2025-06-30 東京科学大学
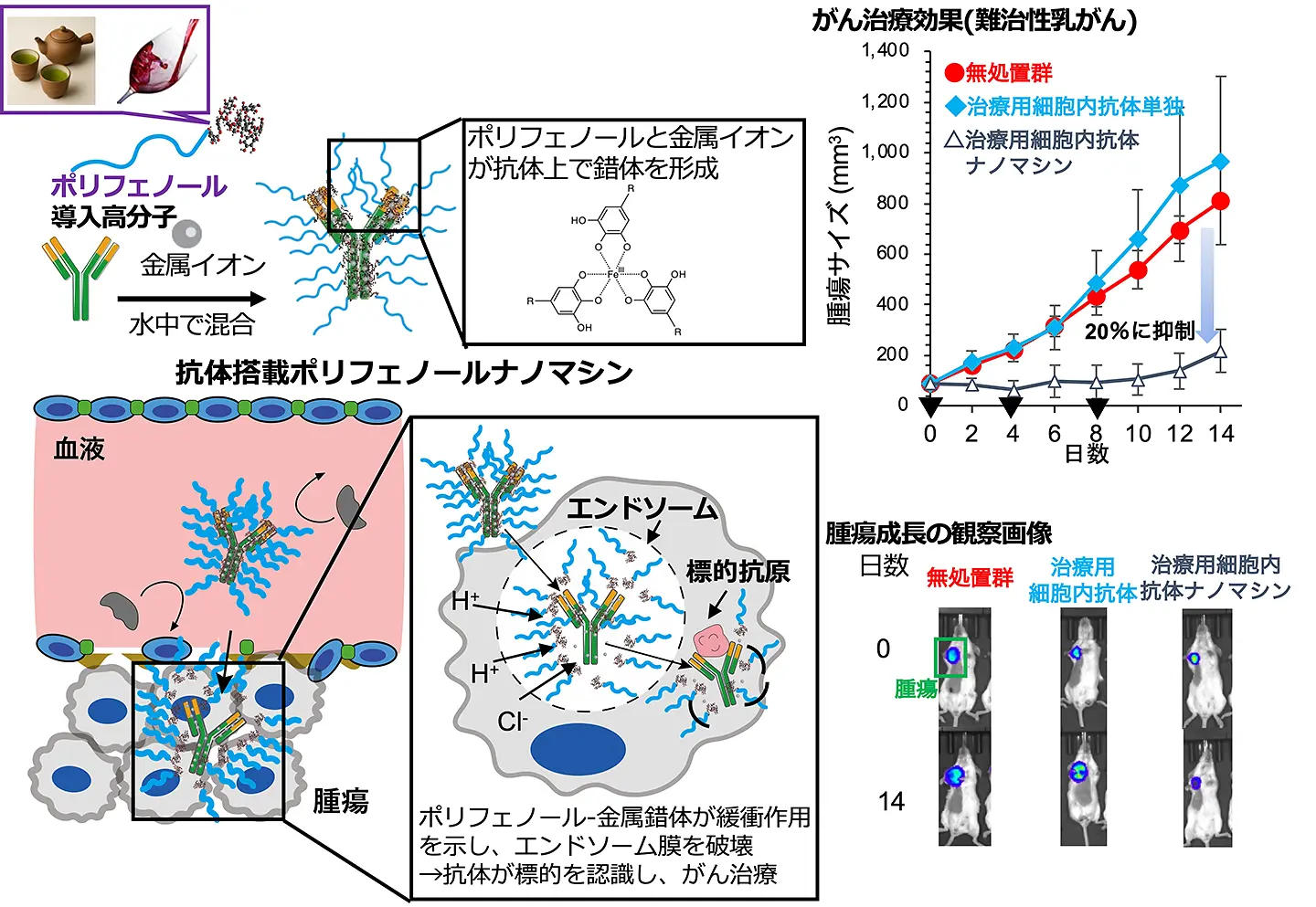
図1. ポリフェノールを活用したナノマシンが抗体をがん細胞内の標的箇所にピンポイントで送達し、がん治療を達成
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/0ydd49xx9mof
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=1820&prevId=&key=5ef7728a30d25a677e5f65e9d2ae07d3.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168365925005498
同所性乳癌への抗体細胞質導入と抗腫瘍効果を促進する金属フェノールネットワークベースポリマーナノキャリア Metal-phenolic network-based polymeric nanocarriers facilitating antibody cytoplasmic delivery and anti-tumor effects to orthotopic breast tumors
Yuto Honda, Haruna Haraguchi, Takeru Tsuda, Rui Ko, Kyohei Muguruma, Haochen Guo, Takahiro Nomoto, Yutaka Miura, Nobuhiro Nishiyama
Journal of Controlled Release Available online: 4 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.113929
Highlights
- Metal-phenolic network (MPN)-based nanocarrier enables systemic cytosolic antibody delivery.
- Neutral, PEG-coated MPN complex improves pharmacokinetics and tumor targeting.
- Antibodies effectively escape endosomes via MPN buffering effect.
- Enhanced antibody therapy observed in breast cancer mouse models.
- Non-cationic approach overcomes toxicity and stability limitations.
Abstract
Intracellular delivery of antibodies holds great promise for targeting cytosolic antigens involved in various diseases, particularly cancer because many key signal-inducing antigens are localized intracellularly. However, the clinical application of intracellular antibodies is hindered by their poor cellular uptake and inefficient endosomal escape owing to their large molecular weight, hydrophilicity, and overall negative charge. To address these challenges, we developed a metal-phenolic network (MPN)-based polymeric nanocarrier for cytosolic antibody delivery. This carrier was composed of a polyphenol-conjugated polymer and metal ions. Upon simple mixing with antibodies, polyphenol-conjugated polymers and metal ions form polymeric MPN complex-encapsulating antibodies with a core-shell structure. The complex, with a diameter of approximately 30 nm and a relatively neutral charge, demonstrated excellent pharmacokinetics and tumor accumulation following intravenous administration. Within tumor cells, the polymeric MPN complex facilitated endosomal escape through a buffering effect triggered by coordination bond dissociation of MPN in the acidic endosomal environment; simultaneously, the antibodies were released from the polymeric MPN complex, leading to binding to the antigen in the cytoplasm. The polymeric MPN complex enhanced the therapeutic effect of cytoplasmic antigen-binding antibodies against orthotopic breast tumors in mice. This study demonstrated the potential of MPN-based polymeric nanocarriers without cationic molecules as a platform for intracellular antibody delivery, enabling systemic administration and cytosolic release in tumors, thus expanding the therapeutic landscape of antibody-based treatments.