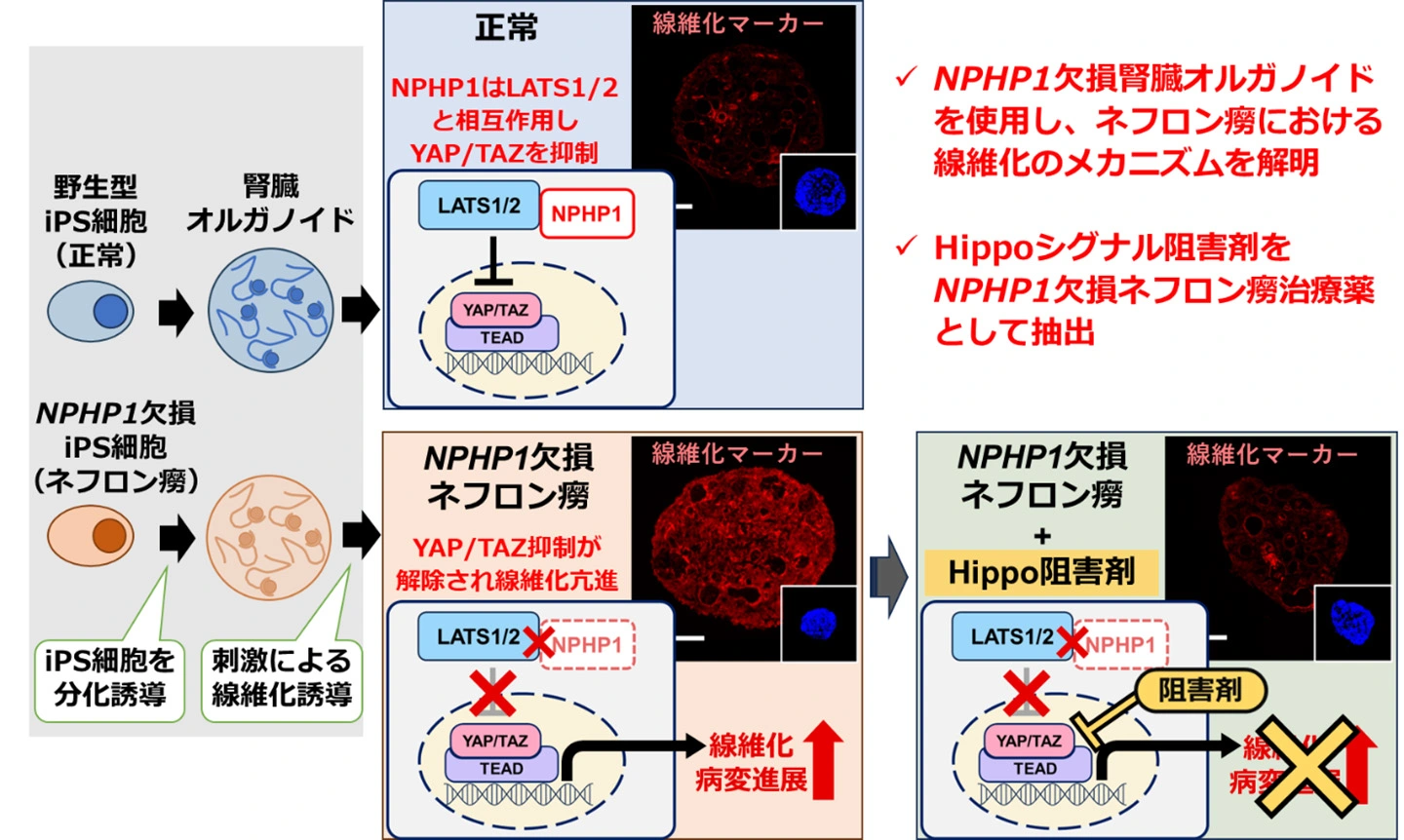
2025-09-22 京都大学iPS細胞研究所

Fig.1 DCM患者さんの心筋における線維化の程度と遺伝子発現
<関連情報>
- https://www.cira.kyoto-u.ac.jp/j/pressrelease/news/250922-140000.html
- https://www.jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.jacbts.2025.101363
拡張型心筋症における統合的トランスクリプトーム・組織学的解析:FGFR1阻害が抗心筋線維化・心保護療法として有効であることを解明 Integrative Transcriptomic-Histological Analysis in Dilated Cardiomyopathy Unveils FGFR1 Inhibition as Anti-Cardiac Fibrotic and Cardioprotective Therapy
Reo Hata, Shunsuke Funakoshi s.funakoshi@cira.kyoto-u.ac.jp, Takeru Makiyama, Takao Kato, Megumi Narita, Yasuko Matsumura, Ryoko Hirohata, … , and Yoshinori Yoshida
JACC: Basic to Translational Science Published:12 September 2025
Highlights
- Cardiac fibrosis is a key driver of dysfunction in dilated cardiomyopathy, with limited targeted therapies.
- FGFR1 expression correlates with fibrosis severity and emerges as a promising therapeutic target.
- FGFR1 inhibition reduces fibrosis and improves cardiac function in organoid and murine heart models.
- Future research should focus on clinical trials of FGFR1 inhibitors to advance fibrotic heart disease treatment.
Summary
Cardiac fibrosis drives dysfunction in dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM); yet, effective therapies are limited. This study identifies FGFR1 as a critical target in cardiac fibrosis using transcriptomic and histological analyses of 58 human DCM biopsies. FGFR1 expression correlated with fibrosis severity, and inhibition by AZD4547 reduced fibrosis and improved cardiac function in organoid and murine models. These findings validate FGFR1 inhibition as a promising therapeutic strategy for mitigating fibrosis and improving outcomes in heart failure associated with DCM.