2023-05-04 ミシガン大学
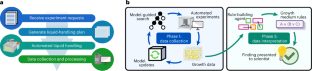
◆BacterAIは、自律的な科学的実験をロボットに割り当て、従来何年もかかる答えを導くことができるとされており、2020年1月以来、約93万の自動化された実験を実施しました。
◆この技術は、医学や農業、環境科学などの分野で、新しい発見を促進する可能性があります。
<関連情報>
- https://news.umich.edu/ai-could-run-a-million-microbial-experiments-per-year/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-023-01376-0
BacterAIは予備知識なしで微生物の代謝をマッピング BacterAI maps microbial metabolism without prior knowledge
Adam C. Dama,Kevin S. Kim,Danielle M. Leyva,Annamarie P. Lunkes,Noah S. Schmid,Kenan Jijakli & Paul A. Jensen
Nature Microbiology Published:04 May 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-023-01376-0
Abstract
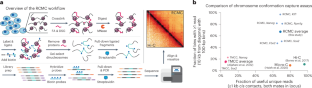
Training artificial intelligence (AI) systems to perform autonomous experiments would vastly increase the throughput of microbiology; however, few microbes have large enough datasets for training such a system. In the present study, we introduce BacterAI, an automated science platform that maps microbial metabolism but requires no prior knowledge. BacterAI learns by converting scientific questions into simple games that it plays with laboratory robots. The agent then distils its findings into logical rules that can be interpreted by human scientists. We use BacterAI to learn the amino acid requirements for two oral streptococci: Streptococcus gordonii and Streptococcus sanguinis. We then show how transfer learning can accelerate BacterAI when investigating new environments or larger media with up to 39 ingredients. Scientific gameplay and BacterAI enable the unbiased, autonomous study of organisms for which no training data exist.