2025-06-30 北海道大学,株式会社FlyWorks
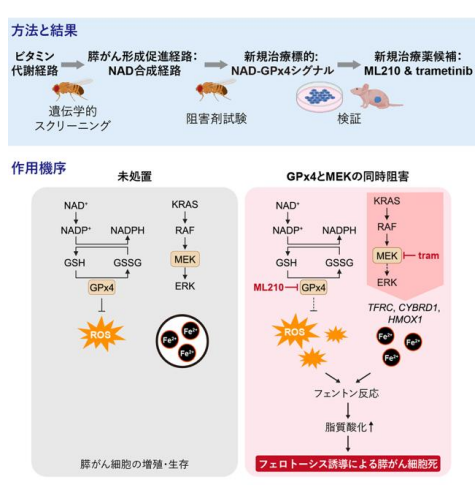
図 1. 本研究の概要図 PDAC 患者の遺伝子変異パターンを模倣したモデルショウジョウバエである 4-hit ハエを用いた遺伝学的スクリーニングにより、GPx4 と MEK を新規治療標的として同定した。また、GPx4 阻害剤 ML210 と MEK 阻害薬 trametinib の同時投与は抗腫瘍効果を示した。MEK の阻害は、鉄取り込み関連遺伝子(TFRC、CYBRD1、HMOX1)の発現を誘導し、細胞内の鉄蓄積が促進した。一方、GPx4 の阻害は細胞内の抗酸化機構を破綻させた。これらの相乗効果により、ROS の蓄積、脂質酸化の亢進、フェロトーシスの誘導が生じた。
<関連情報>
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/2025/06/post-1947.html
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/pdf/250630_pr.pdf
- https://www.cell.com/molecular-therapy-family/molecular-therapy/abstract/S1525-0016(25)00407-1
NAD-GPx4シグナルとMEKの同時阻害は、フェロトーシスを誘導してすい管腺がんの形成を抑制する Inhibition of NAD-GPx4 axis and MEK triggers ferroptosis to suppress pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Hui Jiang ∙ Yusuke Satoh ∙ Ryodai Yamamura ∙ … ∙ Tsuyoshi Osawa ∙ Keisuke Goda ∙ Masahiro Sonoshita
Molecular Therapy Published:May 31, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2025.05.037
Abstract
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) ranks among the most lethal malignancies, highlighting the critical need for innovative therapeutic strategies. In this study, we examined the roles of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) synthesis pathway in PDAC. Targeting the NAD synthesis pathway significantly mitigated lethality in a Drosophila model that recapitulated the PDAC genotype. Within this pathway, we identified Glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPx4) as a critical effector responsible for scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS). The combined application of GPx4 and Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitors, namely ML210 and trametinib, respectively, reduced lethality and tumor-like phenotypes in these flies. Notably, this combination treatment synergistically suppressed the proliferation of human PDAC cells and their corresponding xenografts in mice by inducing ROS accumulation, which triggered ferroptosis. These results suggest that inducing ferroptosis could represent a promising therapeutic strategy for PDAC.