2023-11-02 ノースウェスタン大学
◆この合成メラニンは、肌に塗布することで創傷治癒を促進し、肌自体および全身に影響を及ぼします。合成メラニンを含むクリームを使用すると、肌を太陽光線の影響から保護し、日焼けや化学火傷による肌の損傷を修復できると研究者たちは述べています。合成メラニンは過酸化物自由基を除去し、これらの自由基は日焼けなどの創傷肌で生成されます。未制御のままだと、自由基活性は細胞を損傷し、最終的には肌の老化や皮膚がんの原因となる可能性があります。
<関連情報>
- https://news.northwestern.edu/stories/2023/11/super-melanin-heals-skin-injuries-from-sunburn-chemical-burns/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41536-023-00331-1
合成メラニンの局所塗布が組織の修復を促進する Topical application of synthetic melanin promotes tissue repair
Dauren Biyashev,Zofia E. Siwicka,Ummiye V. Onay,Michael Demczuk,Dan Xu,Madison K. Ernst,Spencer T. Evans,Cuong V. Nguyen,Florencia A. Son,Navjit K. Paul,Naneki C. McCallum,Omar K. Farha,Stephen D. Miller,Nathan C. Gianneschi & Kurt Q. Lu
npj Regenerative Medicine Published:02 November 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41536-023-00331-1
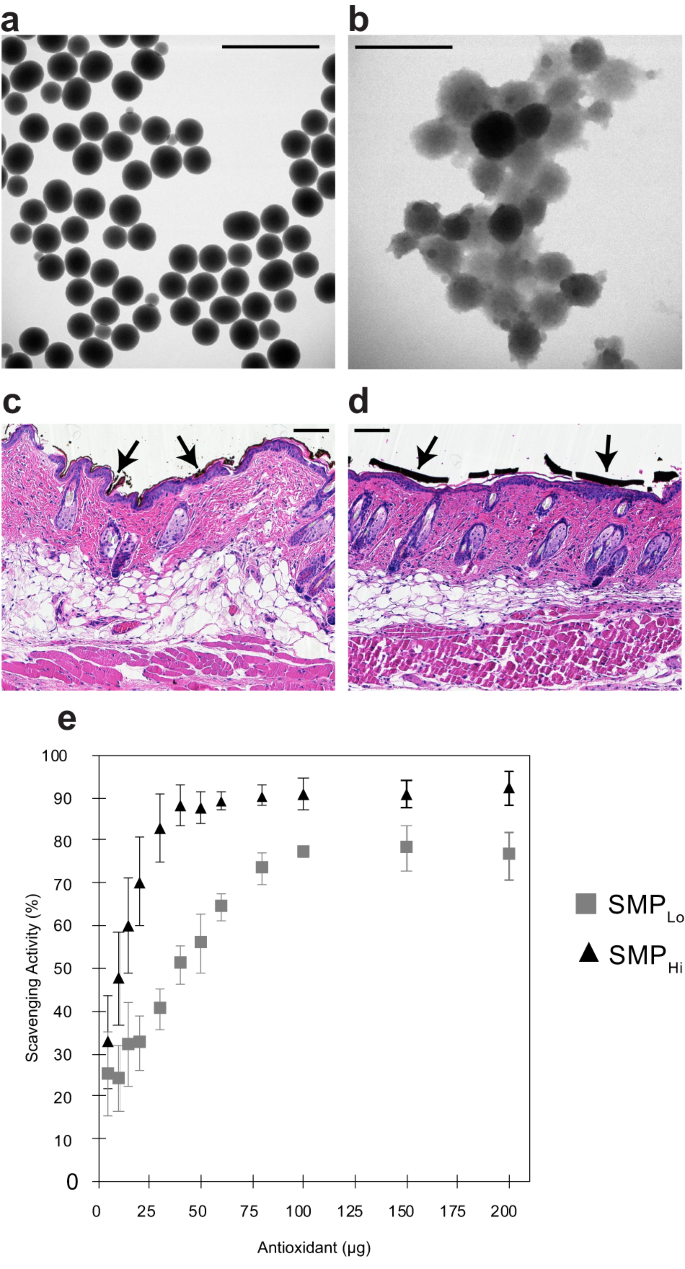
Abstract
In acute skin injury, healing is impaired by the excessive release of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Melanin, an efficient scavenger of radical species in the skin, performs a key role in ROS scavenging in response to UV radiation and is upregulated in response to toxic insult. In a chemical injury model in mice, we demonstrate that the topical application of synthetic melanin particles (SMPs) significantly decreases edema, reduces eschar detachment time, and increases the rate of wound area reduction compared to vehicle controls. Furthermore, these results were replicated in a UV-injury model. Immune array analysis shows downregulated gene expression in apoptotic and inflammatory signaling pathways consistent with histological reduction in apoptosis. Mechanistically, synthetic melanin intervention increases superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, decreases Mmp9 expression, and suppresses ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Furthermore, we observed that the application of SMPs caused increased populations of anti-inflammatory immune cells to accumulate in the skin, mirroring their decrease from splenic populations. To enhance antioxidant capacity, an engineered biomimetic High Surface Area SMP was deployed, exhibiting increased wound healing efficiency. Finally, in human skin explants, SMP intervention significantly decreased the damage caused by chemical injury. Therefore, SMPs are promising and effective candidates as topical therapies for accelerated wound healing, including via pathways validated in human skin.


