2025-09-12 中国科学院(CAS)
 Mtb PknG hijacks the host linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex to evade NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated cytosolic immune surveillance (Image by LIU Cuihua’s group)
Mtb PknG hijacks the host linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex to evade NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated cytosolic immune surveillance (Image by LIU Cuihua’s group)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202509/t20250917_1054974.shtml
- https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(25)01057-5
線状ユビキチン機構の病原性リン酸化が炎症小体センサー分解を引き起こす Pathogenic phosphorylation of linear ubiquitin machinery causes inflammasome sensor degradation
Yang Yu ∙ Shanshan Yu, ∙ Zhe Lu ∙ … ∙ Lingqiang Zhang ∙ Cui Hua Liu ∙ Qiyao Chai
Cell Reports Published:September 12, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2025.116286
Highlights
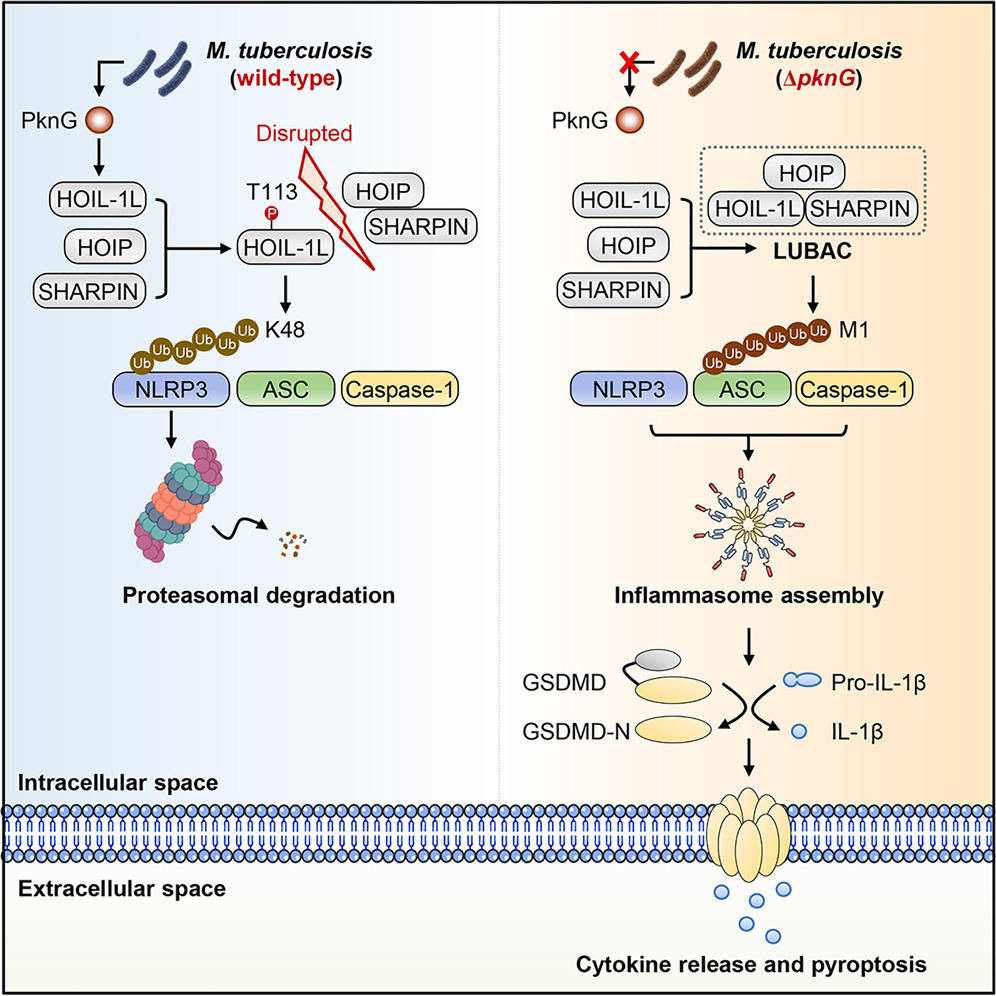
- Mtb PknG inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome assembly by phosphorylating HOIL-1L at Thr113
- PknG-phosphorylated HOIL-1L dampens LUBAC formation and ASC linear ubiquitination
- PknG-phosphorylated HOIL-1L drives K48 ubiquitination of NLRP3 for degradation
- PknG is essential for Mtb counteracting host NLRP3-dependent immunity in vivo
Summary
Host immune cells are equipped with cytosolic sensors to detect invading pathogens and initiate anti-infectious responses. However, how pathogens undermine host intracellular surveillance for persistent infection is not fully understood. Here, we identify that Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein kinase PknG subverts inflammasome sensor NLRP3-mediated cytokine release and pyroptosis by targeting host linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex (LUBAC). Mechanistically, PknG phosphorylates the LUBAC subunit HOIL-1L to prevent it from engaging in LUBAC formation, thereby suppressing linear ubiquitination of inflammasome adaptor ASC to dampen NLRP3 inflammasome assembly. Meanwhile, this phosphorylation stabilizes and activates HOIL-1L, which, in turn, exerts ubiquitin ligase activity to mediate K48-linked ubiquitination of NLRP3 for degradation. Disrupting the kinase activity or HOIL-1L-interacting region of PknG facilitates host NLRP3-dependent anti-Mtb immunity in mice. Thus, the bacterial kinase disrupts host linear ubiquitin machinery and coopts its ubiquitin ligase subunit to constitute an inter-species enzymatic cascade that drives inflammasome sensor degradation for counteracting immune surveillance.