2024-08-28 フィンランド技術研究センター(VTT)
<関連情報>
- https://www.vttresearch.com/en/news-and-ideas/berry-extracts-and-nanocellulose-bioactive-skin-sprays-and-surgical-dressings
- https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/cellular-and-infection-microbiology/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2023.1176755/full
- https://www.mdpi.com/2079-6382/10/12/1481
- https://testpubschina.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsfoodscitech.0c00109
北極ベリー抽出物を用いたメチシリン耐性黄色ブドウ球菌バイオフィルムの成長と発達の抑制 Reduction of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilm growth and development using arctic berry extracts
John Jairo Aguilera-Correa,,Liisa Nohynek,Hanna-Leena Alakomi,Jaime Esteban,,Kirsi-Marja Oksman-Caldentey,Riitta Puupponen-Pimiä,Teemu J. Kinnari,Ramon Perez-Tanoir
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology Published:23 June 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2023.1176755
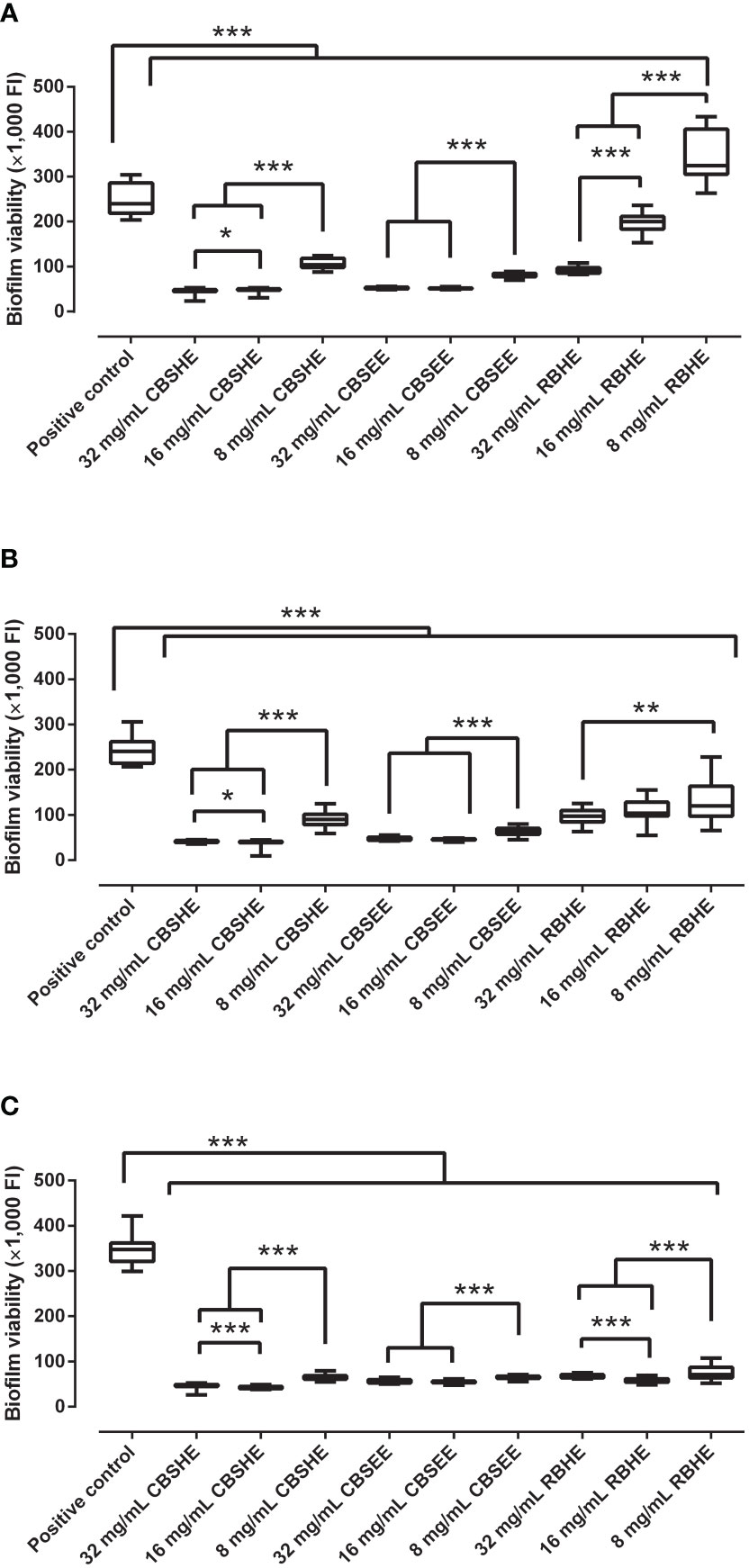
Introduction: Surgical site infection remains a devastating and feared complication of surgery caused mainly by Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). More specifically, methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) infection poses a serious threat to global health. Therefore, developing new antibacterial agents to address drug resistance are urgently needed. Compounds derived from natural berries have shown a strong antimicrobial potential.
Methods: This study aimed to evaluate the effect of various extracts from two arctic berries, cloudberry (Rubus chamaemorus) and raspberry (Rubus idaeus), on the development of an MRSA biofilm and as treatment on a mature MRSA biofilm. Furthermore, we evaluated the ability of two cloudberry seed-coat fractions, hydrothermal extract and ethanol extract, and the wet-milled hydrothermal extract of a raspberry press cake to inhibit and treat biofilm development in a wound-like medium. To do so, we used a model strain and two clinical strains isolated from infected patients.
Results: All berry extracts prevented biofilm development of the three MRSA strains, except the raspberry press cake hydrothermal extract, which produced a diminished anti-staphylococcal effect.
Discussion: The studied arctic berry extracts can be used as a treatment for a mature MRSA biofilm, however some limitations in their use exist.
クラウドベリー(Rubus chamaemorus)の種子から分画されたサンギインH-6は、創傷感染時のメチシリン耐性黄色ブドウ球菌バイオフィルムの発達を防ぐことができる Sanguiin H-6 Fractionated from Cloudberry (Rubus chamaemorus) Seeds Can Prevent the Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Development during Wound Infection
John Jairo Aguilera-Correa,Sara Fernández-López,Iskra Dennisse Cuñas-Figueroa,Sandra Pérez-Rial,Hanna-Leena Alakomi,Liisa Nohynek,Kirsi-Marja Oksman-Caldentey,Juha-Pekka Salminen,Jaime Esteban,Juan Cuadros,Riitta Puupponen-Pimiä,Ramon Perez-Tanoira andTeemu J. Kinnari
Antibiotics https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10121481
Abstract
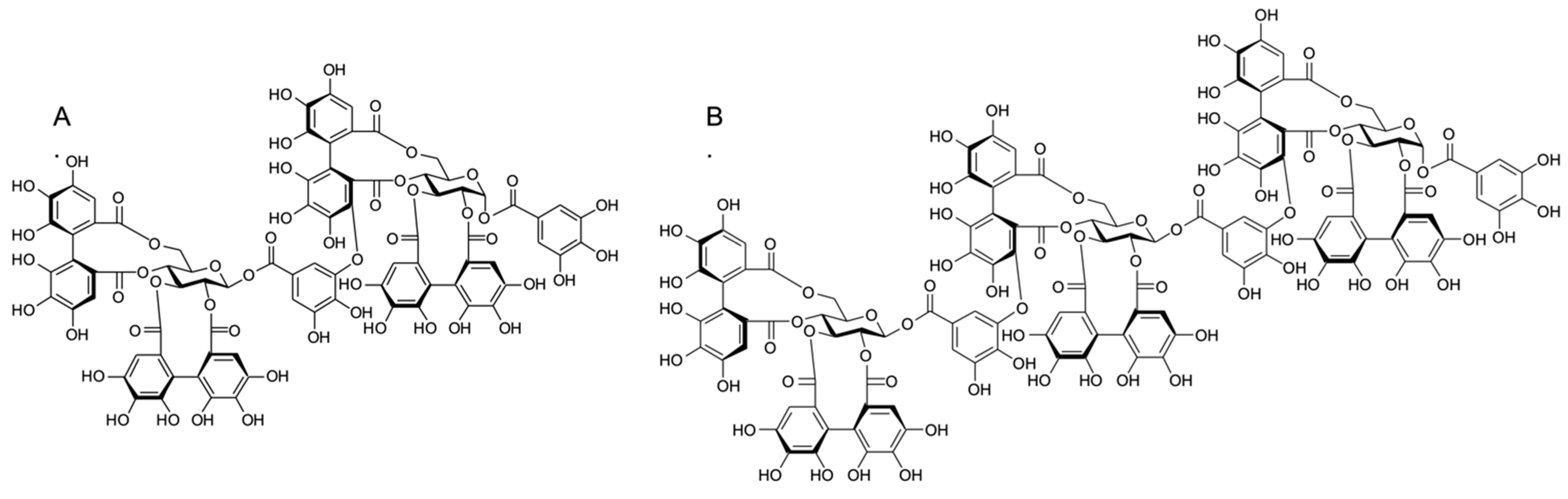
Staphylococcus aureus is the most common cause of surgical site infections and its treatment is challenging due to the emergence of multi-drug resistant strains such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). Natural berry-derived compounds have shown antimicrobial potential, e.g., ellagitannins such as sanguiin H-6 and lambertianin C, the main phenolic compounds in Rubus seeds, have shown antimicrobial activity. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of sanguiin H-6 and lambertianin C fractionated from cloudberry seeds, on the MRSA growth, and as treatment of a MRSA biofilm development in different growth media in vitro and in vivo by using a murine wound infection model where sanguiin H-6 and lambertianin C were used to prevent the MRSA infection. Sanguiin H-6 and lambertianin C inhibited the in vitro biofilm development and growth of MRSA. Furthermore, sanguiin H-6 showed significant anti-MRSA effect in the in vivo wound model. Our study shows the possible use of sanguiin H-6 as a preventive measure in surgical sites to avoid postoperative infections, whilst lambertianin C showed no anti-MRSA activity.
クラウドベリー(Rubus chamaemorus)種子からの天然抗菌剤(サンディングと水熱抽出による) Natural Antimicrobials from Cloudberry (Rubus chamaemorus) Seeds by Sanding and Hydrothermal Extraction
Riitta Puupponen-Pimiä,Liisa Nohynek,Jussi Suvanto,Juha-Pekka Salminen,Tuulikki Seppänen-Laakso,Juha Tähtiharju,Kaisu Honkapää,Kirsi-Marja Oksman-Caldentey
ACS Food Science & Technology
Abstract

We have developed an organic solvent-free process to enrich natural antimicrobials from the important Nordic Rubus berry species, especially from cloudberry. The process utilizes industrial berry byproducts as raw-material, and it is based on seed sanding technology and water-based extraction. The extracts showed strong antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). A concentration of 5 mg/mL totally eliminated these bacteria in 24 h. Effects against Gram-negative bacteria were modest. Polyphenol analysis of the hydrothermal extracts showed that the antimicrobial activity is correlated to ellagitannins, mainly dimeric sanguiin H-6 and sanguiin H-10 isomers. Sanguiin H-10 is not commonly found in intact cloudberry seeds, but it is formed from the dimeric and trimeric ellagitannins, during the extraction. Surprisingly hydrothermal extracts had no or minor effects on beneficial bacteria, Lactobacillus rhamnosus. This interesting finding might offer an application potential in controlling skin microbial pathogens, for example, in wound healing.


