2026-01-27 東京科学大学
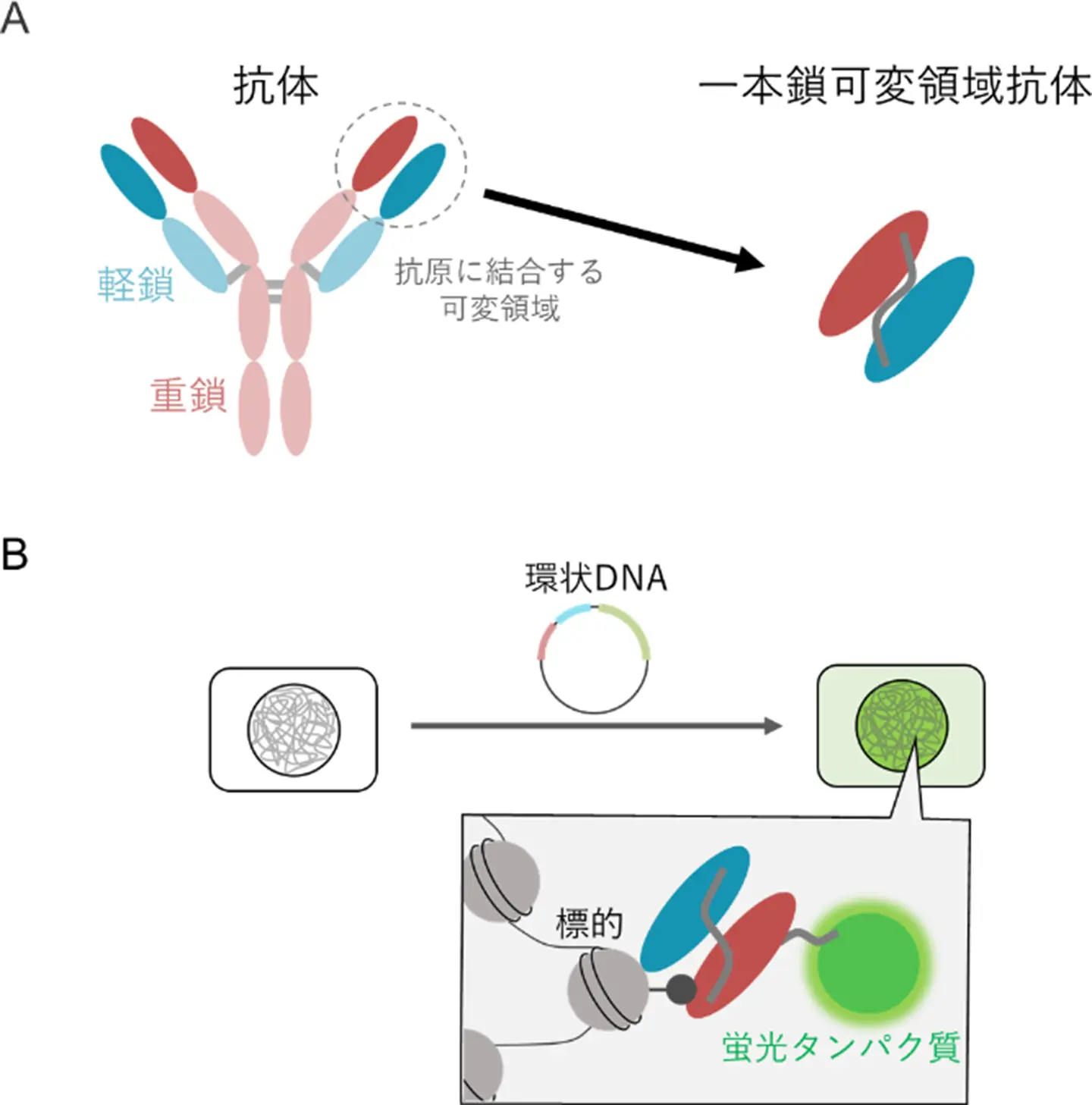
図1. 細胞内抗体。
(A)一本鎖可変領域抗体は、重鎖と軽鎖からなる抗体のうち、抗原に結合する領域のみを結合させたものである。
(B)遺伝子の導入により、細胞内で一本鎖可変領域抗体を発現させることで、細胞内の標的を標識することができる。
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/byn3kppywj5g
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=3099&prevId=&key=a3805fa0ea338880b8890964d9ada984.pdf
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adx8352
多様なペプチドやヒストン修飾を標的とした抗体配列をイントラボディに迅速に変換するためのAI支援タンパク質設計 AI-assisted protein design to rapidly convert antibody sequences to intrabodies targeting diverse peptides and histone modifications
Gabriel Galindo. Daiki Maejima. Jacob DeRoo. Scott R. Burlingham. […] , and Timothy J. Stasevich
Science Advances Published:2 Jan 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adx8352
Abstract
Intrabodies are engineered antibodies that function inside living cells, enabling therapeutic, diagnostic, and imaging applications. While powerful, their development has been hindered by challenges associated with their folding, solubility, and stability in the reduced intracellular environment. Here, we present an artificial intelligence–driven pipeline integrating AlphaFold2, ProteinMPNN, and live-cell screening to optimize antibody framework regions while preserving epitope-binding complementarity-determining regions. Using this approach, we successfully converted 19 of 26 antibody sequences into functional single-chain variable fragment intrabodies, including a panel targeting diverse histone modifications for real-time imaging of chromatin dynamics and gene regulation. Notably, 18 of these 19 sequences had failed to convert using the standard approach, demonstrating the unique effectiveness of our method. As antibody sequence databases expand, our method will accelerate intrabody design, making their development easier, more cost effective, and broadly accessible for biological research.