2025-09-19 中国科学院(CAS)
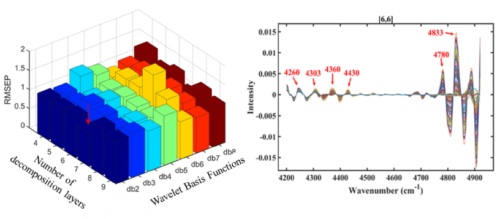
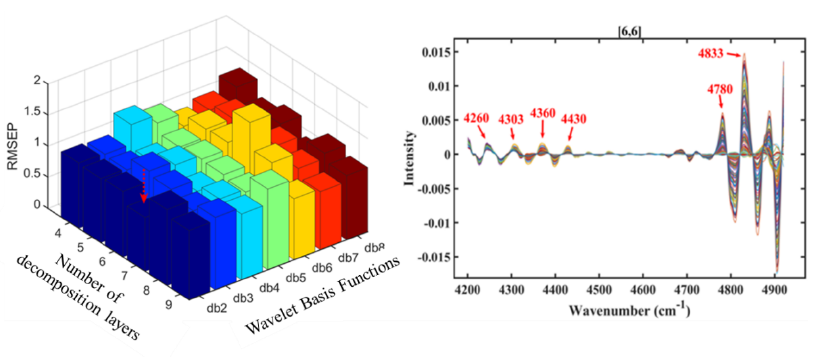
Core parameter determination and Hb-related node reconstruction results (Image by HAN Xin)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/chem/202512/t20251222_1138520.shtml
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1746809425010614
全血NIRS定量分析の精度向上のためのウェーブレットパケットファジーシュリンクノイズ除去モデルに基づくヘモグロビン特徴抽出 Hemoglobin feature extraction based on wavelet packet-fuzzy shrinkage denoising model for improving the accuracy of whole blood NIRS quantitative analysis
Renjie Fang, Jialiang Wang, Xin Han, Xiangxian Li, Jingjing Tong, Minguang Gao, Xiang Huang, Hongzhi Wang
Biomedical Signal Processing and Control Available online: 9 September 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2025.108550
Highlights
- Novel Hybrid Approach: Combines WPT-FS denoising with WOA to enhance NIRS analysis of hemoglobin.
- Innovative Denoising Strategy: Uses adaptive fuzzy shrinkage to reduce noise in NIRS data.
- Optimized Feature Extraction: WOA reorganizes wavelet nodes to isolate key Hb spectral features.
- Robust Quantitative Modeling: Achieves PLS model with RMSEP of 2.0409 and R2 of 0.9746, outperforming conventional methods.
- Clinical Potential: Enables rapid, non-destructive Hb quantification in blood samples for diagnostics.
Abstract
This study introduces a hybrid model that integrates wavelet packet-fuzzy shrinkage denoising (WPT-FS) with the whale optimization algorithm (WOA) to enhance the measurement accuracy of near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) for the quantitative analysis of hemoglobin (Hb). First, a novel threshold denoising function is proposed, which employs the fuzzy shrinkage of wavelet packet coefficients to significantly mitigate noise interference in NIRS data. Subsequently, the denoised wavelet packet nodes are optimized using the WOA to reorganize the nodes that correspond to the Hb information band. Finally, a partial least squares regression (PLS) model is developed for the reconfigured spectrum. Actual blood data analysis demonstrates that this method outperforms the traditional preprocessing techniques in effectively capturing Hb spectral features, and yields a root mean square error of prediction (RMSEP) of 2.0409 and a coefficient of determination (R2p) of 0.9746. These findings suggest that the proposed method substantially enhances the accuracy and precision of quantitative analyses of Hb in near-infrared spectra, offering a novel solution for blood spectroscopic analysis.