未熟児の死因の中で最も多いのが感染症です。このような未熟児の免疫系と、感染症にかかりやすい原因を研究している。 Infections are under the most common causes of death in premature infants. Markus Sperandio studies the immune system in those babies and what makes them so vulnerable to infections.
2023-02-22 ミュンヘン大学(LMU)
特に小さな早産児は感染の脅威が非常に高いため、彼らはしばしば抗生物質で治療されなければなりません。この問題に取り組むため、彼のチームは赤ちゃんの免疫細胞が十分に機能しない理由を探求し、彼らが新しい環境に適応するのに必要な時間がかかることを発見しました。さらに、彼らは細胞の遺伝子活性を比較し、免疫系の炎症反応を制御するNF-κBシグナル伝達経路が特に影響を受けていることを発見しました。これは、早産児における感染のリスクが高い理由の一つです。
<関連情報>
- https://www.lmu.de/en/newsroom/news-overview/news/when-life-begins-too-early.html
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36633909/
A20と非正規NF-κB経路は、胎児の個体形成期における好中球のリクルートメントの重要な制御因子であること A20 and the noncanonical NF-κB pathway are key regulators of neutrophil recruitment during fetal ontogeny
Ina Rohwedder, Lou Martha Wackerbarth, Kristina Heinig, Annamaria Ballweg, Johannes Altstätter, Myriam Ripphahn, Claudia Nussbaum, Melanie Salvermoser, Susanne Bierschenk, Tobias Straub, Matthias Gunzer, Marc Schmidt-Supprian, Thomas Kolben, Christian Schulz, Averil Ma, Barbara Walzog, Matthias Heinig, Markus Sperandio
JCI Insight Published:2023 Feb 22
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.155968
Abstract
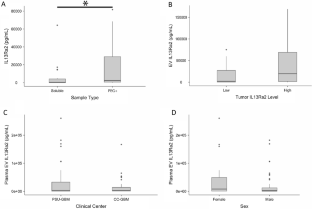
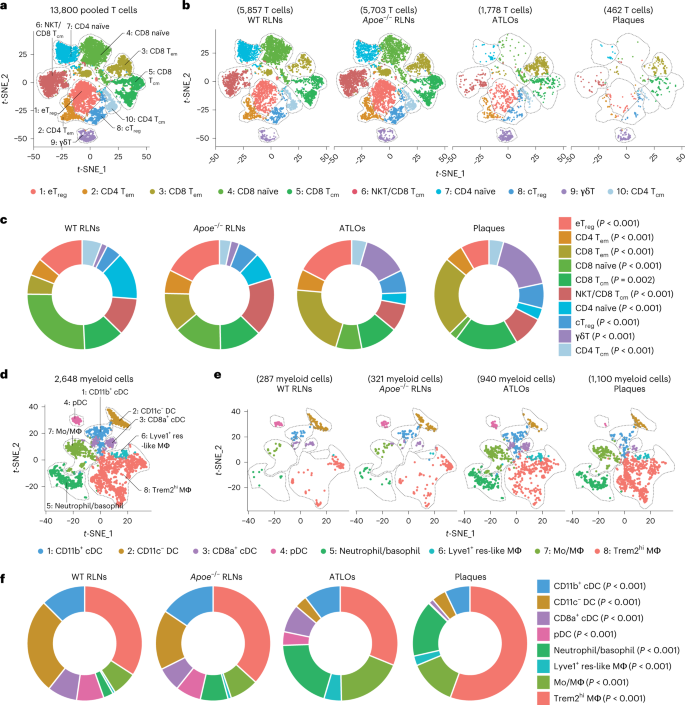
Newborns are at high risk of developing neonatal sepsis, particularly if born prematurely. This has been linked to divergent requirements the immune system has to fulfill during intrauterine compared with extrauterine life. By transcriptomic analysis of fetal and adult neutrophils, we shed new light on the molecular mechanisms of neutrophil maturation and functional adaption during fetal ontogeny. We identified an accumulation of differentially regulated genes within the noncanonical NF-κB signaling pathway accompanied by constitutive nuclear localization of RelB and increased surface expression of TNF receptor type II in fetal neutrophils, as well as elevated levels of lymphotoxin α in fetal serum. Furthermore, we found strong upregulation of the negative inflammatory regulator A20 (Tnfaip3) in fetal neutrophils, which was accompanied by pronounced downregulation of the canonical NF-κB pathway. Functionally, overexpressing A20 in Hoxb8 cells led to reduced adhesion of these neutrophil-like cells in a flow chamber system. Conversely, mice with a neutrophil-specific A20 deletion displayed increased inflammation in vivo. Taken together, we have uncovered constitutive activation of the noncanonical NF-κB pathway with concomitant upregulation of A20 in fetal neutrophils. This offers perfect adaption of neutrophil function during intrauterine fetal life but also restricts appropriate immune responses particularly in prematurely born infants.