2025-01-17 カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校(UCSD)
<関連情報>
- https://today.ucsd.edu/story/ai-driven-approach-reads-heart-cells-inner-electrical-signals-from-the-outside
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-55571-6
インテリジェントな細胞内電気生理学: ナノ電極アレイ記録で学習させた物理情報付きディープラーニングモデルを用いた細胞内活動電位の再構築 Intelligent in-cell electrophysiology: Reconstructing intracellular action potentials using a physics-informed deep learning model trained on nanoelectrode array recordings
Keivan Rahmani,Yang Yang,Ethan Paul Foster,Ching-Ting Tsai,Dhivya Pushpa Meganathan,Diego D. Alvarez,Aayush Gupta,Bianxiao Cui,Francesca Santoro,Brenda L. Bloodgood,Rose Yu,Csaba Forro & Zeinab Jahed
Nature Communications Published:14 January 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-55571-6
Abstract
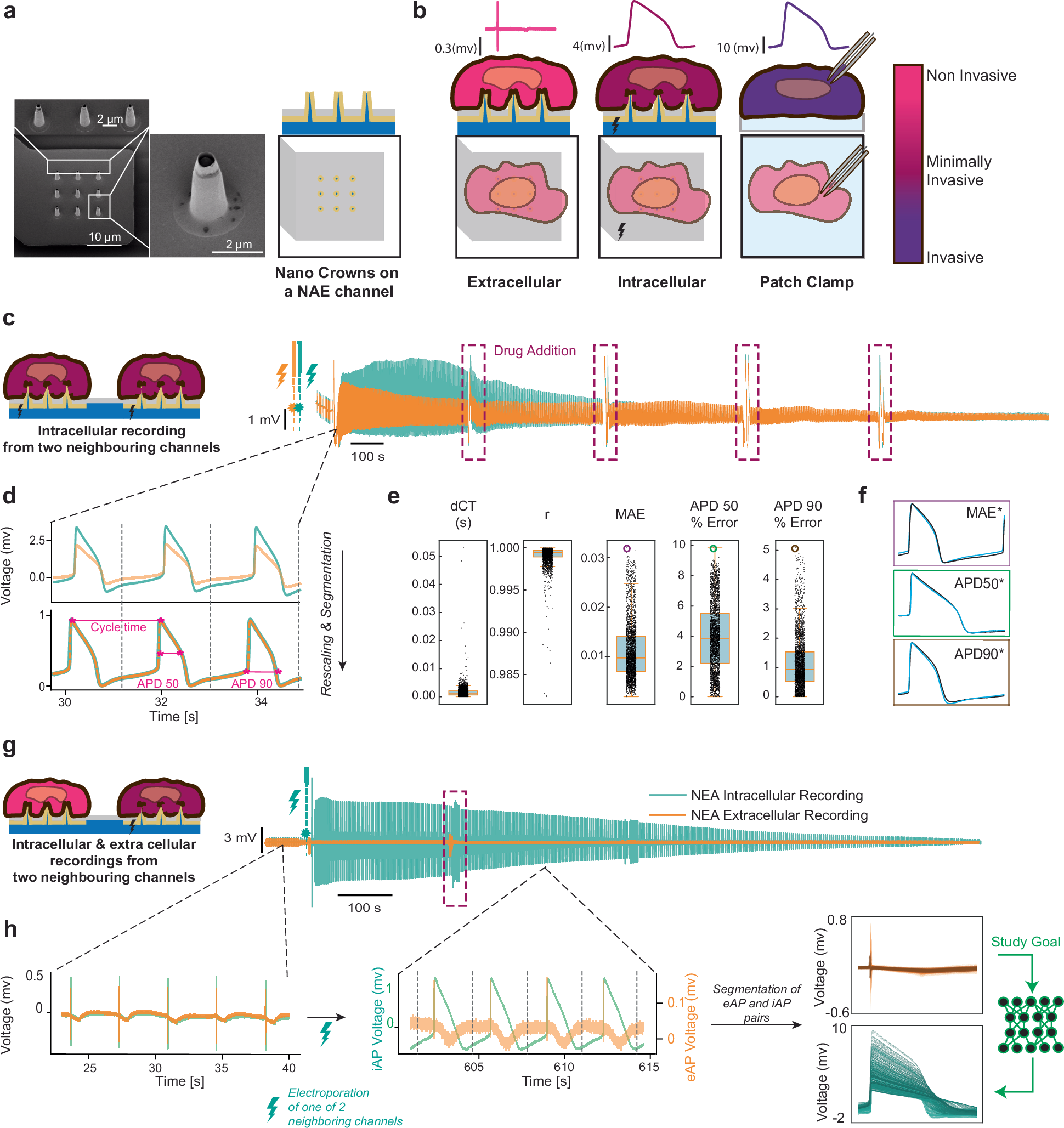
Intracellular electrophysiology is essential in neuroscience, cardiology, and pharmacology for studying cells’ electrical properties. Traditional methods like patch-clamp are precise but low-throughput and invasive. Nanoelectrode Arrays (NEAs) offer a promising alternative by enabling simultaneous intracellular and extracellular action potential (iAP and eAP) recordings with high throughput. However, accessing intracellular potentials with NEAs remains challenging. This study presents an AI-supported technique that leverages thousands of synchronous eAP and iAP pairs from stem-cell-derived cardiomyocytes on NEAs. Our analysis revealed strong correlations between specific eAP and iAP features, such as amplitude and spiking velocity, indicating that extracellular signals could be reliable indicators of intracellular activity. We developed a physics-informed deep learning model to reconstruct iAP waveforms from extracellular recordings recorded from NEAs and Microelectrode arrays (MEAs), demonstrating its potential for non-invasive, long-term, high-throughput drug cardiotoxicity assessments. This AI-based model paves the way for future electrophysiology research across various cell types and drug interactions.