2024-10-31 カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校(UCSD)
<関連情報>
- https://today.ucsd.edu/story/wearable-ultrasound-tech-for-muscle-monitoring-opens-new-possibilities-in-healthcare-and-human-machine-interfaces
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-024-01271-4
単一トランスデューサをベースとしたウェアラブル超音波検査システム A wearable echomyography system based on a single transducer
Xiaoxiang Gao,Xiangjun Chen,Muyang Lin,Wentong Yue,Hongjie Hu,Siyu Qin,Fangao Zhang,Zhiyuan Lou,Lu Yin,Hao Huang,Sai Zhou,Yizhou Bian,Xinyi Yang,Yangzhi Zhu,Jing Mu,Xinyu Wang,Geonho Park,Chengchangfeng Lu,Ruotao Wang,Ray S. Wu,Joseph Wang,Jinghong Li & Sheng Xu
Nature Electronics Published:31 October 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-024-01271-4
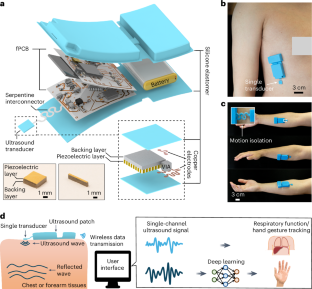
Abstract
Wearable electromyography devices can detect muscular activity for health monitoring and body motion tracking, but this approach is limited by weak and stochastic signals with a low spatial resolution. Alternatively, echomyography can detect muscle movement using ultrasound waves, but typically relies on complex transducer arrays, which are bulky, have high power consumption and can limit user mobility. Here we report a fully integrated wearable echomyography system that consists of a customized single transducer, a wireless circuit for data processing and an on-board battery for power. The system can be attached to the skin and provides accurate long-term wireless monitoring of muscles. To illustrate its capabilities, we use this system to detect the activity of the diaphragm, which allows the recognition of different breathing modes. We also develop a deep learning algorithm to correlate the single-transducer radio-frequency data from forearm muscles with hand gestures to accurately and continuously track 13 hand joints with a mean error of only 7.9°.

