2026-02-02 マサチューセッツ工科大学(MIT)
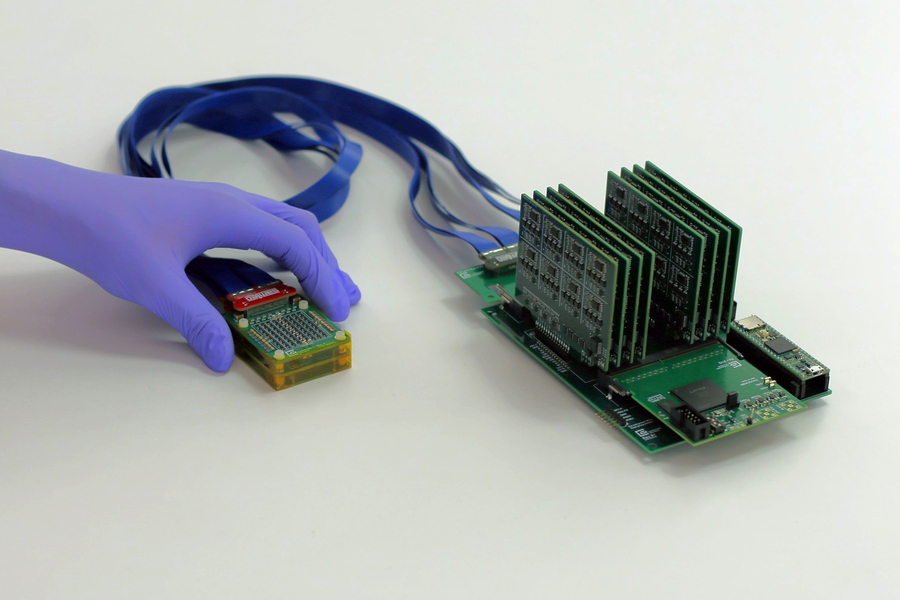

The new system consists of a small ultrasound probe, on left, attached to an acquisition and processing module that is a little larger than a smartphone.Credit: Conformable Decoders Lab at the MIT Media Lab
<関連情報>
- https://news.mit.edu/2026/portable-ultrasound-sensor-may-enable-earlier-detection-breast-cancer-0202
- https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adhm.202505310
超スパース、低消費電力アーキテクチャによるリアルタイム 3D 超音波イメージング Real-Time 3D Ultrasound Imaging with an Ultra-Sparse, Low Power Architecture
Colin Marcus, Md Osman Goni Nayeem, Aastha Shah, Jason Hou, Shrihari Viswanath, Maya Eusebio, David Sadat, Anantha P. Chandrakasan, Tolga Ozmen, Canan Dagdeviren
Advanced Healthcare Materials Published: 29 January 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202505310
ABSTRACT
Effective resource-constrained volumetric ultrasound imaging requires compact, low-power systems capable of wide-angle real-time 3D imaging to accommodate small changes in placement by the operator. However, obtaining such images requires an excessive O(N2) channel count, bulky electronics, and high power consumption. We introduce an end-to-end system architecture to enable high-resolution, real-time 3D ultrasound imaging in a portable form factor. We present: a convolutional optimally distributed array (CODA) geometry that drastically reduces the number of elements (from 1024 to 128), a novel chirped data acquisition (cDAQ) architecture that enhances imaging depth while operating with a 25.3 dB lower transmit amplitude than a pulsed system, and an associated new signal processing methodology. We experimentally demonstrate our system’s ability to perform deep (> 11 cm), high axial resolution (< 600 µm), and wide-angle (57°) imaging, while simultaneously reducing power consumption (29.6x reduction) and drive voltage (18 V). We validated our system in vitro and further performed in vivo human trials, demonstrating the ability to detect both tumors and cysts in breast tissue. This new architectural approach will unlock a new class of medical devices with enhanced diagnostic and long-term monitoring capabilities and open up future wearable designs of real-time 3D ultrasound systems.