2025-07-04 中国科学院(CAS)
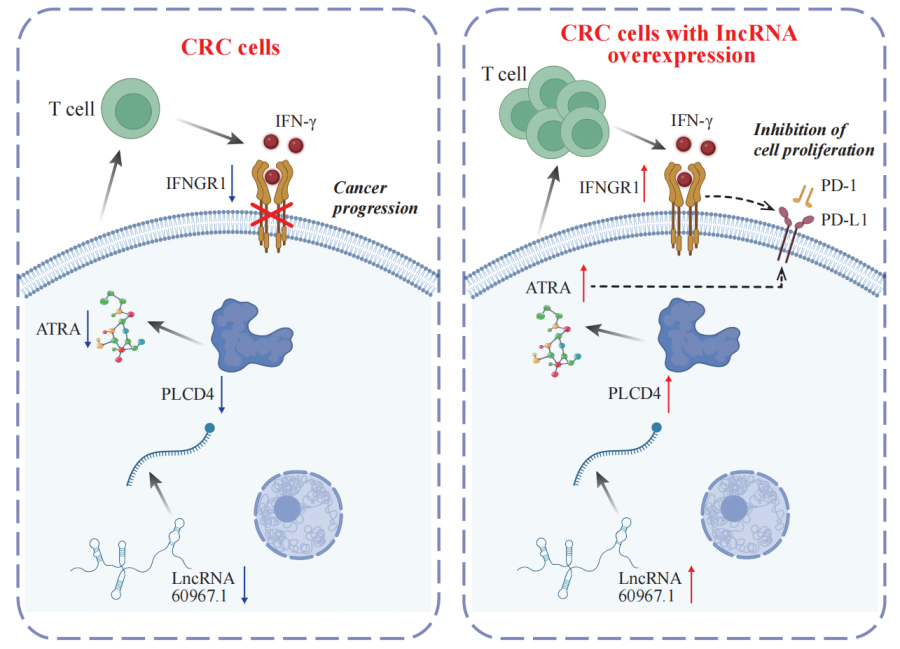 A proposed model suggests that lncRNA 60967.1 plays a regulatory role in modulating the PLCD4/ATRA axis and anti-PD-1 therapy, influencing immune responses and affecting CRC progression. (Image by ZHAO Ningning)
A proposed model suggests that lncRNA 60967.1 plays a regulatory role in modulating the PLCD4/ATRA axis and anti-PD-1 therapy, influencing immune responses and affecting CRC progression. (Image by ZHAO Ningning)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202507/t20250704_1046877.shtml
- https://molecular-cancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12943-025-02359-x
マルチオミクス統合解析により、LncRNA 60967.1-PLCD4-ATRA軸が大腸がんの進行と免疫応答の重要な制御因子であることが明らかになった Integrative multi-omics analysis reveals the LncRNA 60967.1–PLCD4–ATRA axis as a key regulator of colorectal cancer progression and immune response
Yiyi Chen,Ningning Zhao,Lingna Xu,Xiya Jia,Fang Liu,Jian Huang,Xuhua Li,Yunfei Wang,Chuanxi Lai,Yanbin Shen,Fei Wang,Yiming Lv,Xuefeng Huang,Fan Zhang,Hongcang Gu & Sheng Dai
Molecular Cancer Published:06 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-025-02359-x
Abstract
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a major global health concern, characterized by high morbidity and mortality rates. CRC progression involves intricate molecular networks that remain incompletely understood. In this study, we conducted an integrative multi-omics analysis of transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic profiles from CRC tissues and matched normal adjacent tissues (NATs). Our analysis revealed 1,394 differentially expressed long non-Coding RNAs (lncRNAs), 2,788 genes, 548 proteins, and 91 metabolites. A significant interaction network comprising 22 lncRNAs, 14 mRNAs/proteins, and 9 metabolites was identified, among which lncRNA 60967.1 emerged as a pivotal regulator. Functional validation demonstrated that lncRNA 60967.1 is markedly downregulated in CRC cell lines and patient tissues. Overexpression of lncRNA 60967.1 restored expression of the tumor suppressor PLCD4 and increased levels of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA). This modulation enhanced IFN-γ-induced apoptosis and increased expression of the IFN-γ receptor subunit IFNGR1, thereby partially reversing IFN-γ resistance. In murine models, lncRNA 60967.1 overexpression promoted immune cell infiltration and synergized with anti–PD-1 therapy to inhibit tumor growth. Collectively, our findings uncover a novel lncRNA-mRNA/protein-metabolite network, the lncRNA 60967.1-PLCD4-ATRA axis, that plays a critical role in CRC progression and immune modulation, offering promising therapeutic targets for improved treatment efficacy.