2023-03-02 ワシントン州立大学(WSU)
この研究では、母親の12か月時点での赤ちゃんに対する中立的または不自然な行動が、7歳の子供の遺伝子NR3C1にメチル基を加えることが関連していることが明らかになった。この遺伝子はストレス反応の調節に関与している。この研究は、赤ちゃんとの質の高い相互作用とこの遺伝子のメチル化との関係があることを示唆している。しかし、母親の行動のわずかな変化が、人間の正常なバリエーションにつながる可能性があるため、長期的な影響を決定することは困難である。
<関連情報>
- https://news.wsu.edu/press-release/2023/03/02/small-differences-in-moms-behavior-may-show-up-in-childs-epigenome/
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ajhb.23876
母子相互作用の質は、7歳時の子どものNR3C1 CpG部位メチル化と関連する Maternal–infant interaction quality is associated with child NR3C1 CpG site methylation at 7 years of age
Elizabeth A. Holdsworth, Lawrence M. Schell, Allison A. Appleton
American Journal of Human Biology Published: 13 February 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/ajhb.23876
Abstract
Objective
Infancy is both a critical window for hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis development, and a sensitive period for social–emotional influences. We hypothesized that the social–emotional quality of maternal–infant interactions are associated with methylation of HPA-axis gene NR3C1 later in childhood.
Methods
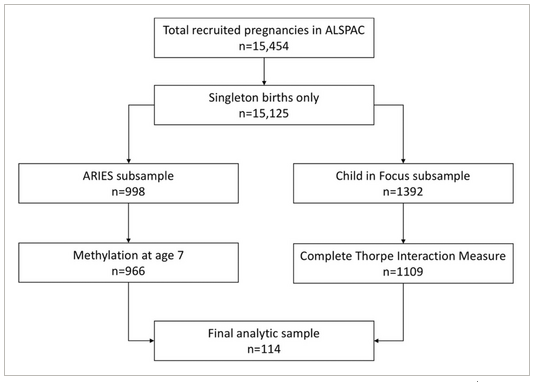
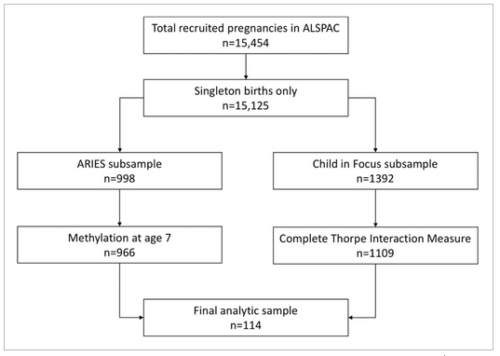
Using a subsample of 114 mother-infant pairs from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC), linear regression models were created to predict variance in methylation of seven selected CpG sites from NR3C1 in whole blood at age 7 years, including the main predictor variable of the first principal component score of observed maternal–infant interaction quality (derived from the Thorpe Interaction Measure at 12 months of age) and covariates of cell-type proportion, maternal financial difficulties and marital status at 8 months postnatal, child birthweight, and sex.
Results
CpG site cg27122725 methylation was negatively associated with warmer, more positive maternal interaction with her infant (β = 0.19, p = .02, q = 0.13). In sensitivity analyses, the second highest quartile of maternal behavior (neutral, hesitant behavior) was positively associated with cg12466613 methylation. The other five CpG sites were not significantly associated with maternal–infant interaction quality.
Conclusions
Narrow individual variation of maternal interaction with her infant is associated with childhood methylation of two CpG sites on NR3C1 that may be particularly sensitive to environmental influences. Infancy may be a sensitive period for even small influences from the social–emotional environment on the epigenetic determinants of HPA-axis function.