2024-06-10 リンショーピング大学
<関連情報>
- https://liu.se/en/news-item/disturbed-blood-flow-can-damage-the-aorta
- https://academic.oup.com/ehjcimaging/advance-article/doi/10.1093/ehjci/jeae130/7674339
4DフローCMRで測定された壁せん断応力は、軽度から中等度の上行大動脈拡張および三尖大動脈弁における炎症およびコラーゲン合成のバイオマーカーと相関する Wall shear stress measured with 4D flow CMR correlates with biomarkers of inflammation and collagen synthesis in mild-to-moderate ascending aortic dilation and tricuspid aortic valves
Filip Hammaréus, Chiara Trenti, Hanna M Björck, Jan Engvall, Hanna Lekedal, Aleksandra Krzynska-Trzebiatowska, David Kylhammar, Marcus Lindenberger, Anna K Lundberg, Fredrik Nilsson …
European Heart Journal – Cardiovascular Imaging Published:15 May 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjci/jeae130
Abstract
Aims
Understanding the mechanisms underlying ascending aortic dilation is imperative for refined risk stratification of these patients, particularly among incidentally identified patients, most commonly presenting with tricuspid valves. The aim of this study was to explore associations between ascending aortic haemodynamics, assessed using four-dimensional flow cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (4D flow CMR), and circulating biomarkers in aortic dilation.
Methods and results
Forty-seven cases with aortic dilation (diameter ≥ 40 mm) and 50 sex-and age-matched controls (diameter < 40 mm), all with tricuspid aortic valves, underwent 4D flow CMR and venous blood sampling. Associations between flow displacement, wall shear stress (WSS), and oscillatory shear index in the ascending aorta derived from 4D flow CMR, and biomarkers including interleukin-6, collagen type I α1 chain, metalloproteinases (MMPs), and inhibitors of MMPs derived from blood plasma, were investigated. Cases with dilation exhibited lower peak systolic WSS, higher flow displacement, and higher mean oscillatory shear index compared with controls without dilation. No significant differences in biomarkers were observed between the groups. Correlations between haemodynamics and biomarkers were observed, particularly between maximum time-averaged WSS and interleukin-6 (r = 0.539, P < 0.001), and maximum oscillatory shear index and collagen type I α1 chain (r = -0.575, P < 0.001 in cases).
Conclusion
Significant associations were discovered between 4D flow CMR derived whole-cardiac cycle WSS and circulating biomarkers representing inflammation and collagen synthesis, suggesting an intricate interplay between haemodynamics and the processes of inflammation and collagen synthesis in patients with early aortic dilation and tricuspid aortic valves.
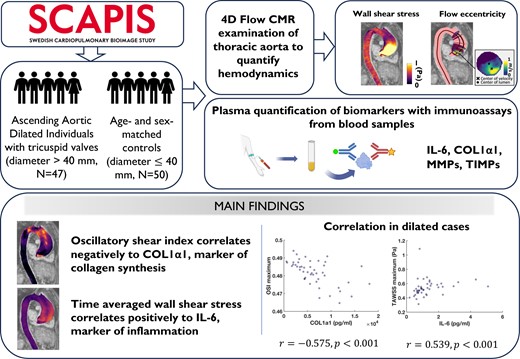
Graphical Abstract
Individuals with tricuspid aortic valves and ascending aortic dilation (diameter ≥ 40 mm, n = 47) and sex- and age-matched controls (diameter < 40 mm, n = 50) were recruited from the SCAPIS study and underwent a 4D flow CMR examination to quantify wall shear stress and flow eccentricity, while plasma biomarkers were quantified with immunoassays, showing that biomarkers of collagen synthesis and inflammation correlated with altered ascending aortic haemodynamics. 4D flow CMR, four-dimensional flow cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; IL-6, interleukin-6; COL1α1, type I collagen α1 chain; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; TIMP, tissue inhibitor of MMP; WSS, wall shear stress; TAWSS, time-averaged WSS; OSI, oscillatory shear index; TAV, tricuspid aortic valve.


