肺炎で生命を脅かす肺障害の主な原因をブロックする設計されたペプチド Designed peptide blocks top cause of life-threatening lung damage with pneumonia
2023-01-17 カリフォルニア大学校アーバイン校(UCI)
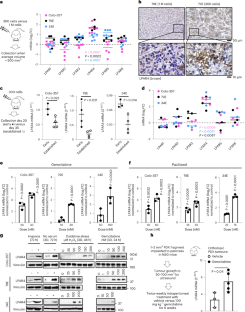
このマウス研究では、C6ペプチドが好中球と呼ばれる白血球の電位依存性Hv1プロトンチャネルを遮断し、有害な活性酸素種、プロテアーゼ、サイトカインの産生を抑制する仕組みが明らかにされた。これにより、深刻な損傷を受けた肺に見られる無秩序な炎症と体液の蓄積を引き起こす、これらの細胞による肺組織への浸潤が抑制された。
この研究は、カリフォルニア大学アーバイン校の小児科、生理学・生物物理学、薬学の著名な教授であるSteven A.N. Goldstein博士、同校のプロジェクト科学者補佐のRuiming Zhao、UCLAの小児科准教授であるAndreas Schwingshackl博士が主導したものです。
<関連情報>
- https://news.uci.edu/2023/01/17/uc-irvine-ucla-researchers-identify-new-therapeutic-approach-to-prevent-ards/
- https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(22)02174-5
電位依存性プロトンチャネルを阻害するように設計されたペプチドによる急性肺傷害からの保護 Protection from acute lung injury by a peptide designed to inhibit the voltage-gated proton channel
Ruiming Zhao,Benjamin Lopez,Andreas Schwingshackl,Steve A.N. Goldstein
iScience Published:December 28, 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2022.105901

Highlights
•C6 suppresses Acute Lung Injury (ALI) induced in mice by intratracheal bacterial LPS
•C6 inhibits Hv1 channels to reduce neutrophil influx and inflammatory mediator release
•Genetic knockout experiments in mice confirm the in vivo target for C6 is Hv1
•Inhibition of Hv1 by C6 is a targeted therapeutic approach for LPS-induced ALI
Summary
There are no targeted medical therapies for Acute Lung Injury (ALI) or its most severe form acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Infections are the most common cause of ALI/ARDS and these disorders present clinically with alveolar inflammation and barrier dysfunction due to the influx of neutrophils and inflammatory mediator secretion. We designed the C6 peptide to inhibit voltage-gated proton channels (Hv1) and demonstrated that it suppressed the release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and proteases from neutrophils in vitro. We now show that intravenous C6 counteracts bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI in mice, and suppresses the accumulation of neutrophils, ROS, and proinflammatory cytokines in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Confirming the salutary effects of C6 are via Hv1, genetic deletion of the channel similarly protects mice from LPS-induced ALI. This report reveals that Hv1 is a key regulator of ALI, that Hv1 is a druggable target, and that C6 is a viable agent to treat ALI/ARDS.