LMUの研究者は、3Dで分子構造を迅速に区別するための超解像顕微鏡法を開発しました。 LMU researchers have developed a super-resolution microscopy method for the rapid differentiation of molecular structures in 3D.
2023-03-08 ミュンヘン大学(LMU)
GET-pMINFLUXの高精度は、超解像度顕微鏡法を改善する新しい手法を開くことになる。また、L-PAINT手法を開発することにより、超解像度顕微鏡法の速度をさらに高めた。
DNA-PAINTとは異なり、L-PAINT DNA鎖には2つの結合配列があり、結合階層を設計することで、分子位置を迅速にスキャンすることができる。GET-pMINFLUXとL-PAINTの組み合わせにより、細胞内の生物分子反応の理解に不可欠な分子レベルの構造とダイナミクスを調べることができる。
<関連資料>
- https://www.cup.uni-muenchen.de/news/en/archive/2023/microscopy-highest-resolution-in-three-dimensions/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-023-01111-8
pMINFLUX、グラフェンエネルギー移動、DNA-PAINTを組み合わせたナノメートル精度の3次元超解像顕微鏡の実現に向けて Combining pMINFLUX, graphene energy transfer and DNA-PAINT for nanometer precise 3D super-resolution microscopy
Jonas Zähringer,Fiona Cole,Johann Bohlen,Florian Steiner,Izabela Kamińska & Philip Tinnefeld
Light: Science & Applications Published:10 March 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-023-01111-8
Abstract
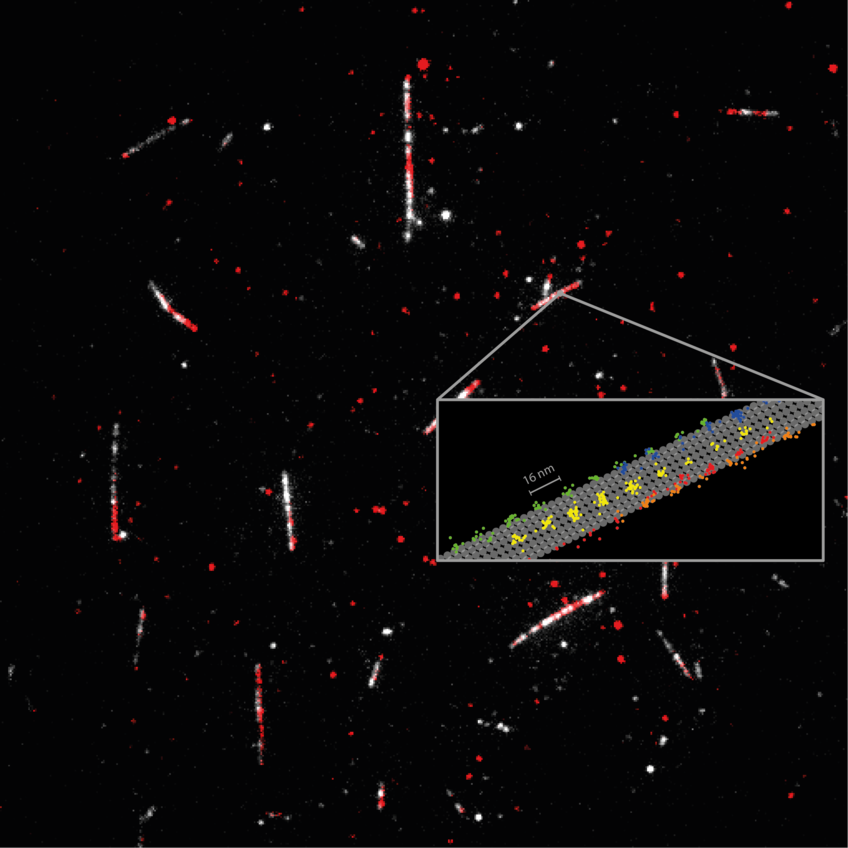
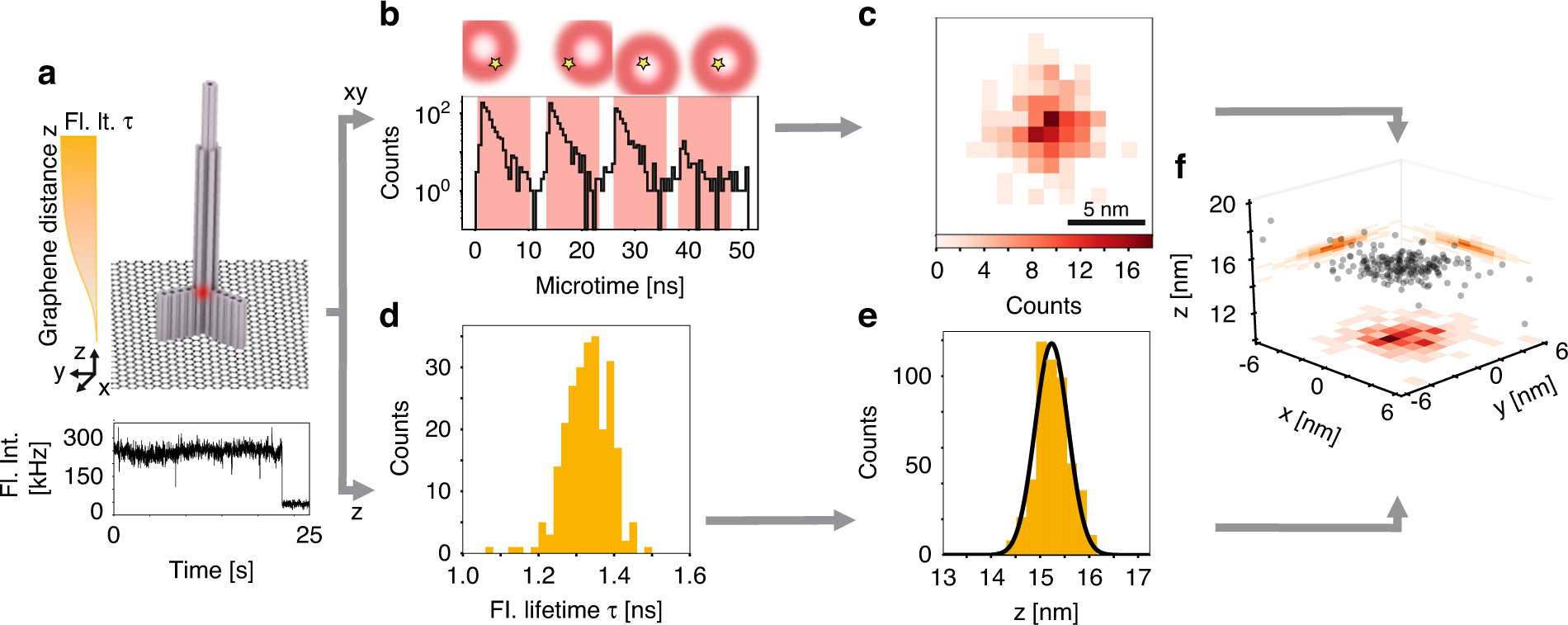
3D super-resolution microscopy with nanometric resolution is a key to fully complement ultrastructural techniques with fluorescence imaging. Here, we achieve 3D super-resolution by combining the 2D localization of pMINFLUX with the axial information of graphene energy transfer (GET) and the single-molecule switching by DNA-PAINT. We demonstrate <2 nm localization precision in all 3 dimension with axial precision reaching below 0.3 nm. In 3D DNA-PAINT measurements, structural features, i.e., individual docking strands at distances of 3 nm, are directly resolved on DNA origami structures. pMINFLUX and GET represent a particular synergetic combination for super-resolution imaging near the surface such as for cell adhesion and membrane complexes as the information of each photon is used for both 2D and axial localization information. Furthermore, we introduce local PAINT (L-PAINT), in which DNA-PAINT imager strands are equipped with an additional binding sequence for local upconcentration improving signal-to-background ratio and imaging speed of local clusters. L-PAINT is demonstrated by imaging a triangular structure with 6 nm side lengths within seconds.