2023-12-15 カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校(UCSD)
◆カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校医学部の研究者は、うつ病と細胞代謝の関連性を見出し、自殺のリスクを予測するためのバイオマーカーを発見しました。性別による差異も明らかになり、これがメンタルヘルスケアの個別化や将来の薬物開発に貢献する可能性があります。
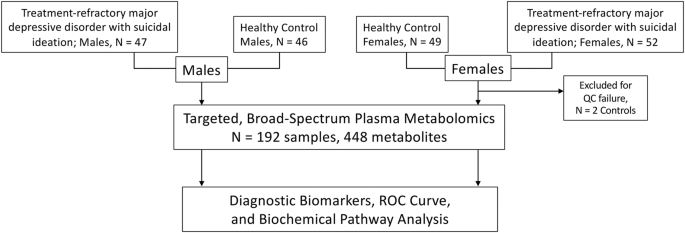
◆研究は、うつ病治療において効果が薄い患者の血液を分析し、性別ごとに異なる5つの代謝物質がリスクを示すことを示唆しています。これが具体的な診断や治療の向上に繋がり、またミトコンドリアの機能障害との関連から新たな薬物の開発にも寄与する可能性があります。
<関連情報>
- https://today.ucsd.edu/story/blood-testing-identifies-biomarkers-of-suicidal-thoughts
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41398-023-02696-9
自殺念慮を伴う治療抵抗性の大うつ病性障害の代謝的特徴 Metabolic features of treatment-refractory major depressive disorder with suicidal ideation
Lisa A. Pan,Jane C. Naviaux,Lin Wang,Kefeng Li,Jonathan M. Monk,Sai Sachin Lingampelly,Anna Maria Segreti,Kaitlyn Bloom,Jerry Vockley,Mark A. Tarnopolsky,David N. Finegold,David G. Peters & Robert K. Naviaux
Translational Psychiatry Published:15 December 2023
DO:Ihttps://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-023-02696-9
Abstract
Peripheral blood metabolomics was used to gain chemical insight into the biology of treatment-refractory Major Depressive Disorder with suicidal ideation, and to identify individualized differences for personalized care. The study cohort consisted of 99 patients with treatment-refractory major depressive disorder and suicidal ideation (trMDD-SI n = 52 females and 47 males) and 94 age- and sex-matched healthy controls (n = 48 females and 46 males). The median age was 29 years (IQR 22–42). Targeted, broad-spectrum metabolomics measured 448 metabolites. Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) and growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15) were measured as biomarkers of mitochondrial dysfunction. The diagnostic accuracy of plasma metabolomics was over 90% (95%CI: 0.80–1.0) by area under the receiver operator characteristic (AUROC) curve analysis. Over 55% of the metabolic impact in males and 75% in females came from abnormalities in lipids. Modified purines and pyrimidines from tRNA, rRNA, and mRNA turnover were increased in the trMDD-SI group. FGF21 was increased in both males and females. Increased lactate, glutamate, and saccharopine, and decreased cystine provided evidence of reductive stress. Seventy-five percent of the metabolomic abnormalities found were individualized. Personalized deficiencies in CoQ10, flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), citrulline, lutein, carnitine, or folate were found. Pathways regulated by mitochondrial function dominated the metabolic signature. Peripheral blood metabolomics identified mitochondrial dysfunction and reductive stress as common denominators in suicidal ideation associated with treatment-refractory major depressive disorder. Individualized metabolic differences were found that may help with personalized management.