2023-07-07 インペリアル・カレッジ・ロンドン(ICL)
◆この研究結果は、肥満を遺伝子レベルで理解し、個別化された治療法の開発につながる重要な進展です。
<関連情報>
- https://www.imperial.ac.uk/news/245916/pollinator-tracking-decoding-obesity-news-from/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-38439-z
脂肪細胞における統合的ゲノム解析により、ヒトの肥満と糖尿病におけるDNAメチル化が示唆される Integrative genomic analyses in adipocytes implicate DNA methylation in human obesity and diabetes
Liam McAllan,Damir Baranasic,Sergio Villicaña,Scarlett Brown,Weihua Zhang,Benjamin Lehne,Marco Adamo,Andrew Jenkinson,Mohamed Elkalaawy,Borzoueh Mohammadi,Majid Hashemi,Nadia Fernandes,Nathalie Lambie,Richard Williams,Colette Christiansen,Youwen Yang,Liudmila Zudina,Vasiliki Lagou,Sili Tan,Juan Castillo-Fernandez,James W. D. King,Richie Soong,Paul Elliott,James Scott,Inga Prokopenko,Inês Cebola,Marie Loh,Boris Lenhard,Rachel L. Batterham,Jordana T. Bell,John C. Chambers,Jaspal S. Kooner & William R. Scott
Nature Communications Published:15 May 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38439-z
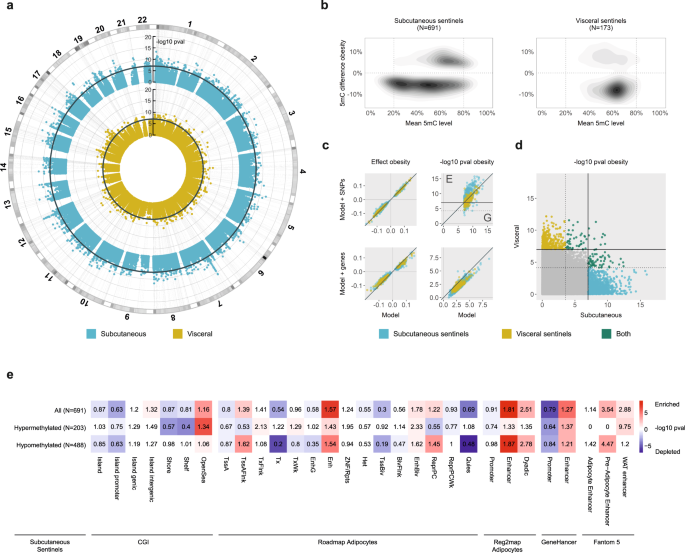
Abstract
DNA methylation variations are prevalent in human obesity but evidence of a causative role in disease pathogenesis is limited. Here, we combine epigenome-wide association and integrative genomics to investigate the impact of adipocyte DNA methylation variations in human obesity. We discover extensive DNA methylation changes that are robustly associated with obesity (N = 190 samples, 691 loci in subcutaneous and 173 loci in visceral adipocytes, P < 1 × 10-7). We connect obesity-associated methylation variations to transcriptomic changes at >500 target genes, and identify putative methylation-transcription factor interactions. Through Mendelian Randomisation, we infer causal effects of methylation on obesity and obesity-induced metabolic disturbances at 59 independent loci. Targeted methylation sequencing, CRISPR-activation and gene silencing in adipocytes, further identifies regional methylation variations, underlying regulatory elements and novel cellular metabolic effects. Our results indicate DNA methylation is an important determinant of human obesity and its metabolic complications, and reveal mechanisms through which altered methylation may impact adipocyte functions.