この発見は、新しい治療法や予防法につながる可能性があります。 Findings could lead to new therapies, prevention strategies
2022-12-29 ワシントン大学セントルイス
このたび、ワシントン大学医学部(セントルイス)の研究者らが、慢性白血病から侵攻性白血病への移行における重要な転換点を特定した。研究チームは、この転移経路の重要な分子を阻害することで、白血病のモデルマウスとヒトの患者から採取した腫瘍を持つマウスにおいて、この危険な病気の進行を防ぐことができることを明らかにした。この研究成果は、12月29日付のNature Cancer誌に掲載されます。
「二次性急性骨髄性白血病の予後は厳しいものです」と、医学部の准教授で血液学部門の共同ディレクターである筆頭著者Stephen T. Oh医学博士が述べています。「骨髄増殖性新生物の既往があり、急性白血病を発症した患者は、ほぼ全員がこの病気で死亡することになります。従って、我々の研究の主要な焦点は、この慢性疾患から攻撃的な疾患への転換をより良く理解し、これらの患者のためのより良い治療法、できれば予防策を開発することです。”
この研究は、DUSP6と呼ばれるこの重要な移行分子を阻害することで、これらの癌が、通常治療に使われるJAK2阻害剤に対してしばしば発症する抵抗性を克服することが出来ることを示唆しています。JAK2阻害剤は、関節リウマチの治療にも使用される抗炎症療法です。
<関連情報>
- https://source.wustl.edu/2022/12/study-reveals-how-chronic-blood-cancer-transitions-to-aggressive-disease/
- https://medicine.wustl.edu/news/study-reveals-how-chronic-blood-cancer-transitions-to-aggressive-disease/?_ga=2.41245217.2094597223.167
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s43018-022-00486-8
DUSP6はJAK2阻害に対する抵抗性を媒介し、白血病の進行を促進する DUSP6 mediates resistance to JAK2 inhibition and drives leukemic progression
Tim Kong,Angelo B. A. Laranjeira,Kangning Yang,Daniel A. C. Fisher,LaYow Yu,Laure Poittevin De La Frégonnière,Anthony Z. Wang,Marianna B. Ruzinova,Jared S. Fowles,Mary C. Fulbright,Maggie J. Cox,Hamza Celik,Grant A. Challen,Sidong Huang & Stephen T. Oh
Nature Cancer Published:29 December 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-022-00486-8
Abstract
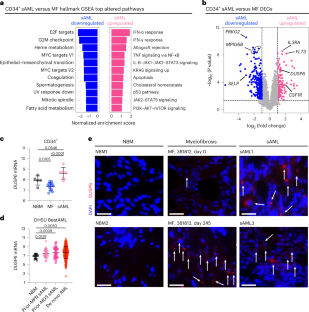
Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) exhibit a propensity for transformation to secondary acute myeloid leukemia (sAML), for which the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood, resulting in limited treatment options and dismal clinical outcomes. Here, we performed single-cell RNA sequencing on serial MPN and sAML patient stem and progenitor cells, identifying aberrantly increased expression of DUSP6 underlying disease transformation. Pharmacologic dual-specificity phosphatase (DUSP)6 targeting led to inhibition of S6 and Janus kinase (JAK)–signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signaling while also reducing inflammatory cytokine production. DUSP6 perturbation further inhibited ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK)1, which we identified as a second indispensable candidate associated with poor clinical outcome. Ectopic expression of DUSP6 mediated JAK2-inhibitor resistance and exacerbated disease severity in patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models. Contrastingly, DUSP6 inhibition potently suppressed disease development across Jak2V617F and MPLW515L MPN mouse models and sAML PDXs without inducing toxicity in healthy controls. These findings underscore DUSP6 in driving disease transformation and highlight the DUSP6–RSK1 axis as a vulnerable, druggable pathway in myeloid malignancies.