2024-06-04 マサチューセッツ工科大学(MIT)
<関連情報>
- https://news.mit.edu/2024/ultrasound-offers-new-way-perform-deep-brain-stimulation-0604
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-48748-6
脳深部活性化のための埋め込み型圧電超音波刺激装置(ImPULS) An implantable piezoelectric ultrasound stimulator (ImPULS) for deep brain activation
Jason F. Hou,Md Osman Goni Nayeem,Kian A. Caplan,Evan A. Ruesch,Albit Caban-Murillo,Ernesto Criado-Hidalgo,Sarah B. Ornellas,Brandon Williams,Ayeilla A. Pearce,Huseyin E. Dagdeviren,Michelle Surets,John A. White,Mikhail G. Shapiro,Fan Wang,Steve Ramirez & Canan Dagdeviren
Nature Communications Published:04 June 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-48748-6
Abstract
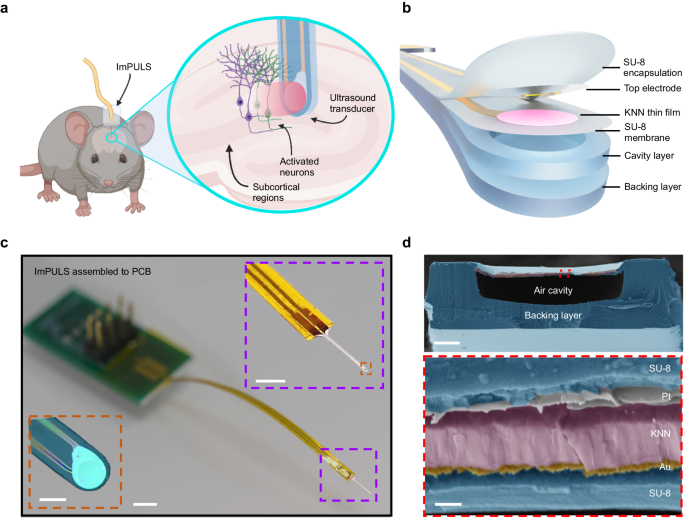
Precise neurostimulation can revolutionize therapies for neurological disorders. Electrode-based stimulation devices face challenges in achieving precise and consistent targeting due to the immune response and the limited penetration of electrical fields. Ultrasound can aid in energy propagation, but transcranial ultrasound stimulation in the deep brain has limited spatial resolution caused by bone and tissue scattering. Here, we report an implantable piezoelectric ultrasound stimulator (ImPULS) that generates an ultrasonic focal pressure of 100 kPa to modulate the activity of neurons. ImPULS is a fully-encapsulated, flexible piezoelectric micromachined ultrasound transducer that incorporates a biocompatible piezoceramic, potassium sodium niobate [(K,Na)NbO3]. The absence of electrochemically active elements poses a new strategy for achieving long-term stability. We demonstrated that ImPULS can i) excite neurons in a mouse hippocampal slice ex vivo, ii) activate cells in the hippocampus of an anesthetized mouse to induce expression of activity-dependent gene c-Fos, and iii) stimulate dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta to elicit time-locked modulation of nigrostriatal dopamine release. This work introduces a non-genetic ultrasound platform for spatially-localized neural stimulation and exploration of basic functions in the deep brain.


