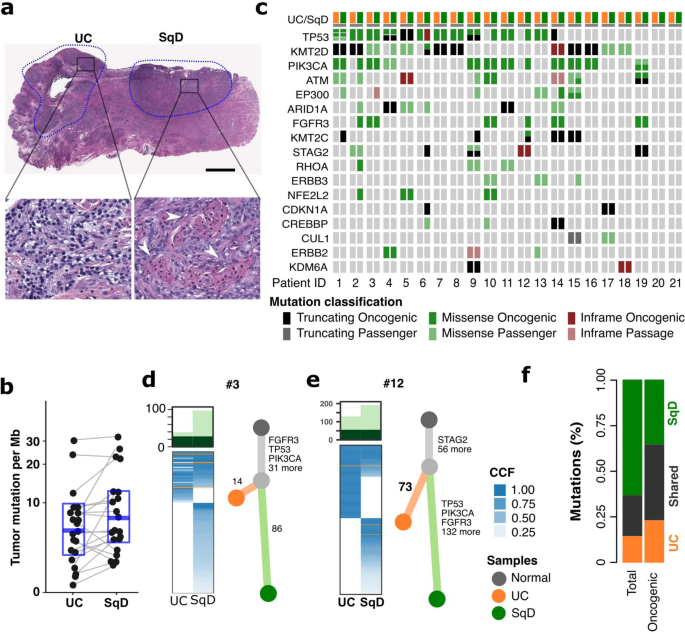
Cancers arising from the bladder urothelium often exhibit lineage plasticity with regions of urothelial carcinoma adjacent to or admixed with regions of divergent histomorphology, most commonly squamous differentiation. To define the biologic basis for and clinical significance of this morphologic heterogeneity, here we perform integrated genomic analyses of mixed histology bladder cancers with separable regions of urothelial and squamous differentiation. We find that squamous differentiation is a marker of intratumoral genomic and immunologic heterogeneity in patients with bladder cancer and a biomarker of intrinsic immunotherapy resistance. Phylogenetic analysis confirms that in all cases the urothelial and squamous regions are derived from a common shared precursor. Despite the presence of marked genomic heterogeneity between co-existent urothelial and squamous differentiated regions, no recurrent genomic alteration exclusive to the urothelial or squamous morphologies is identified. Rather, lineage plasticity in bladder cancers with squamous differentiation is associated with loss of expression of FOXA1, GATA3, and PPARG, transcription factors critical for maintenance of urothelial cell identity. Of clinical significance, lineage plasticity and PD-L1 expression is coordinately dysregulated via FOXA1, with patients exhibiting morphologic heterogeneity pre-treatment significantly less likely to respond to immune checkpoint inhibitors.