2023-12-11 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
◆研究では142人の幼児を対象にし、魚の摂取が18ヶ月時点での神経発達の遅れと関連していることが示されました。この影響は子供の腸内細菌叢によって増幅され、社会的および環境的要因を超えて存在することが確認されました。研究者は、魚の消費が神経発達に及ぼす影響は微生物の多様性によって強化される可能性があると述べています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/research/story/early-childhood-fish-consumption-may-protect-against-neurodevelopmental-delays/
- https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/11/8/2111
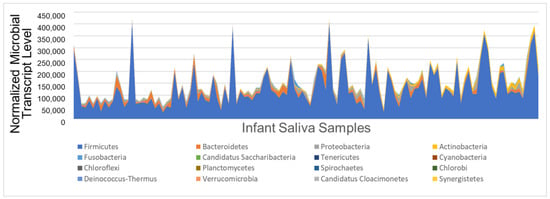
乳児の唾液マイクロバイオーム活性が神経発達への栄養影響を調節する Infant Saliva Microbiome Activity Modulates Nutritional Impacts on Neurodevelopment
Terrah Keck-Kester and Steven D. Hicks
Microorganisms Published: 18 August 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082111
Abstract
Neurodevelopment is influenced by complex interactions between environmental factors, including social determinants of health (SDOH), nutrition, and even the microbiome. This longitudinal cohort study of 142 infants tested the hypothesis that microbial activity modulates the effects of nutrition on neurodevelopment. Salivary microbiome activity was measured at 6 months using RNA sequencing. Infant nutrition was assessed longitudinally with the Infant Feeding Practices survey. The primary outcome was presence/absence of neurodevelopmental delay (NDD) at 18 months on the Survey of Wellbeing in Young Children. A logistic regression model employing two microbial factors, one nutritional factor, and two SDOH accounted for 33.3% of the variance between neurodevelopmental groups (p < 0.001, AIC = 77.7). NDD was associated with Hispanic ethnicity (OR 18.1, 2.36–139.3; p = 0.003), no fish consumption (OR 10.6, 2.0–54.1; p = 0.003), and increased Candidatus Gracilibacteria activity (OR 1.43, 1.00–2.07; p = 0.007). Home built after 1977 (OR 0.02, 0.001–0.53; p = 0.004) and Chlorobi activity (OR 0.76, 0.62–0.93, p = 0.001) were associated with reduced risk of NDD. Microbial alpha diversity modulated the effect of fish consumption on NDD (X2 = 5.7, p = 0.017). These data suggest the benefits of fish consumption for neurodevelopment may be mediated by microbial diversity. Confirmation in a larger, randomized trial is required.