2025-10-02 ワシントン大学セントルイス校
<関連情報>
- https://source.washu.edu/2025/10/circadian-clock-protein-linked-to-brain-aging-neurodegenerative-disease/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s43587-025-00950-x
REV-ERBαはNFIL3-CD38軸を介して脳内のNAD+レベルとタウオパチーを制御する REV-ERBα regulates brain NAD+ levels and tauopathy via an NFIL3–CD38 axis
Jiyeon Lee,Ryeonghwa Kang,Sohui Park,Ibrahim O. Saliu,Minsoo Son,Jaymie R. Voorhees,Julie M. Dimitry,Elsa I. Quillin,Lauren N. Woodie,Brian V. Lananna,Li Gan,Young-Ah Goo,Guoyan Zhao,Mitchell A. Lazar,Thomas P. Burris & Erik S. Musiek
Nature Aging Published:01 September 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s43587-025-00950-x
Abstract
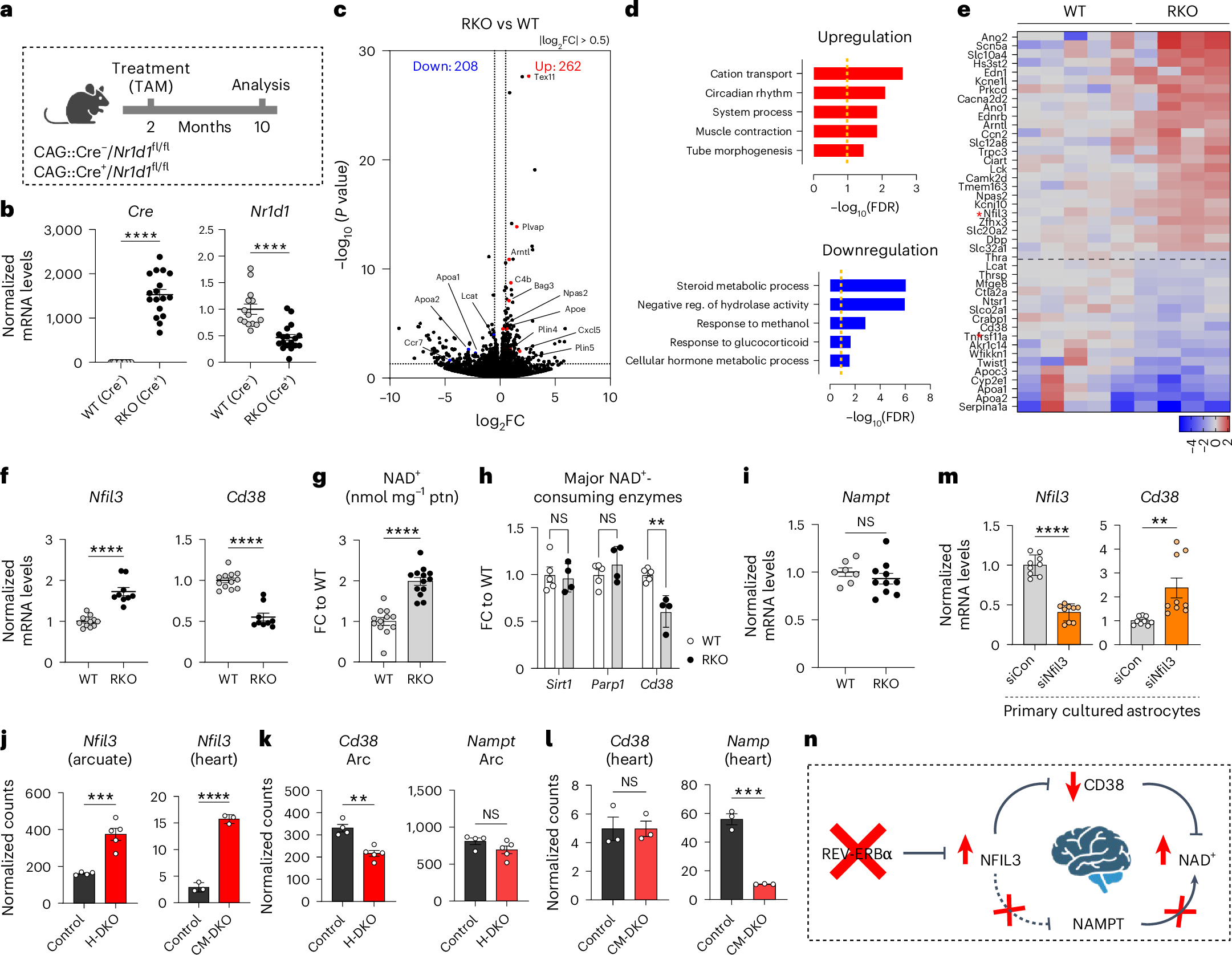
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is a critical metabolic co-enzyme implicated in brain aging, and augmenting NAD+ levels in the aging brain is an attractive therapeutic strategy for neurodegeneration. However, the molecular mechanisms of brain NAD+ regulation are incompletely understood. In cardiac tissue, the circadian nuclear receptor REV-ERBα has been shown to regulate NAD+ via control of the NAD+-producing enzyme NAMPT. Here we show that REV-ERBα controls brain NAD+ levels through a distinct pathway involving NFIL3-dependent suppression of the NAD+-consuming enzyme CD38, particularly in astrocytes. REV-ERBα deletion does not affect NAMPT expression in the brain and has an opposite effect on NAD+ levels as in the heart. Astrocytic REV-ERBα deletion augments brain NAD+ and prevents tauopathy in P301S mice. Our data reveal that REV-ERBα regulates NAD+ in a tissue-specific manner via opposing regulation of NAMPT versus CD38 and define an astrocyte REV-ERBα–NFIL3–CD38 pathway controlling brain NAD+ metabolism and neurodegeneration.


