2023-07-27 マサチューセッツ大学アマースト校
◆ライム病は、感染したシカマダニによって広がる米国で最も一般的な媒介される病気で、毎年約47万6000人が診断されています。感染したシカマダニは抗生物質に必ずしも反応せず、重篤な疾患になる可能性もあります。
◆研究ではがん細胞とライム病を引き起こすバチルスの成長について共通の特徴があることが見つかり、がん治療薬のLDH阻害剤がライム病治療にも効果的かもしれないとの仮説が提起されました。
◆今後はマウスモデルなどで実験を続け、人間に対する治療の可能性を探る予定です。この薬剤療法は、マラリア様感染症であるBabesiosisという別のマダニ媒介疾患にも有効かもしれないとされています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.umass.edu/news/article/research-points-potential-new-medical-therapy-lyme-disease
- https://www.mdpi.com/2076-0817/12/7/962
乳酸脱水素酵素阻害剤が試験管内でボレリア・ブルグドルフェリの増殖を抑える Lactate Dehydrogenase Inhibitors Suppress Borrelia burgdorferi Growth In Vitro
Adam Lynch,Patrick Pearson,Sergey N. Savino ,Andrew Y. Li and tephen M. Rich
Pathogens Published:Published: 22 July 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12070962
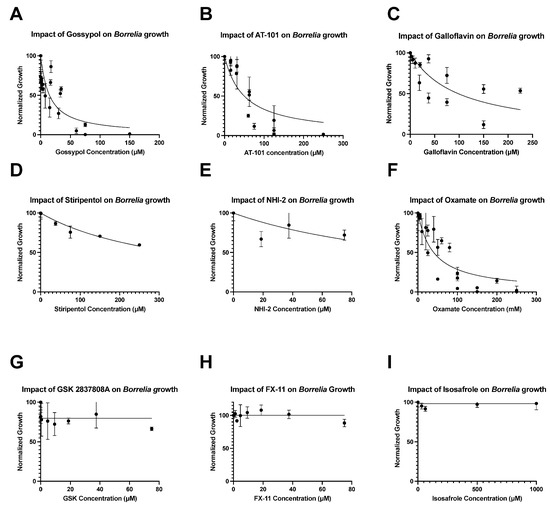
Abstract
Borrelia burgdorferi, the causative agent of Lyme disease, has a highly reduced genome and relies heavily on glycolysis for carbon metabolism. As such, established inhibitors of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) were evaluated in cultures to determine the extent of their impacts on B. burgdorferi growth. Both racemic and enantiopure (AT-101) gossypol, as well as oxamate, galloflavin, and stiripentol, caused the dose-dependent suppression of B. burgdorferi growth in vitro. Racemic gossypol and AT-101 were shown to fully inhibit spirochetal growth at concentrations of 70.5 and 187.5 μM, respectively. Differences between racemic gossypol and AT-101 efficacy may indicate that the dextrorotatory enantiomer of gossypol is a more effective inhibitor of B. burgdorferi growth than the levorotatory enantiomer. As a whole, LDH inhibition appears to be a promising mechanism for suppressing Borrelia growth, particularly with bulky LDH inhibitors like gossypol.