最先端ツールを使って、UHのチームが新しいバイオマーカーを発見 Using Cutting Edge Tools, UH Team Discovers New Biomarkers
2023-04-27 ヒューストン大学(UH)
現在の診断法である侵襲的な膀胱鏡検査に代わる、簡単な尿検査が新たな標準となる可能性がある。
本研究では、1,317種類のタンパク質の尿中での発現を調べた結果、血栓の分解産物であるD-ダイマーが膀胱がんの初期診断や再発検出に役立つ可能性があることが判明した。さらに、IL-8とIgAは、病気の進行を判別するための潜在的なバイオマーカーとして、膀胱がんの診断と治療に革新的な役割を果たすことが期待されている。
<関連情報>
- https://uh.edu/news-events/stories/2023/april-2023/04272023-bladder-cancer-biomarker-mohan.php
- https://bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916-023-02813-x
膀胱癌の診断と病期分類のための尿中バイオマーカーの包括的プロテオミクスとプラットフォームバリデーション Comprehensive proteomics and platform validation of urinary biomarkers for bladder cancer diagnosis and staging
Kamala Vanarsa,Jessica Castillo,Long Wang,Kyung Hyun Lee,Claudia Pedroza,Yair Lotan & Chandra Mohan
BMC Medicine Published:05 April 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-023-02813-x
Abstract
Background
Bladder cancer (BC) is among the most common cancers diagnosed in men in the USA. The current gold standards for the diagnosis of BC are invasive or lack the sensitivity to correctly identify the disease.
Methods
An aptamer-based screen analyzed the expression of 1317 proteins in BC compared to urology clinic controls. The top hits were subjected to systems biology analyses. Next, 30 urine proteins were ELISA-validated in an independent cohort of 68 subjects. Three of these proteins were next validated in an independent BC cohort of differing ethnicity.
Results
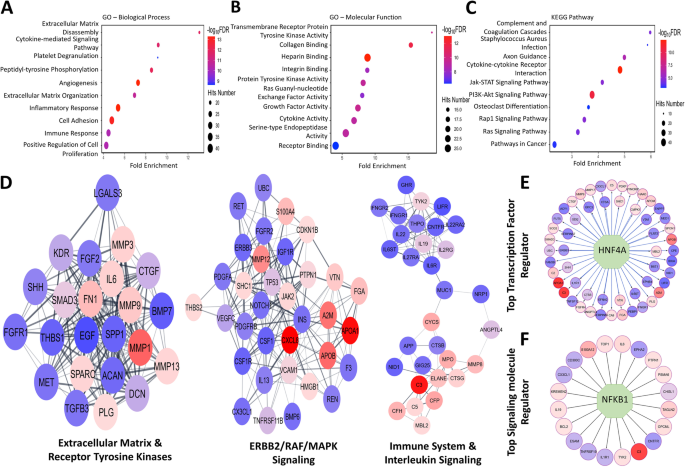
Systems biology analysis implicated molecular functions related to the extracellular matrix, collagen, integrin, heparin, and transmembrane tyrosine kinase signaling in BC susceptibility, with HNF4A and NFKB1 emerging as key molecular regulators. STEM analysis of the dysregulated pathways implicated a functional role for the immune system, complement, and interleukins in BC disease progression. Of 21 urine proteins that discriminated BC from urology clinic controls (UC), urine D-dimer displayed the highest accuracy (0.96) and sensitivity of 97%. Furthermore, 8 urine proteins significantly discriminated MIBC from NMIBC (AUC = 0.75–0.99), with IL-8 and IgA being the best performers. Urine IgA and fibronectin exhibited the highest specificity of 80% at fixed sensitivity for identifying advanced BC.
Conclusions
Given the high sensitivity (97%) of urine D-dimer for BC, it may have a role in the initial diagnosis or detection of cancer recurrence. On the other hand, urine IL-8 and IgA may have the potential in identifying disease progression during patient follow-up. The use of these biomarkers for initial triage could have a significant impact as the current cystoscopy-based diagnostic and surveillance approach is costly and invasive when compared to a simple urine test.


