2025-07-31 ロイヤルメルボルン工科大学(RMIT)
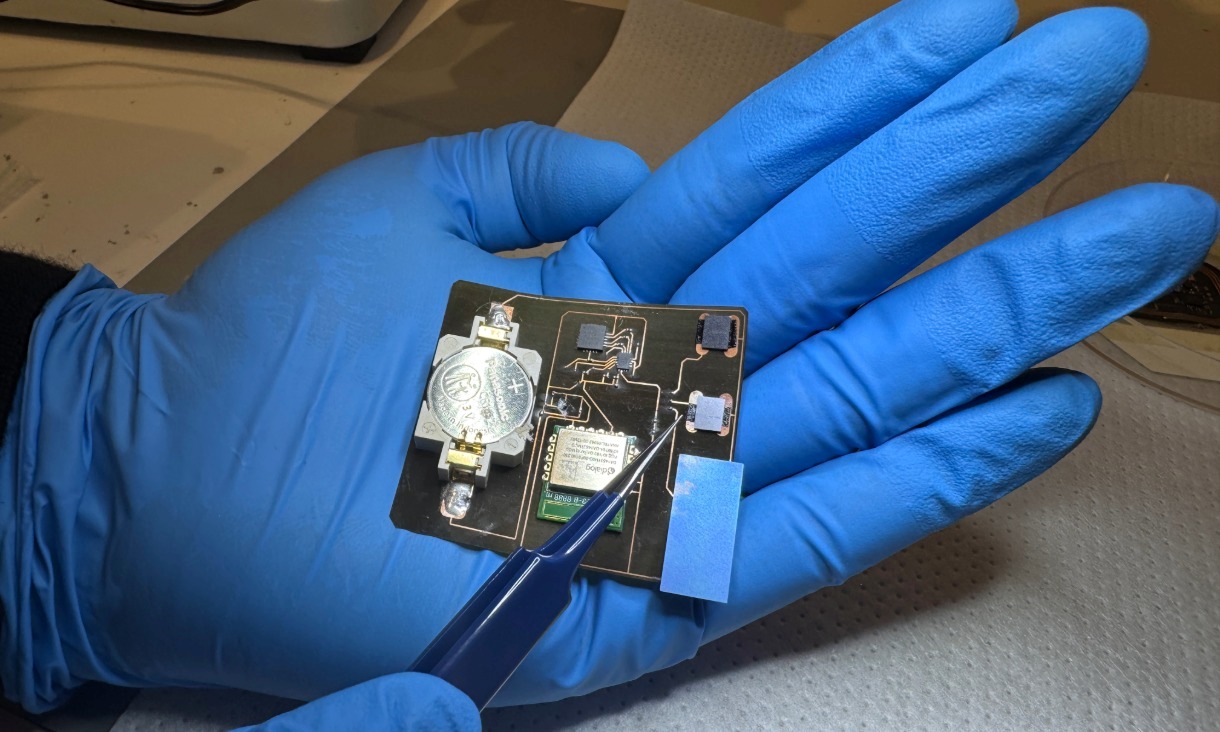 Precision in the palm: Proof-of-concept wearable wound monitor being developed at RMIT University. Credit: Will Wright, RMIT University
Precision in the palm: Proof-of-concept wearable wound monitor being developed at RMIT University. Credit: Will Wright, RMIT University
<関連情報>
- https://www.rmit.edu.au/news/all-news/2025/jul/wound-monitor
- https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anbr.202500142
ポイントオブケア応用向けのマルチプレックス皮膚創傷モニター Multiplexed Cutaneous Wound Monitor for Point-of-Care Applications
Peter Francis Mathew Elango, Ganganath Perera, Mingjie Yang, Mei Xian Low, Ying Zhi Cheong, Bharath Babu Manjunath, Md. Ataur Rahman, Rajesh Ramanathan, Sharath Sriram …
Advanced NanoBiomed Research Published: 30 July 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/anbr.202500142
Abstract
Wearable wound health monitors can radically revolutionize the methods of contemporary wound care monitoring, thereby greatly reducing the burden on the healthcare system. By integrating sensors that can monitor parameters of the wound bed and interfacing them with wireless capabilities, continuous and remote monitoring can be achieved. The focus of this work is to demonstrate a system-on-chip, multiplexed wound healing monitor on a flexible wireless platform. A triangulated approach of measuring CRP, IL-6 proteins, pH, and temperature is used to wirelessly track changes in parameters that indicate the progress or lack thereof of wound healing. Further, to mimic functionality on skin conditions, the dependency of biomarkers and pH responses with temperature has been investigated. These systems can find imminent applications in clinical point-of-care diagnostics.


