2024-05-28 バーミンガム大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.birmingham.ac.uk/news/2024/brain-damage-reveals-part-of-the-brain-necessary-for-helping-others
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41562-024-01899-4
ヒトの前頭前皮質は向社会的動機づけに必要である Human ventromedial prefrontal cortex is necessary for prosocial motivation
Patricia L. Lockwood,Jo Cutler,Daniel Drew,Ayat Abdurahman,Deva Sanjeeva Jeyaretna,Matthew A. J. Apps,Masud Husain & Sanjay G. Manohar
Nature Human Behaviour Published:27 May 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-024-01899-4
Abstract
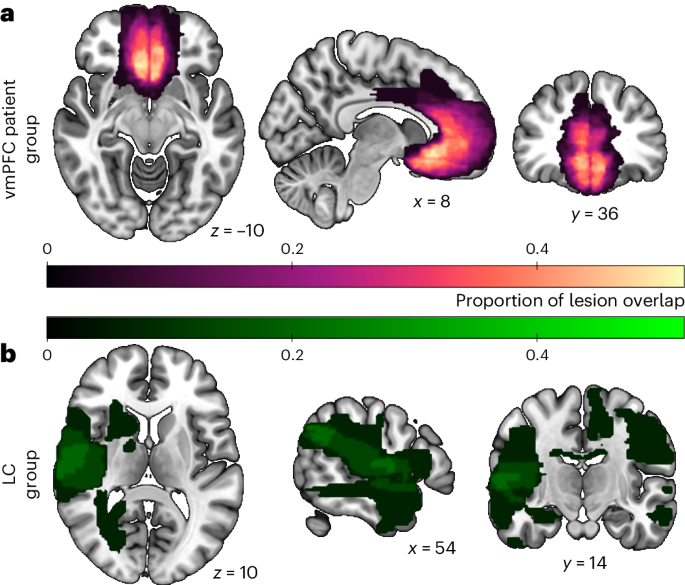
Ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) is vital for decision-making. Functional neuroimaging links vmPFC to processing rewards and effort, while parallel work suggests vmPFC involvement in prosocial behaviour. However, the necessity of vmPFC for these functions is unknown. Patients with rare focal vmPFC lesions (n = 25), patients with lesions elsewhere (n = 15) and healthy controls (n = 40) chose between rest and exerting effort to earn rewards for themselves or another person. vmPFC damage decreased prosociality across behavioural and computational measures. vmPFC patients earned less, discounted rewards by effort more, and exerted less force when another person benefited, compared to both control groups. Voxel-based lesion mapping revealed dissociations between vmPFC subregions. While medial damage led to antisocial behaviour, lateral damage increased prosocial behaviour relative to patients with damage elsewhere. vmPFC patients also showed reduced effort sensitivity overall, but reward sensitivity was limited to specific subregions. These results reveal multiple causal contributions of vmPFC to prosocial behaviour, effort and reward.