2025-10-15 東京科学大学
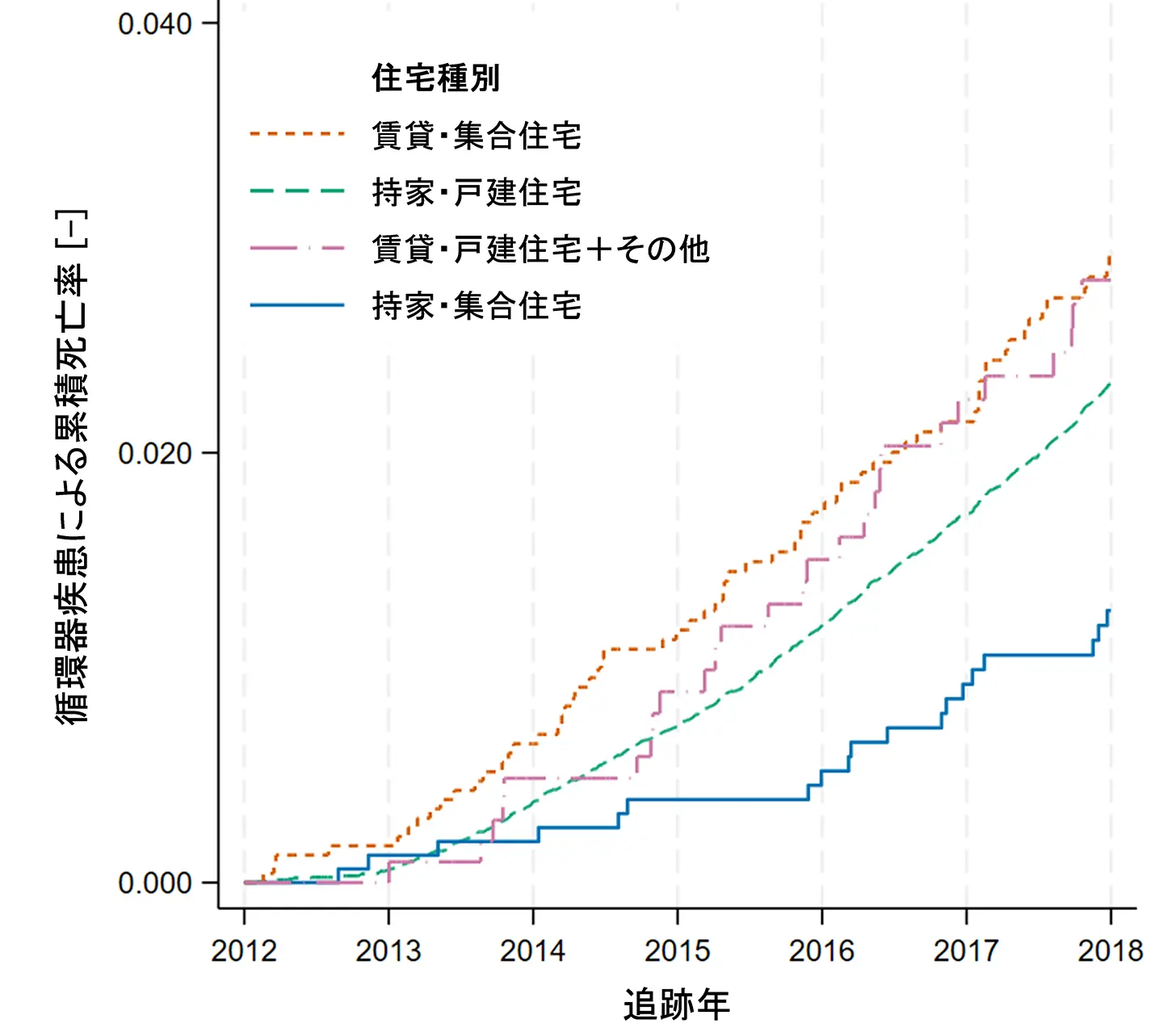
図1. 循環器疾患による累積死亡率(住宅種別)
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/13hrx5sf7rn8
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=2463&prevId=&key=1479c5c253939d9bdf05644a2cf6141b.pdf
- https://bmjpublichealth.bmj.com/content/3/2/e003073
住宅の種類(戸建て住宅 vs アパート)と所有形態(持ち家 vs 賃貸)の組み合わせと心血管疾患による死亡率の関連:日本における6年間のコホート研究の結果 Combination of housing type (detached houses vs flats) and tenure (owned vs rented) in relation to cardiovascular mortality: findings from a 6-year cohort study in Japan
Wataru Umishio,Sakura Kiuchi ,Toshiyuki Ojima,Masashige Saito ,Masamichi Hanazato,Jun Aida
BMJ Public Health Published:8 September 2025
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjph-2025-003073
Abstract
Introduction The WHO Housing and Health Guidelines have highlighted the impact of housing quality on cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), including pathways such as cold-induced hypertension. Major factors influencing housing quality include architectural type (detached houses vs flats) and tenure (owned vs rented), but few studies have examined their effects on CVDs.
Methods 46 850 occupants were included during the follow-up period from 1 January 2012 to 31 December 2017 in the Japan Gerontological Evaluation Study. By linking survey data with cause-of-death records, the Kaplan-Meier curves were constructed. Competing risk regression models were applied to calculate the subdistribution HRs (SHRs) for cardiovascular mortality risks across housing statuses, adjusted for demographics, socioeconomic factors and lifestyle behaviours. Sex-stratified analyses and Cox regression analyses were also conducted to calculate the HRs.
Results A total of 38 731 participants (46.6% men) were analysed, with a mean age of 73.6 years and a median follow-up period of 2091 days. The cardiovascular mortality rate was 3.97 per 1000 person-years, with 2.3% experiencing CVD-related deaths. The Kaplan-Meier curve indicated higher cardiovascular mortality for those living in rental flats and owned detached houses compared with those in owned flats. Competing risk regression models indicated a significantly higher risk of cardiovascular deaths among occupants living in rental flats compared with those in owned flats (SHR=1.78; 95% CI 1.05–3.02). For men, the risk was notably higher (SHR=2.32; 95% CI 1.13–4.75), though not statistically significant in women. Sensitivity analyses using Cox regression supported these findings, showing higher risk estimates for men (HR=2.36; 95% CI 1.16–4.82).
Conclusions Rental housing and detached houses are likely to have lower temperatures and greater temperature instabilities, raising blood pressure and increasing CVDs. Improving housing quality can contribute to cardiovascular health at the population level.