2025-01-16 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/research/story/discovery-could-eliminate-need-refrigerate-vaccines-and-protein-based-drugs
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-55304-9
熱に安定で本質的に無菌の液体タンパク質製剤 Heat stable and intrinsically sterile liquid protein formulations
Atip Lawanprasert,Harminder Singh,Sopida Pimcharoen,Mariangely González Vargas,Arshiya Dewan,Girish S. Kirimanjeswara & Scott H. Medina
Nature Communications Published:30 December 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-55304-9
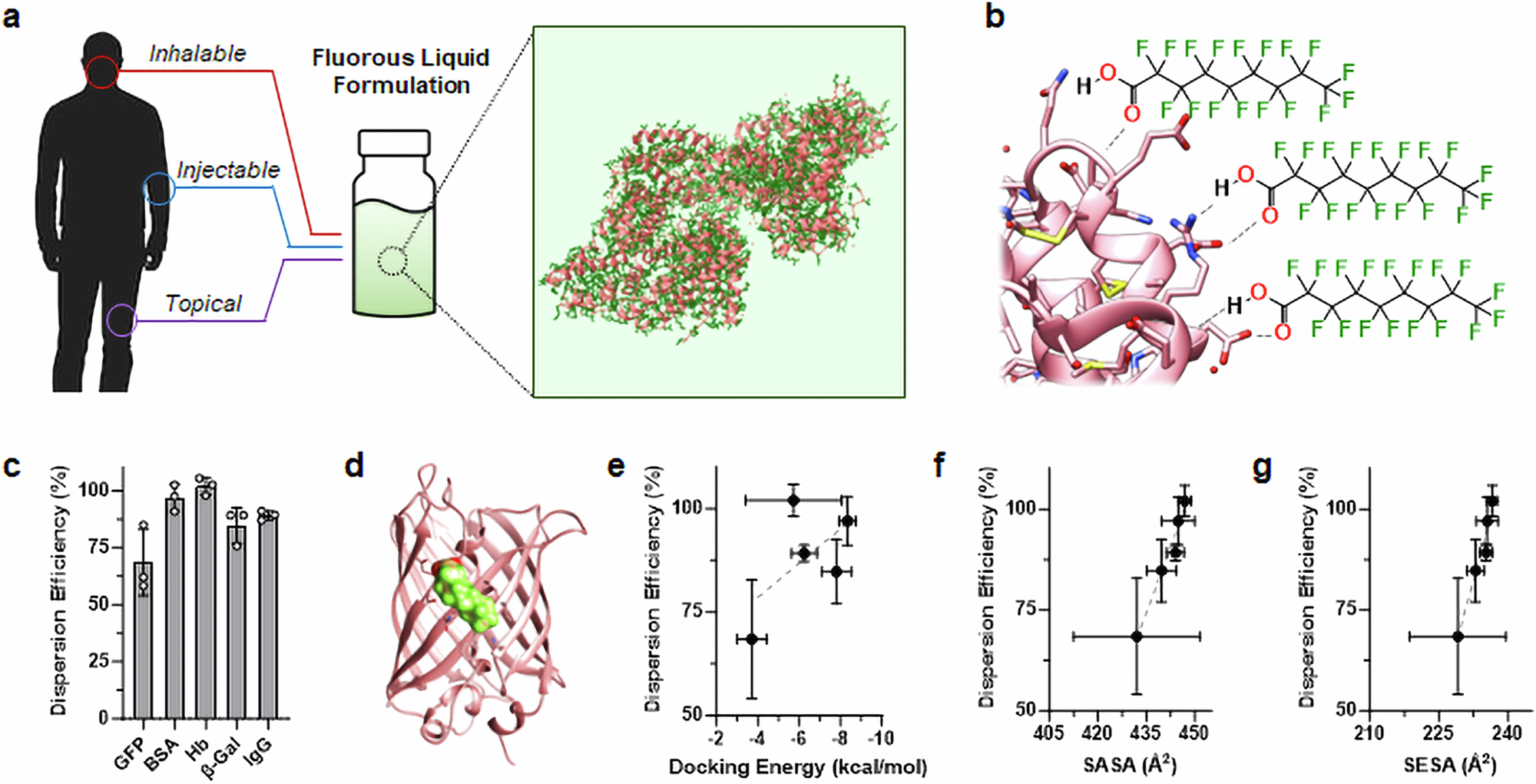
Abstract
Over 80% of biologic drugs, and 90% of vaccines, require temperature-controlled conditions throughout the supply chain to minimize thermal inactivation and contamination. This cold chain is costly, requires stringent oversight, and is impractical in remote environments. Here, we report chemical dispersants that non-covalently solvate proteins within fluorous liquids to alter their thermodynamic equilibrium and reduce conformational flexibility. This generates non-aqueous, fluorine-based liquid protein formulations that biochemically rigidify protein structure to yield thermally stable biologics at extreme temperatures (up to 90 °C). These non-aqueous formulations are impervious to contamination by microorganismal pathogens, degradative enzymes, and environmental impurities, and display comparable pre-clinical pharmacokinetics and safety profiles to standard saline protein samples. As a result, we deliver a fluorochemical formulation paradigm that may limit the need for cold chain logistics of protein reagents and biopharmaceuticals.