2024-05-31 ワシントン大学セントルイス校
<関連情報>
- https://source.wustl.edu/2024/05/alzheimers-biomarker-strem2-plays-a-causal-potentially-modifiable-role-in-disease/
- https://molecularneurodegeneration.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13024-023-00687-4
脳脊髄液中の可溶性TREM2のプロテオゲノミクスが新たな知見を提供し、アルツハイマー病の新規モジュレーターを同定する Proteo-genomics of soluble TREM2 in cerebrospinal fluid provides novel insights and identifies novel modulators for Alzheimer’s disease
Lihua Wang,Niko-Petteri Nykänen,Daniel Western,Priyanka Gorijala,Jigyasha Timsina,Fuhai Li,Zhaohua Wang,Muhammad Ali,Chengran Yang,Menghan Liu,William Brock,Marta Marquié,Mercè Boada,Ignacio Alvarez,Miquel Aguilar,Pau Pastor,Agustín Ruiz,Raquel Puerta,Adelina Orellana,Jarod Rutledge,Hamilton Oh,Michael D Greicius,Yann Le Guen,Richard J. Perrin,… Carlos Cruchaga
Molecular Neurodegeneration Published:03 January 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-023-00687-4
Abstract
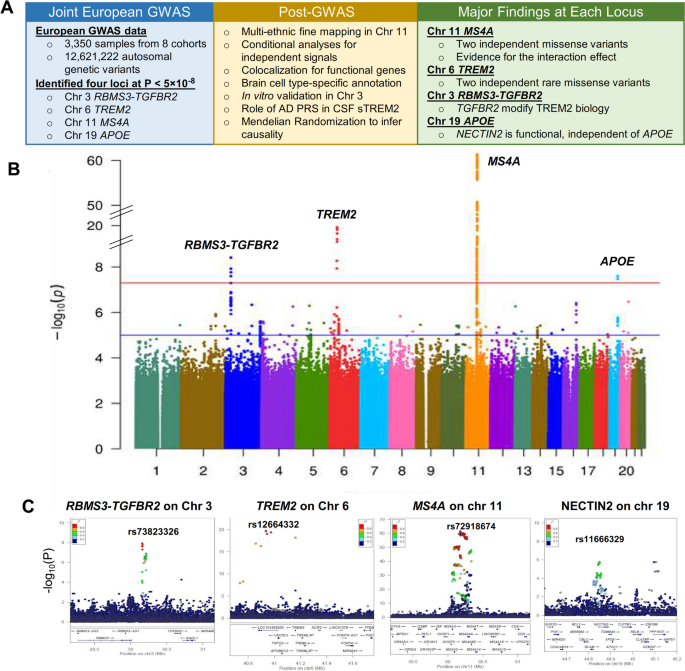
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) plays a critical role in microglial activation, survival, and apoptosis, as well as in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathogenesis. We previously reported the MS4A locus as a key modulator for soluble TREM2 (sTREM2) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). To identify additional novel genetic modifiers of sTREM2, we performed the largest genome-wide association study (GWAS) and identified four loci for CSF sTREM2 in 3,350 individuals of European ancestry. Through multi-ethnic fine mapping, we identified two independent missense variants (p.M178V in MS4A4A and p.A112T in MS4A6A) that drive the association in MS4A locus and showed an epistatic effect for sTREM2 levels and AD risk. The novel TREM2 locus on chr 6 contains two rare missense variants (rs75932628 p.R47H, P=7.16×10-19; rs142232675 p.D87N, P=2.71×10-10) associated with sTREM2 and AD risk. The third novel locus in the TGFBR2 and RBMS3 gene region (rs73823326, P=3.86×10-9) included a regulatory variant with a microglia-specific chromatin loop for the promoter of TGFBR2. Using cell-based assays we demonstrate that overexpression and knock-down of TGFBR2, but not RBMS3, leads to significant changes of sTREM2. The last novel locus is located on the APOE region (rs11666329, P=2.52×10-8), but we demonstrated that this signal was independent of APOE genotype. This signal colocalized with cis-eQTL of NECTIN2 in the brain cortex and cis-pQTL of NECTIN2 in CSF. Overexpression of NECTIN2 led to an increase of sTREM2 supporting the genetic findings. To our knowledge, this is the largest study to date aimed at identifying genetic modifiers of CSF sTREM2. This study provided novel insights into the MS4A and TREM2 loci, two well-known AD risk genes, and identified TGFBR2 and NECTIN2 as additional modulators involved in TREM2 biology.