2024-06-04 レンセラー工科大学 (RPI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.rpi.edu/2024/06/04/rensselaer-researcher-sheds-new-light-circadian-rhythms#
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-47761-z
時計タンパク質の相互作用と電荷ブロックの乱れが、砂時計を持続的な概日振動子に変える Disordered clock protein interactions and charge blocks turn an hourglass into a persistent circadian oscillator
Meaghan S. Jankowski,Daniel Griffith,Divya G. Shastry,Jacqueline F. Pelham,Garrett M. Ginell,Joshua Thomas,Pankaj Karande,Alex S. Holehouse & Jennifer M. Hurley
Nature Communications Published:25 April 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-47761-z
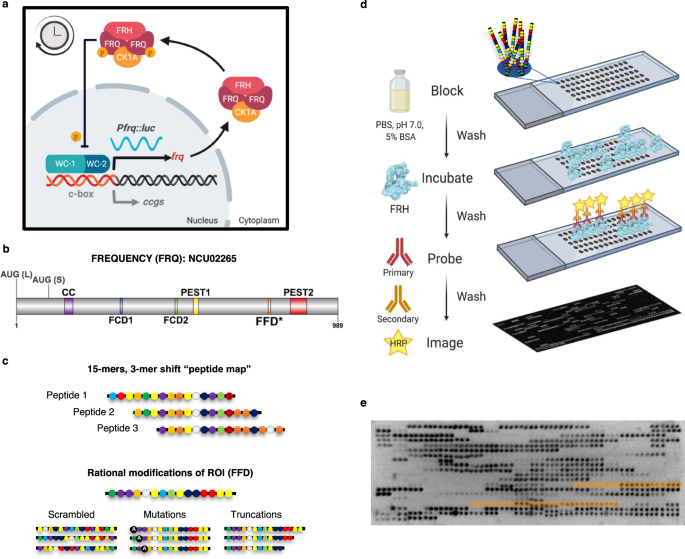
Abstract
Organismal physiology is widely regulated by the molecular circadian clock, a feedback loop composed of protein complexes whose members are enriched in intrinsically disordered regions. These regions can mediate protein-protein interactions via SLiMs, but the contribution of these disordered regions to clock protein interactions had not been elucidated. To determine the functionality of these disordered regions, we applied a synthetic peptide microarray approach to the disordered clock protein FRQ in Neurospora crassa. We identified residues required for FRQ’s interaction with its partner protein FRH, the mutation of which demonstrated FRH is necessary for persistent clock oscillations but not repression of transcriptional activity. Additionally, the microarray demonstrated an enrichment of FRH binding to FRQ peptides with a net positive charge. We found that positively charged residues occurred in significant “blocks” within the amino acid sequence of FRQ and that ablation of one of these blocks affected both core clock timing and physiological clock output. Finally, we found positive charge clusters were a commonly shared molecular feature in repressive circadian clock proteins. Overall, our study suggests a mechanistic purpose for positive charge blocks and yielded insights into repressive arm protein roles in clock function.