2022-08-05 ワシントン大学セントルイス
アルファ粒子は放射線の一種で、細胞に対して局所的に強力な毒性効果を発揮する。研究チームは、さまざまな試験において、提案した低カウント定量的単一光子放射型コンピュータ断層撮影法(LC-QSPECT)が、放射性核種の取り込みを確実に測定できることを確認した。この情報は、そのような治療を受けた患者のケアの指針として役立つ。
<関連情報>
- https://source.wustl.edu/2022/08/new-imaging-based-approach-to-measure-radiation-dose/
- https://engineering.wustl.edu/news/2022/Engineers-develop-new-way-to-use-low-count-imaging-for-effective-radiopharmaceutical-therapy.html
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9780276
α粒子放出放射性医薬品治療のための投影領域低カウント定量SPECT法 A projection-domain low-count quantitative SPECT method for α-particle emitting radiopharmaceutical therapy
Zekun Li,Diane S. Abou,Brian C. Baumann,Farrokh Dehdashti,David H. Ballard,Jonathan Liu,Uday Jammalamadaka,Richard Laforest,Richard L. Wahl,Daniel L. J. Thorek,Abhinav K. Jha
IEEE Transactions on Radiation and Plasma Sciences Published:23 May 2022
DOI: 10.1109/TRPMS.2022.3175435
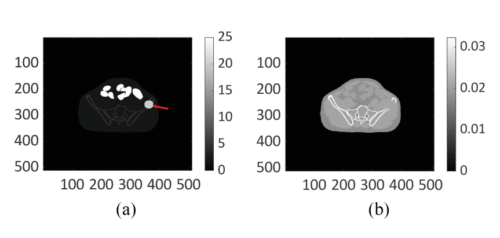
Digital (a) activity map and (b) attenuation map for the pelvic region generated using the anthropomorphic XCAT phantom.
Abstract
Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) provides a mechanism to estimate regional isotope uptake in lesions and at-risk organs after administration of α-particle-emitting radiopharmaceutical therapies (α-RPTs). However, this estimation task is challenging due to the complex emission spectra, the very low number of detected counts ( 20 times lower than in conventional SPECT), the impact of stray-radiation-related noise at these low counts, and the multiple image-degrading processes in SPECT. The conventional reconstruction-based quantification methods are observed to be erroneous for α-RPT SPECT. To address these challenges, we developed a low-count quantitative SPECT (LC-QSPECT) method that directly estimates the regional activity uptake from the projection data (obviating the reconstruction step), compensates for stray-radiation-related noise, and accounts for the radioisotope and SPECT physics, including the isotope spectra, scatter, attenuation, and collimator-detector response, using a Monte Carlo-based approach. The method was validated in the context of three-dimensional SPECT with 223Ra, a commonly used radionuclide for α-RPT. Validation was performed using both realistic simulation studies, including a virtual clinical trial, and synthetic and 3D-printed anthropomorphic physical-phantom studies. Across all studies, the LC-QSPECT method yielded reliable regional-uptake estimates and outperformed the conventional ordered subset expectation maximization (OSEM)-based reconstruction and geometric transfer matrix (GTM)-based post-reconstruction partial-volume compensation methods. Further, the method yielded reliable uptake across different lesion sizes, contrasts, and different levels of intra-lesion heterogeneity. Additionally, the variance of the estimated uptake approached the Cramér-Rao bound-defined theoretical limit. In conclusion, the proposed LC-QSPECT method demonstrated the ability to perform reliable quantification for α-RPT SPECT.