2023-06-27 ワシントン大学セントルイス校
◆研究では、ダイエット療法だけでは体重減少が効果的でない肥満者と糖尿病予備軍の参加者を対象にして行われ、運動と体重減少を組み合わせることがインスリン感受性に与える劇的な影響が示されました。この結果は、運動を含めた体重管理療法の重要性を強調しています。
<関連情報>
- https://source.wustl.edu/2023/06/in-battling-obesity-and-prediabetes-combining-exercise-with-weight-loss-is-key/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s42255-023-00829-4
肥満と糖尿病予備軍における食事誘発性減量による代謝機能の改善は運動によって増強される Diet-induced weight loss improvements in metabolic function are enhanced by exercise in people with obesity and prediabetes
Joseph W. Beals,Brandon D. Kayser,Gordon I. Smith,George G. Schweitzer,Kyleigh Kirbach,Monica L. Kearney,Jun Yoshino,Gibraan Rahman,Rob Knight,Bruce W. Patterson & Samuel Klein
Nature Metabolism Published:26 June 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-023-00829-4
Abstract
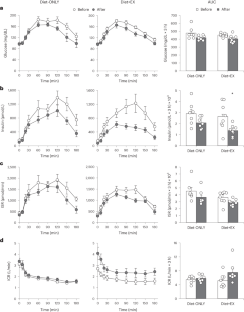
The additional therapeutic effects of regular exercise during a dietary weight loss program in people with obesity and prediabetes are unclear. Here, we show that whole-body (primarily muscle) insulin sensitivity (primary outcome) was 2-fold greater (P = 0.006) after 10% weight loss induced by calorie restriction plus exercise training (Diet+EX; n = 8, 6 women) than 10% weight loss induced by calorie restriction alone (Diet-ONLY; n = 8, 4 women) in participants in two concurrent studies. The greater improvement in insulin sensitivity was accompanied by increased muscle expression of genes involved in mitochondrial biogenesis, energy metabolism and angiogenesis (secondary outcomes) in the Diet+EX group. There were no differences between groups in plasma branched-chain amino acids or markers of inflammation, and both interventions caused similar changes in the gut microbiome. Few adverse events were reported. These results demonstrate that regular exercise during a diet-induced weight loss program has profound additional metabolic benefits in people with obesity and prediabetes.
Trial Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02706262 and NCT02706288)