2025-12-04 東京科学大学
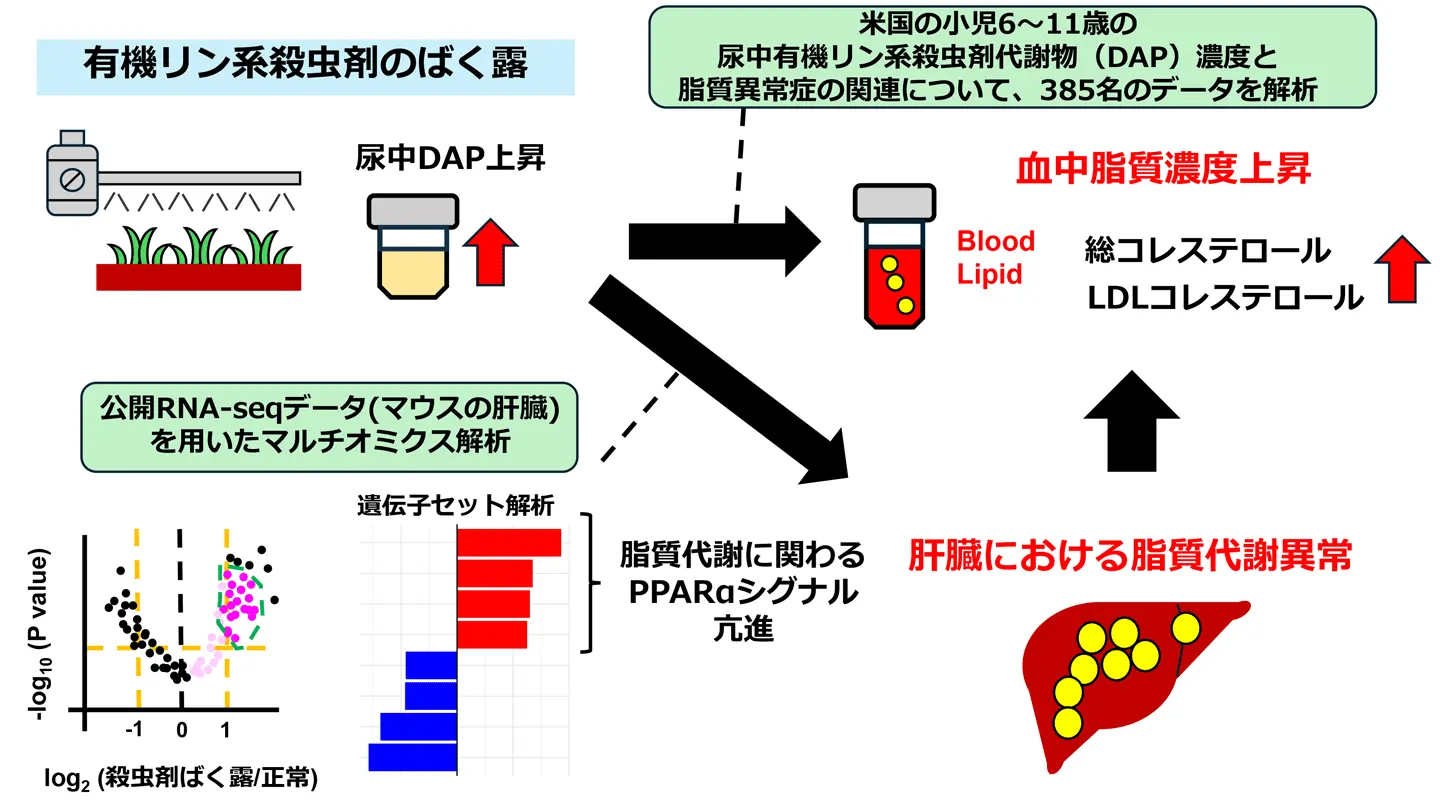
図1.本研究で検証した関連性
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/lvuzs1849eki
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=2723&prevId=&key=027c15fc56e7db81dea8f26873da213d.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0147651325016756
米国の子供の尿中有機リン系農薬代謝物と血中脂質濃度の関連性 Association between urinary organophosphate pesticide metabolites and blood lipid levels in US children
Nobuhisa Morimoto, Hiroaki Kikuchi, Yukiko Nishihama, Eisei Sohara, Shinichi Uchida, Shoji F. Nakayama
Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety Available online: 6 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2025.119330
Highlights
- Urinary DETP level was positively associated with blood TC and LDL-C in children.
- A higher level of DAP mixture was associated with higher blood TC and LDL-C.
- Enhanced mouse hepatic PPARα and PPARγ target gene expression by fenthion exposure.
- Enhanced PPAR signaling may induce hepatic lipid uptake, oxidation, and synthesis.
Abstract
Background
While previous studies showed associations between greater organophosphate pesticide (OPP) exposure and higher blood cholesterol levels in adults, the association in children and its underlying mechanism remain unclear. We investigated the association between urinary dialkylphosphate concentrations (DAP), which reflect recent OPP exposure, and blood lipid levels in preadolescent children. We examined the effect of OPP exposure on mouse hepatic transcription factors to explore underlying mechanisms.
Methods
Using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2002, we examined the association between DAP and blood lipid levels in 385 children aged 6–11 years, using Bayesian linear regression adjusted for potential confounders. The association between DAP and the presence of dyslipidemia was examined by Bayesian logistic regression. Using published RNA-seq data of mouse liver, we evaluated the relative abundances of target gene expressions of transcription factors relevant to hepatic lipid metabolism in mice on a fenthion-containing diet and a control diet.
Results
Over 50 % of children had detectable levels of dimethylphosphate, diethylphosphate, dimethylthiophosphate, and diethylthiophosphate. Higher diethylthiophosphate was associated with high total cholesterol level (highest vs lowest quartile group: odds ratio = 4.35, 95 % credible interval = 1.63–11.70). Target gene-set analyses revealed higher expression of PPARα and PPARγ target genes upon fenthion exposure, suggesting upregulated fatty acid oxidation and triglyceride synthesis, resembling transcriptomic changes observed in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Conclusion
Higher diethylthiophosphate was associated with high blood cholesterol levels. Upregulated PPARα and PPARγ target genes may partly explain the association between OPP exposure and dyslipidemia.