アールト大学、ヘルシンキ大学、ヘルシンキ大学病院総合がんセンターの研究者らが、全く新しい治療法が進行したメラノーマ患者の免疫系にどのような影響を与えるかを研究しました。 Researchers at Aalto University, the University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital Comprehensive Cancer Center have studied how a completely new treatment option affects the immune system in patients with advanced melanoma.
2023-03-02 フィンランド・アールト大学
研究は、新しい薬剤の2つの組み合わせ、ニボルマブとレラトリマブの効果を、非反応性患者のT細胞だけでなく、自然殺傷細胞(NK細胞)にも焦点を当てて調査しました。
その結果、レラトリマブは、T細胞の機能を高めるだけでなく、NK細胞を活性化することがわかり、この発見が、NK細胞を活用したがん治療につながる可能性があるとされています。研究には、シングルセルシーケンシング技術と深層学習手法が活用され、機械学習モデルのscVIとTCRGPが使用されました。
<関連情報>
- https://www.aalto.fi/en/news/scientists-unravel-the-effects-of-new-medication-for-advanced-melanoma-with-the-help-of-ai
- https://www.jci.org/articles/view/164809
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-33720-z
メラノーマ患者における抗LAG3+抗PD1治療のシングルセルキャラクタリゼーション Single-cell characterization of anti-LAG3+anti-PD1 treatment in melanoma patients
Jani Huuhtanen,Henna H.E. Kasanen,Katriina Peltola,Tapio Lönnberg,Virpi Glumoff,Oscar Brück,Olli Dufva,Karita Peltonen,Johanna Vikkula,Emmi Jokinen,Mette Ilander,Moon Hee Lee,Siru Mäkelä,Marta Nyakas,Bin Li,Micaela Hernberg,Petri Bono,Harri Lähdesmäki,Anna Kreutzman and Satu Mustjoki
Journal of Clinical Investigation Published January 31, 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI164809

Abstract
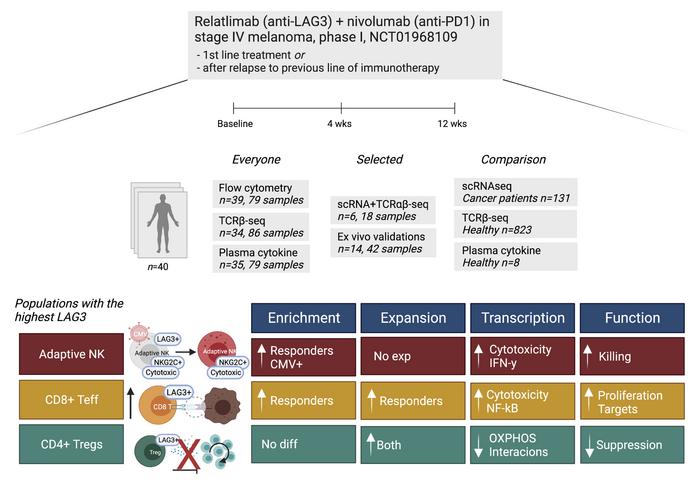
BACKGROUND. Relatlimab+nivolumab (anti-LAG3+anti-PD1) has been approved by FDA as a 1st-line therapy in stage III/IV melanoma, but its detailed effect on the immune system is unknown.
METHODS. We evaluated blood samples from 40 immunotherapy-naïve or prior immunotherapy-refractory patients with metastatic melanoma treated with anti-LAG3+anti-PD1 in a phase I trial (NCT01968109) using single-cell RNA and T cell receptor (TCR) sequencing (scRNA+TCRαβ-seq) combined with other multiomics profiling.
RESULTS. The highest LAG3 expression was noted in NK cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs), and CD8+ T cells, and these cell populations underwent the most significant changes during the treatment. Adaptive NK cells were enriched in responders and underwent profound transcriptomic changes during the therapy resulting in an active phenotype. LAG3+ Tregs expanded but based on the transcriptome profile became metabolically silent during the treatment. Lastly, higher baseline TCR clonality was observed in responding patients, and their expanding CD8+ T cell clones gained more cytotoxic and NK-like phenotype.
CONCLUSION. Anti-LAG3+anti-PD1 therapy has profound effects on NK cells and Tregs in addition to CD8+ T cells.
TRIAL REGISTRATION. ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01968109)
FUNDING. Cancer Foundation Finland, Sigrid Juselius Foundation, Signe and Ane Gyllenberg Foundation, Relander Foundation, State funding for university-level health research in Finland, a Helsinki Institute of Life Sciences Fellow grant, Academy of Finland, and an investigator-initiated research grant from BMS.
メラノーマ患者における抗原特異的T細胞応答の進化と変調 Evolution and modulation of antigen-specific T cell responses in melanoma patients
Jani Huuhtanen,Liang Chen,Emmi Jokinen,Henna Kasanen,Tapio Lönnberg,Anna Kreutzman,Katriina Peltola,Micaela Hernberg,Chunlin Wang,Cassian Yee,Harri Lähdesmäki,Mark M. Davis & Satu Mustjoki
Nature Communications Published:11 October 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33720-z
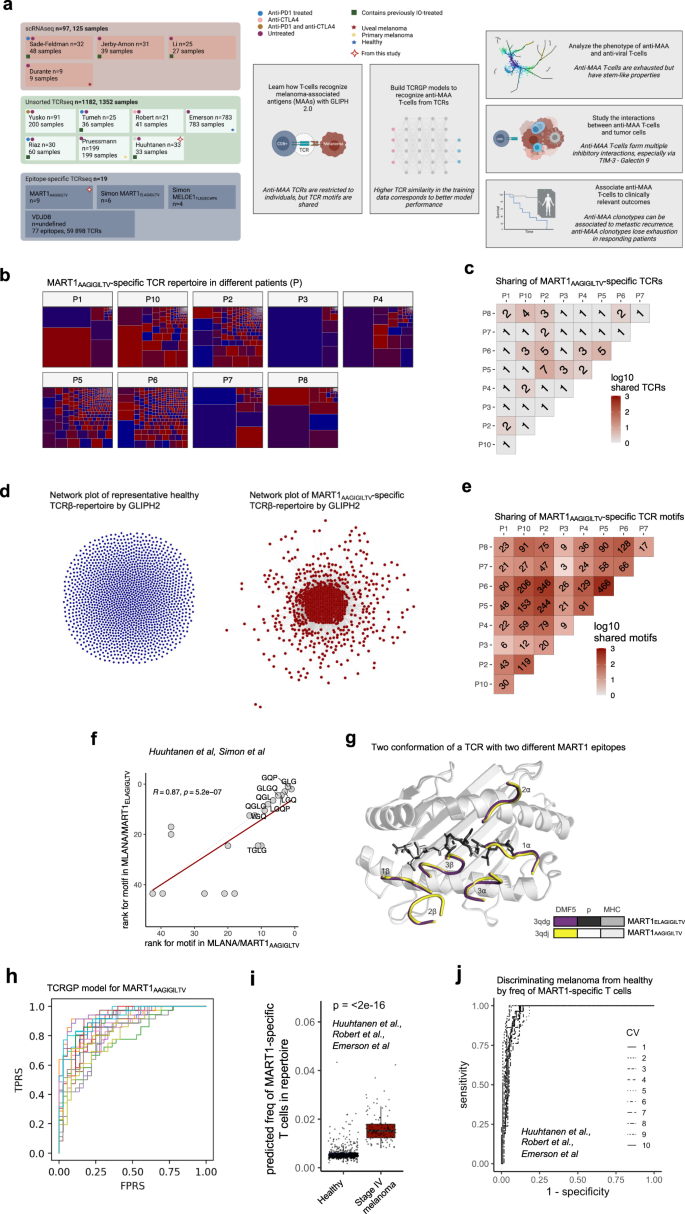
Abstract
Analyzing antigen-specific T cell responses at scale has been challenging. Here, we analyze three types of T cell receptor (TCR) repertoire data (antigen-specific TCRs, TCR-repertoire, and single-cell RNA + TCRαβ-sequencing data) from 515 patients with primary or metastatic melanoma and compare it to 783 healthy controls. Although melanoma-associated antigen (MAA) -specific TCRs are restricted to individuals, they share sequence similarities that allow us to build classifiers for predicting anti-MAA T cells. The frequency of anti-MAA T cells distinguishes melanoma patients from healthy and predicts metastatic recurrence from primary melanoma. Anti-MAA T cells have stem-like properties and frequent interactions with regulatory T cells and tumor cells via Galectin9-TIM3 and PVR–TIGIT -axes, respectively. In the responding patients, the number of expanded anti-MAA clones are higher after the anti-PD1(+anti-CTLA4) therapy and the exhaustion phenotype is rescued. Our systems immunology approach paves the way for understanding antigen-specific responses in human disorders.